TP-5660 11/9860 Installation
cables, negative (--) leads last; and reconnect power to
the generator engine start battery chargers, if installed.
6.6 Functional Tests
6.6.1 Voltage Check
Perform a voltage check to verify that the voltages and
phasing of all power sources are compatible with the
transferswitchbefore energizing theload orconnecting
the power switching device and controller wire
harnesses together.
Thenominalvoltageandfrequencyofthenormal(utility)
source, transfer switch nameplate, and generator set
output and nameplate should all be the same to avoid
damage to loads and the transfer switch.
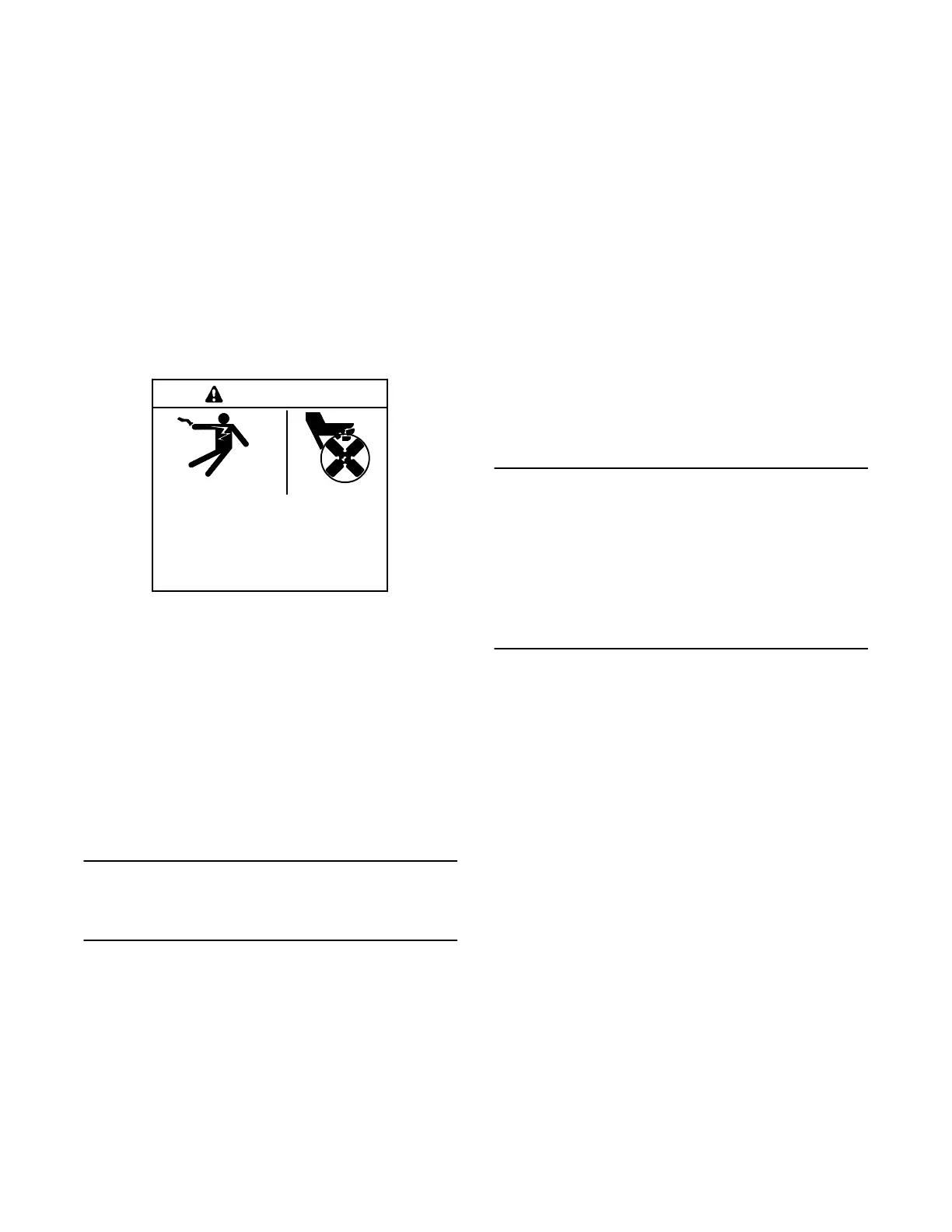
Hazardous voltage.
Movingrotor.
Can cause severe injury or death.
Operate generator set only with all
guards and electrical enclosures in
place.
WARNING
Short circuits. Hazardous voltage/current can cause
severe injury ordeath. Short circuitscan cause bodilyinjury
and/or equipment damage. Do not contact electrical
connections with tools or jewelry while makingadjustments or
repairs. Remove wristwatch, rings, and jewelry before
servicing equipment.
Read and understand all instructions on installation
drawings and labels affixed to the switch. Note any
optional accessories that have been furnished with the
switch and review their operation.
Voltage Check Procedure
NOTE
Perform voltage checks in the order given to avoid
damaging the transfer switch.
1. Disconnect all power sources before opening the
transfer switch enclosure by opening upstream
circuit breakers or switches to the transfer switch.
2. Disconnect the power switching device and the
logic controller wire harnesses at the inline
disconnect plug if they are connected.
3. Move the generator set master switch to the OFF
position to inhibit generator set starting.
4. Manually transfer the load to the emergency
source. See Section 2.3.
5. Reapply the normal source by closing circuit
breakers or switches.
6. Use an accurate voltmeter to check the normal
source phase-to-phase and phase-to-neutral
terminal voltages. Use accurate test equipment to
check the phase rotation at the normal source
terminals. If the nominal normal source voltage or
frequency is not what is shown on the transfer
switch nameplate, STOP! Do not proceed further
in installation because the transfer switch is not
designed for the application—call a local service
center to order the correct transfer switch. Rewire
the transfer switch normal source terminals to
obtain a phase sequence of A-B-C if required on
transfer switches with microprocessor controls
(see NOTE.)
NOTE
Thepowersourceleads mustbe phasedA-B-Cfor
option DD-34-Z (phase sequence and loss
monitoring) to function correctly on
microprocessor-based controls. If the power
source phase sequence is not A-B-C and option
DD-34-Z is enabled the controller considers the
source to have failed.
7. Disconnect the normal power source by opening
upstream circuit breakers or switches to the
transfer switch.
8. Manually transfer the load to the normal source.
See Section 2.3.
9. Reapply the emergency source by closing circuit
breakers or switches.
10. Move the generator set master switch to the RUN
position. The generator set should start.
11. Useanaccuratevoltmetertochecktheemergency
source phase-to-phase and phase-to-neutral
terminal voltages. Use accurate test equipment to
check the phase rotationat theemergency-source
terminals. Rewire the transfer switch emergency
source terminals if the emergency source phase
rotation is not the same as the normal source.

 Loading...
Loading...