15
Adjusting the block size towards your disk usage can result in some performance gain.
In a typical RAID configuration, data of the virtual drive is striped (or spread across) the physical drives. Having a
smaller array block size will increase the likelihood of accessing all physical drives when processing large I/O requests.
Multiple physical drives working in parallel increases the throughput, meaning better performance.
For smaller I/O requests (512 bytes to 4 kilobytes), it is better to have each individual disks handle their own I/O
request, improving the IOPS (I/O per second), rather than having one tiny I/O request being handled by multiple
disks.
Capacity (Default: Maximum)
The total amount of space you want the RAID array to take up. When creating RAID levels, disk capacities are limited
by the smallest disk.
An example of how disk capacities are limited by smallest disk.
• You have 2 drives connected to the enclosure.
• The first drive is 6 TB, the second is 4 TB
• After creating a RAID level 1 using both drives and maximum capacity, the first drive will have 2 TB, the
second 0 TB of free capacity
• The free capacity on the second drive can be used to create a separate array with other drives.
You may also choose how much space each array will utilize. You can use the remaining space to create another array
(up to 4 arrays are supported).
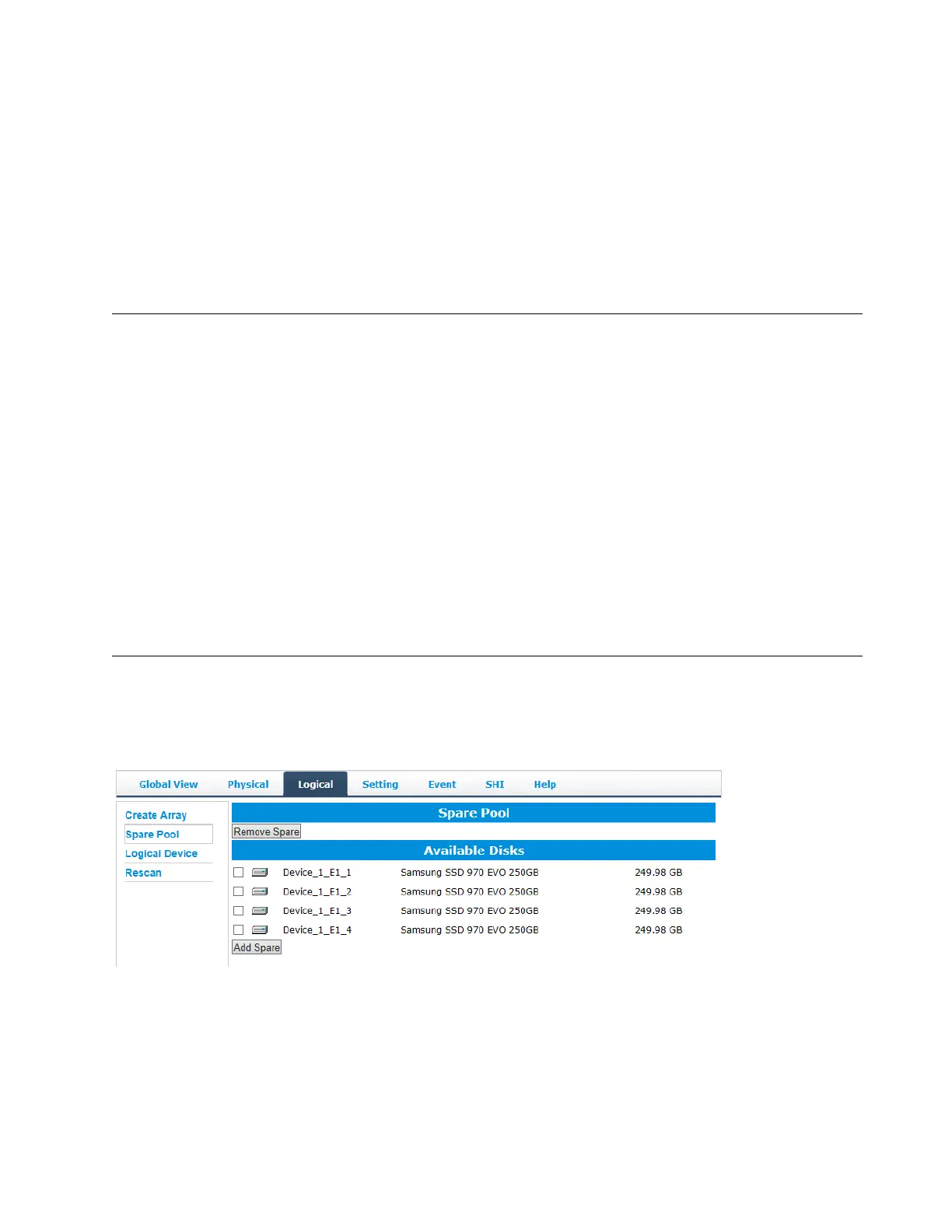
Adding Spare Disks
Spare disks are physical disks that will immediately replace critical disks in an array.
 Loading...
Loading...











