HP StorageWorks P2000 G3 MSA System SMU Reference Guide 31
Network operating system, databases, high availability applications, workgroup servers 5
Very large databases, web server, video on demand 50
Mission-critical environments that demand high availability and use large sequential workloads 6
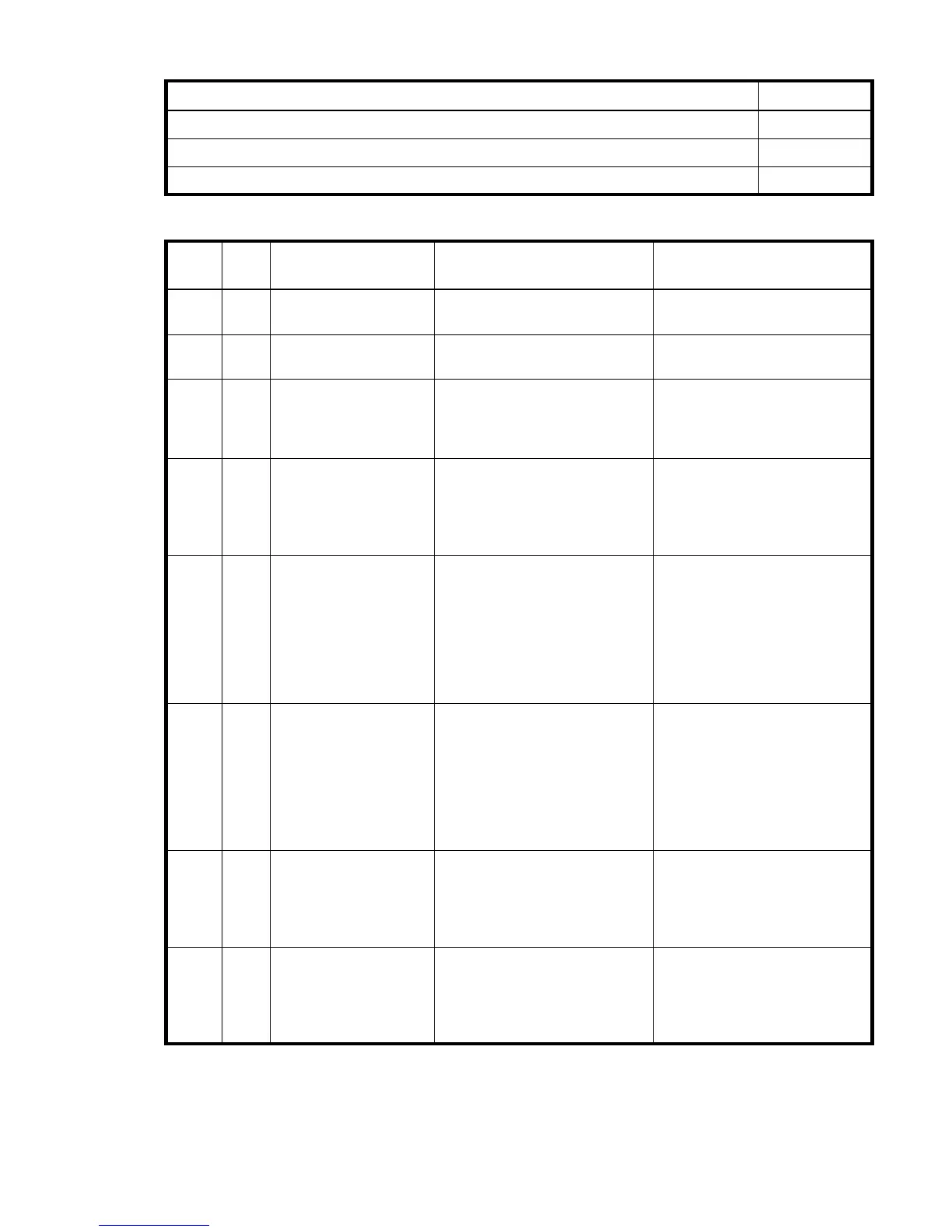
Table 5 RAID level comparison
RAID
level
Min.
disks
Description Strengths Weaknesses
NRAID 1 Non-RAID, nonstriped
mapping to a single disk
Ability to use a single disk to store
additional data
Not protected, lower performance
(not striped)
0 2 Data striping without
redundancy
Highest performance No data protection: if one disk
fails all data is lost
1 2 Disk mirroring Very high performance and data
protection; minimal penalty on
write performance; protects
against single disk failure
High redundancy cost overhead:
because all data is duplicated,
twice the storage capacity is
required
3 3 Block-level data striping
with dedicated parity
disk
Excellent performance for large,
sequential data requests (fast
read); protects against single disk
failure
Not well-suited for
transaction-oriented network
applications: single parity disk
does not support multiple,
concurrent write requests
5 3 Block-level data striping
with distributed parity
Best cost/performance for
transaction-oriented networks;
very high performance and data
protection; supports multiple
simultaneous reads and writes;
can also be optimized for large,
sequential requests; protects
against single disk failure
Write performance is slower than
RAID 0 or RAID 1
6 4 Block-level data striping
with double distributed
parity
Best suited for large sequential
workloads; non-sequential read
and sequential read/write
performance is comparable to
RAID 5; protects against dual disk
failure
Higher redundancy cost than
RAID 5 because the parity
overhead is twice that of RAID 5;
not well-suited for
transaction-oriented network
applications; non-sequential write
performance is slower than RAID
5
10
(1+ 0)
4Stripes data across
multiple RAID-1
sub-vdisks
Highest performance and data
protection (protects against
multiple disk failures)
High redundancy cost overhead:
because all data is duplicated,
twice the storage capacity is
required; requires minimum of four
disks
50
(5+0)
6Stripes data across
multiple RAID-5
sub-vdisks
Better random read and write
performance and data protection
than RAID 5; supports more disks
than RAID 5; protects against
multiple disk failures
Lower storage capacity than RAID
5
Table 4 Example applications and RAID levels
Application RAID level

 Loading...
Loading...











