MIPI DSI to OpenLDI/FPD-Link/LVDS Interface Bridge Soft IP
User Guide
© 2016 Lattice Semiconductor Corp. All Lattice trademarks, registered trademarks, patents, and disclaimers are as listed at www.latticesemi.com/legal. All other brand or product names are
trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. The specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice.
FPGA-IPUG-02003-1.2 15
3. Parameter Settings
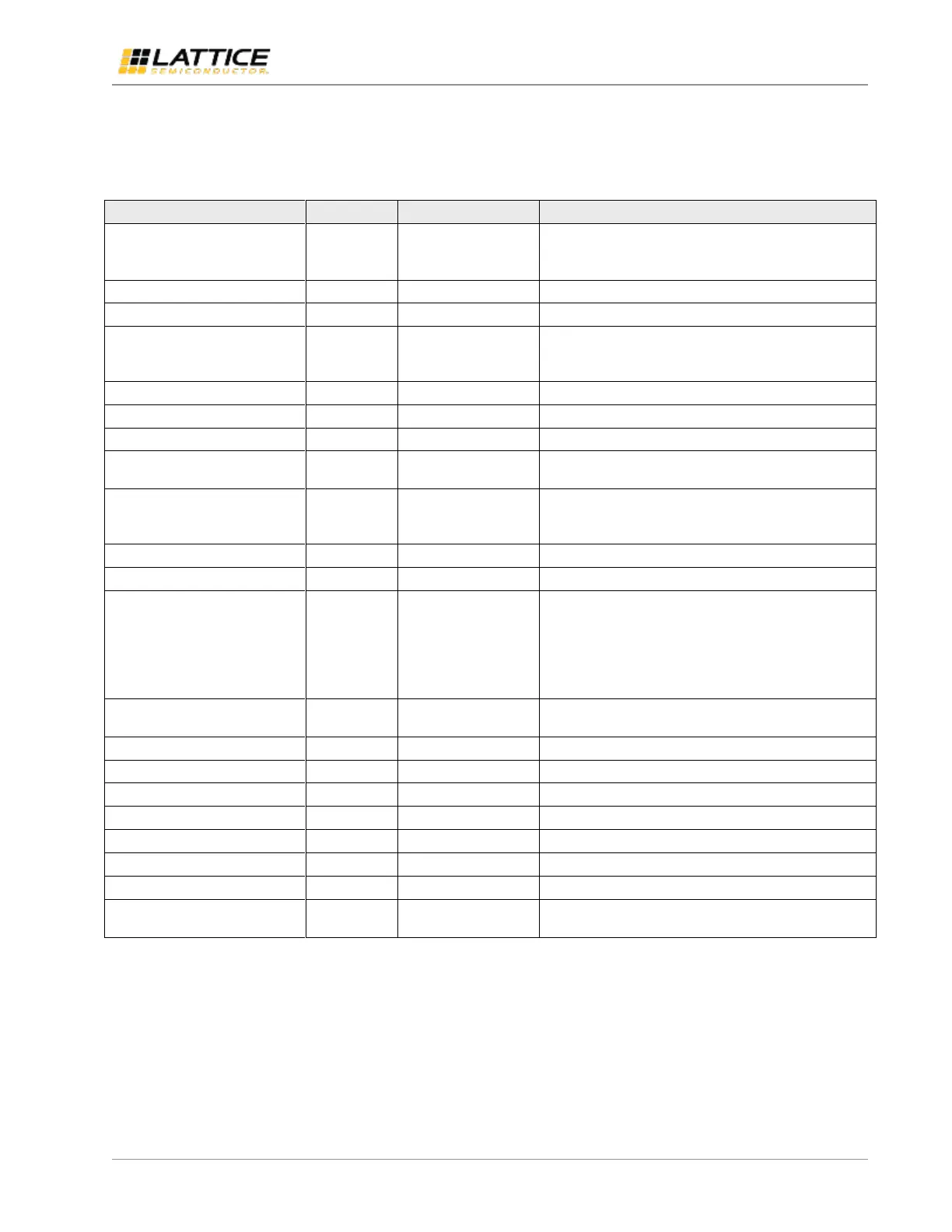
Table 3.1 shows the parameters used to generate MIPI DSI to OpenLDI/FPD-Link/LVDS Interface Bridge IP.
Table 3.1. MIPI DSI to OpenLDI/FPD-Link/LVDS Interface Bridge IP Parameter Settings
Number of MIPI D-PHY channels.
If 2 is selected, the following Rx settings will be applied
to both Rx channels
Number of MIPI D-PHY data lanes
Gearbox ratio of receive interface, automatically
selected based on Rx data rate (see Reset and Clocking
section on page 13)
MIPI D-PHY Implementation
Transmit interface (FPD-Link)
Derived from data type: 3 lanes for RGB666 while 4
lanes for RGB888
Gearbox ratio of transmit interface, automatically
selected based on Rx data rate (see Reset and Clocking
section on page 13)
Data rate per MIPI D-PHY lane
MIPI D-PHY clock frequency (DCK).
t
HS-SETTLE
MIPI D-PHY timing parameter is also derived
from this setting (85 ns + 6 UI).
t
HS-SETTLE
counter is implemented in byte clock domain.
The expected actual t
HS-SETTLE
is ~2 byte clock cycles
more than the computed value.
Continuous or Non-
continuous
Serializer clock frequency
Reference Clock Frequency
Reference clock frequency
Brings out miscellaneous status signals to port
Supported MIPI DSI data types
Selects between RGB666 Packed and Loosely Packed
formats
 Loading...
Loading...