356
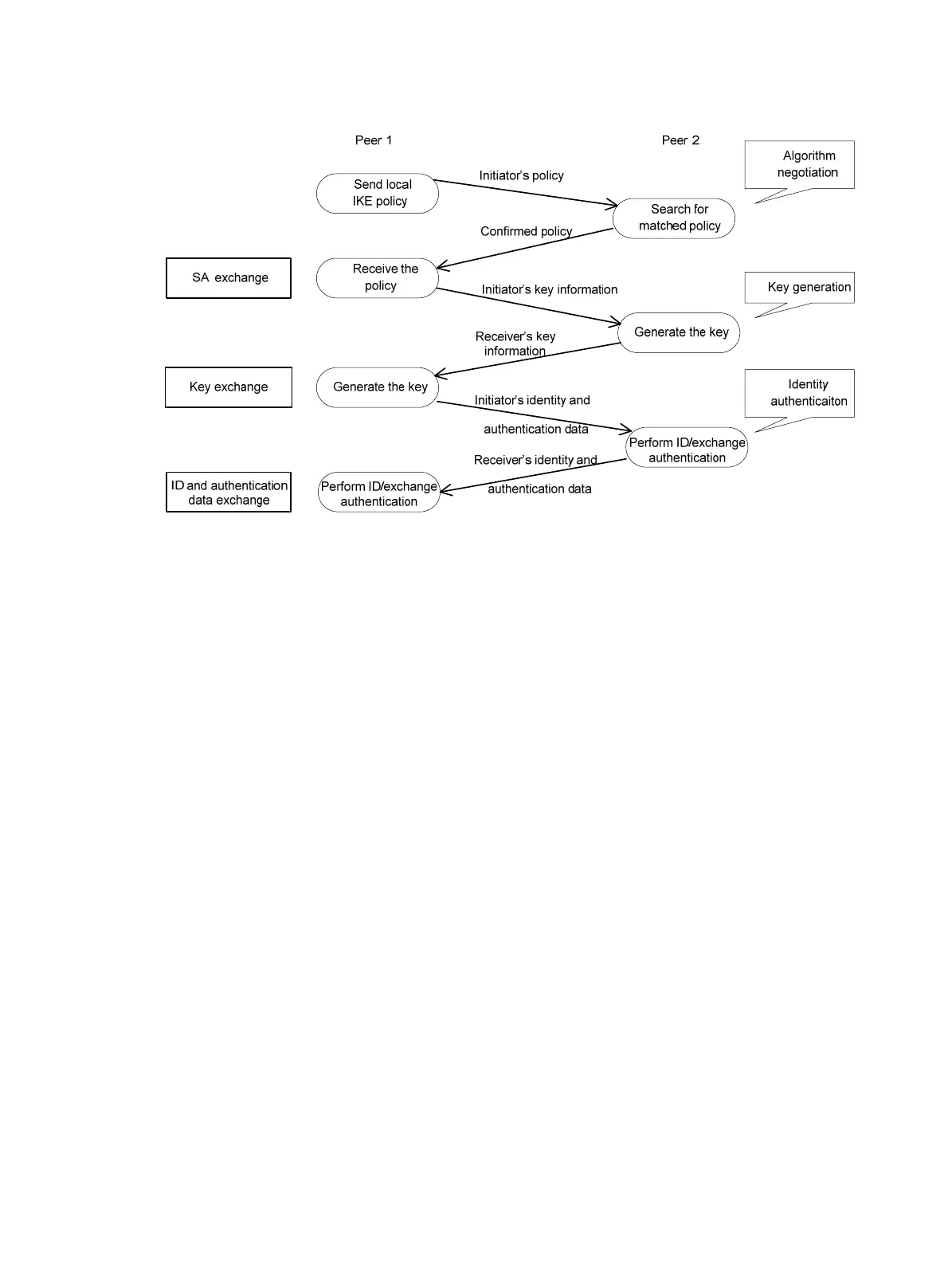
Figure 119 IKE exchange process in main mode
As shown in Figure 124, the main mode of IKE negotiation in phase 1 involves three pairs of messages:
• SA exchange, used for negotiating the security policy.
• Key exchange, used for exchanging the Diffie-Hellman public value and other values like the
random number. Key data is generated in this stage.
• ID and authentication data exchange, used for identity authentication and authentication of data
exchanged in phase 1.
IKE functions
IKE provides the following functions for IPsec:
• Automatically negotiates IPsec parameters such as the keys.
• Performs DH exchange when establishing an SA, making sure that each SA has a key independent
of other keys.
• Automatically negotiates SAs when the sequence number in the AH or ESP header overflows,
making sure that IPsec provides the anti-replay service normally by using the sequence number.
• Provides end-to-end dynamic authentication.
• Identity authentication and management of peers influence IPsec deployment. A large-scale IPsec
deployment needs the support of certificate authorities (CAs) or other institutes which manage
identity data centrally.

 Loading...
Loading...











