80
Motor Measurement (Motor Analysis-Equipped Model)
Motor analysis mode
This mode can analyze motors performances by measuring signal inputted from torque sensors and
tachometers.
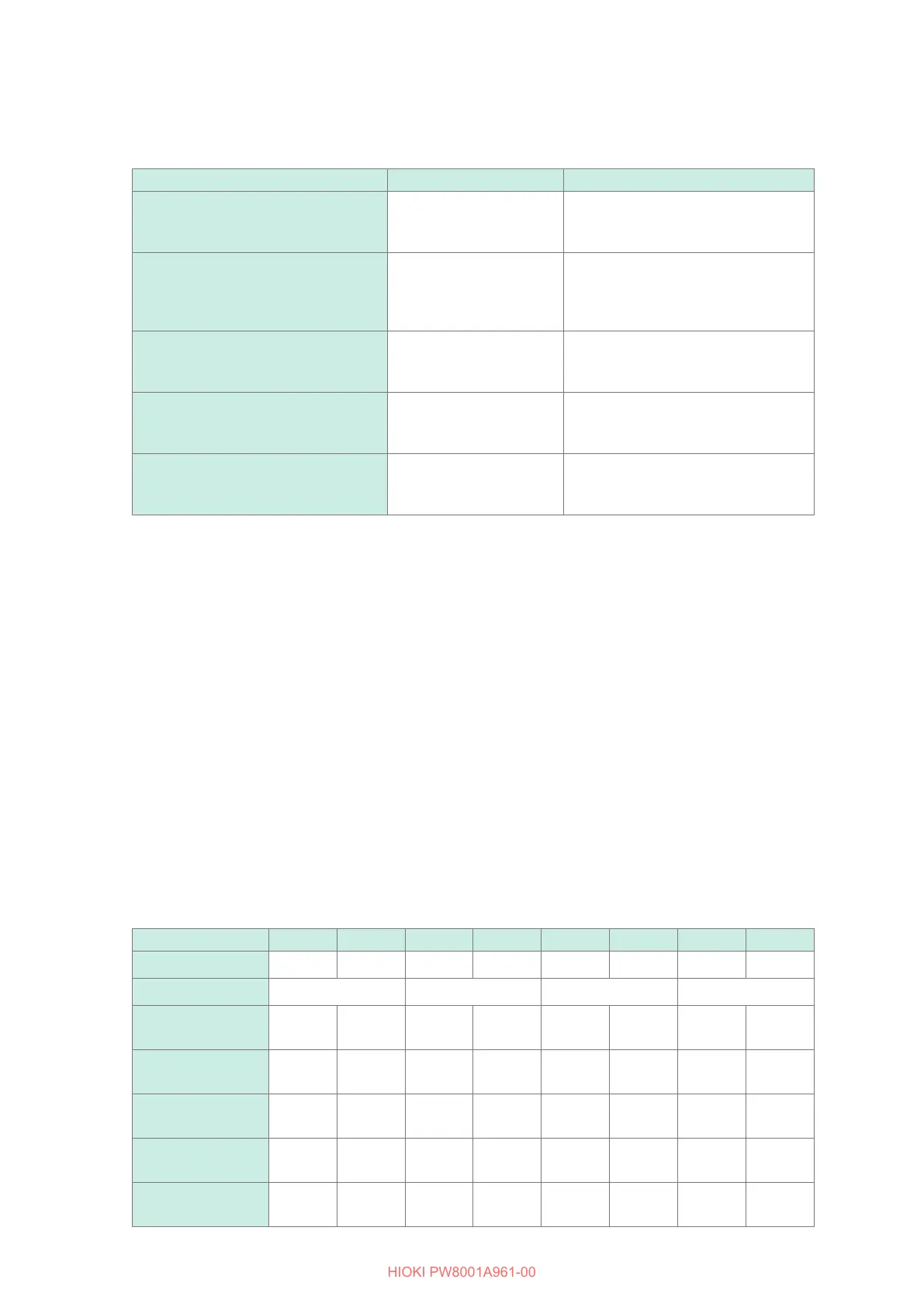
Connection pattern Settable channels Description
Pattern 1
Torque, Speed(Pulse)
AB, CD, EF, GH
Simultaneous analysis of
up to four motors
Motor analysis based on inputs of
torque signal and RPM pulse signal
Pattern 2
Torque, Speed, Direction, Origin
ABCD, EFGH
Simultaneous analysis of
up to two motors
Motor analysis based on inputs of
torque signal, RPM pulse signal,
rotational direction signal, and origin
signal
Pattern 3
Torque, Speed, Direction
ABCD, EFGH
Simultaneous analysis of
up to two motors
Motor analysis based on inputs of
torque signal, RPM pulse signal, and
rotational direction signal
Pattern 4
Torque, Speed, Origin
ABCD, EFGH
Simultaneous analysis of
up to two motors
Motor analysis based on inputs of
torque signal, RPM pulse signal, and
origin signal
Pattern 5
Torque, Speed(Analog)
ABCD, EFGH
Simultaneous analysis of
up to two motors
Motor analysis based on inputs of
torque signal and RPM analog DC
signal
Pattern 1: This mode can analyze motors using a pair of adjacent channels. Motor power and
motor eciency can be measured for up to four systems simultaneously.
Pattern 2, 3, 4, and 5: This mode can analyze motors using one set of four channels. Up to two systems
can be measured simultaneously. These patterns permit more advanced analysis,
measuring not only motor power and motor eciency, but also rotational direction
and regeneration/power running in combination, or electrical angle measurement.
Furthermore, these patterns allow for measurement based on one motor revolution (one
cycle of the mechanical angle).
• When inputting the origin (Z-phase pulse) signal in motor analysis mode, always input the pulses
outputted from the same encoder. If the order of the RPM pulse signal’s rising edges and the
origin signal’s rising edges reversed, RPM measurement may become unstable.
• When taking measurement using a pulse as a reference for motor analysis, use a signal with the
number of pulses that is an integer multiple of the number of motor pole pairs (which is half the
total number of poles in the motor). (p. 58)
• In an electrically noisy environment, ground the instrument and the connected sensors at the
same electric potential.
Motor analysis option wiring
Ch. A Ch. B Ch. C Ch. D Ch. E Ch. F Ch. G Ch. H
Individual Input
Indiv. Indiv. Indiv. Indiv. Indiv. Indiv. Indiv. Indiv.
Motor 1 Motor 2 Motor 3 Motor 4
Torque
Speed(Pulse)
Torque Speed Torque Speed Torque Speed Torque Speed
Torque Speed
Direction Origin
Torque Speed Direction Origin Torque Speed Direction Origin
Torque Speed
Direction
Torque Speed Direction OFF Torque Speed Direction OFF
Torque Speed
Origin
Torque Speed OFF Origin Torque Speed OFF Origin
Torque
Speed(Analog)
Torque OFF Speed OFF Torque OFF Speed OFF

 Loading...
Loading...