Series 2600 System SourceMeters Reference Manual TSP Programming Fundamentals 2-41
Return to Section 2 topics 2600S-901-01 Rev. A / May 2006
Script using a function
TSL facilitates grouping commands and statements using the function keyword.
Therefore, a script can also consist of one or more functions. Once a script has
been RUN, the host computer can then call a function in the script directly.
The script in Table 2-2 contains an ICL command to set measurement speed
(NPLC) and a function (named sourcev). When this script is run, the
measurement speed will set to 0.5 PLC and make the
sourcev function available
for calling.
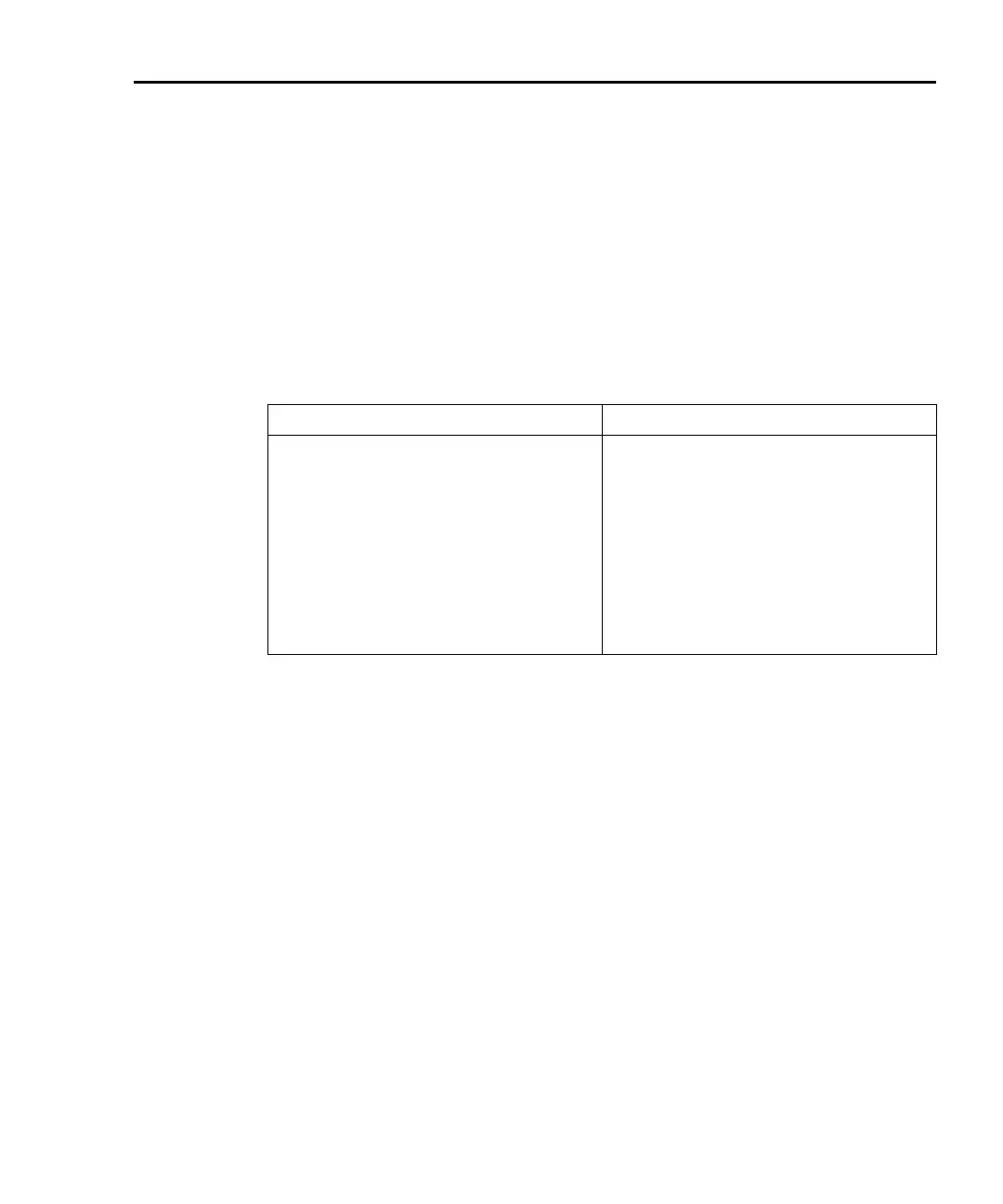
Table 2-2
Example script using a function
Test Script Builder User’s Program Script
loadscript
smua.measure.nplc = 0.5 smua.measure.nplc = 0.5
function sourcev(v) function sourcev(v)
smua.source.levelv = v smua.source.levelv = v
i = smua.measure.i() i = smua.measure.i()
print(i) print(i)
return(i) return(i)
end end
endscript
When calling the function, you must specify the source voltage in the argument for
the function. For example, to set the source to 2V, call the function as follows:
sourcev(2)
Assuming SMU A output is on, it will output 2V and measure the current. The
current reading is sent to the host PC and displayed.
Interactive script
An interactive script prompts the operator (via the SourceMeter display) to input test
parameters (via the SourceMeter front panel). The chunk fragment in
Table 2-3
uses display messages to prompt the operator to select an SMU Channel (A or B),
a source function (I or V), and to input the source level. When an input prompt is
displayed, the script will wait until the operator inputs the parameter and/or presses
the ENTER key.
The display.prompt command, in the following script, prompts the user to input
a source level. If a value is not entered, the default level (1mA or 1V) will be set
when ENTER is pressed. The operator will not be able to input values that are not
within the minimum (0.5mA or 0.1V) and maximum (3mA or 10V) limits.
 Loading...
Loading...











