Processor Thermal/Mechanical Information
18 Thermal and Mechanical Design Guidelines
The thermal profiles for the Intel Core™2 Duo processor E8000 series with 6 MB
cache, Intel Core™2 Duo processor E7000 series with 3 MB cache, and Intel Pentium
dual-core processor E6000 and E5000 series with 2 MB cache, and Intel Celeron
processor E3000 series with 1 MB cache are defined such that there is a single
thermal solution for all of the 775_VR_CONFIG_06 processors.
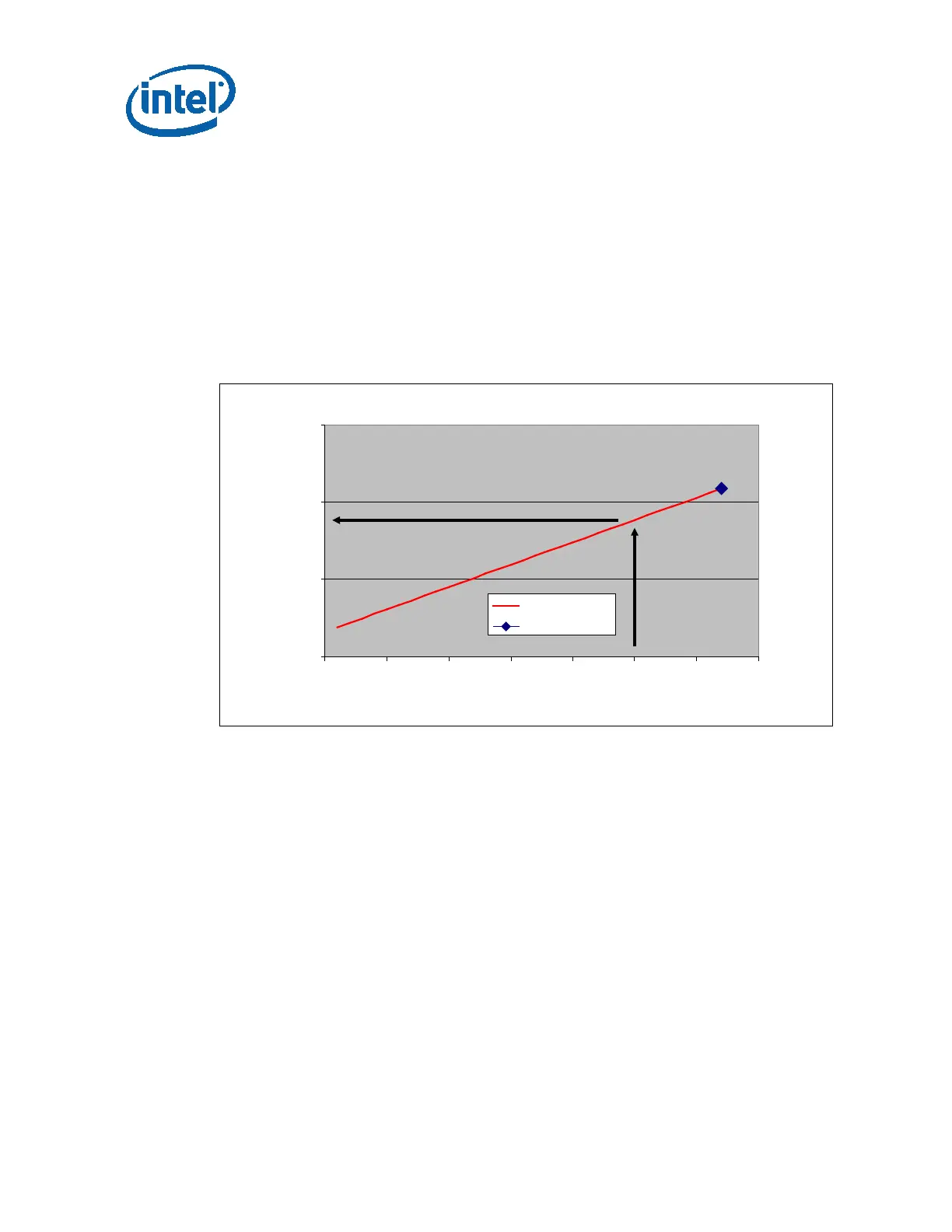
To determine compliance to the thermal profile, a measurement of the actual
processor power dissipation is required. The measured power is plotted on the
Thermal Profile to determine the maximum case temperature. Using the example in
Figure 2-3 for a processor dissipating 50 W the maximum case temperature is 58 °C.
See the datasheet for the thermal profile.
Figure 2-3. Example Thermal Profile
2.2.4 T
CONTROL
T
CONTROL
defines the maximum operating temperature for the digital thermal sensor
when the thermal solution fan speed is being controlled by the digital thermal sensor.
The T
CONTROL
parameter defines a very specific processor operating region where fan
speed can be reduced. This allows the system integrator a method to reduce the
acoustic noise of the processor cooling solution, while maintaining compliance to the
processor thermal specification.
Note: The T
CONTROL
value for the processor is relative to the Thermal Control Circuit (TCC)
activation set point which will be seen as 0 using the digital thermal sensor. As a
result the T
CONTROL
value will always be a negative number. See Chapter 4 for the
discussion the thermal management logic and features and Chapter 7 on Intel Quiet
System Technology (Intel QST).
The value of T
CONTROL
is driven by a number of factors. One of the most significant of
these is the processor idle power. As a result a processor with a high (closer to 0)
T
CONTROL
will dissipate more power than a part with lower value (farther from 0, such
as larger negative number) of T
CONTROL
when running the same application.
40
50
60
70
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70

 Loading...
Loading...











