D–6
Appendix D
Parameter and what it does Definition Notes
csdev
Cyclic standard deviation: Standard
deviation of data values from mean value
over integral number of periods. Contrary
to sdev, calculation performed over
integral number of cycles, eliminating
bias caused by fractional intervals.
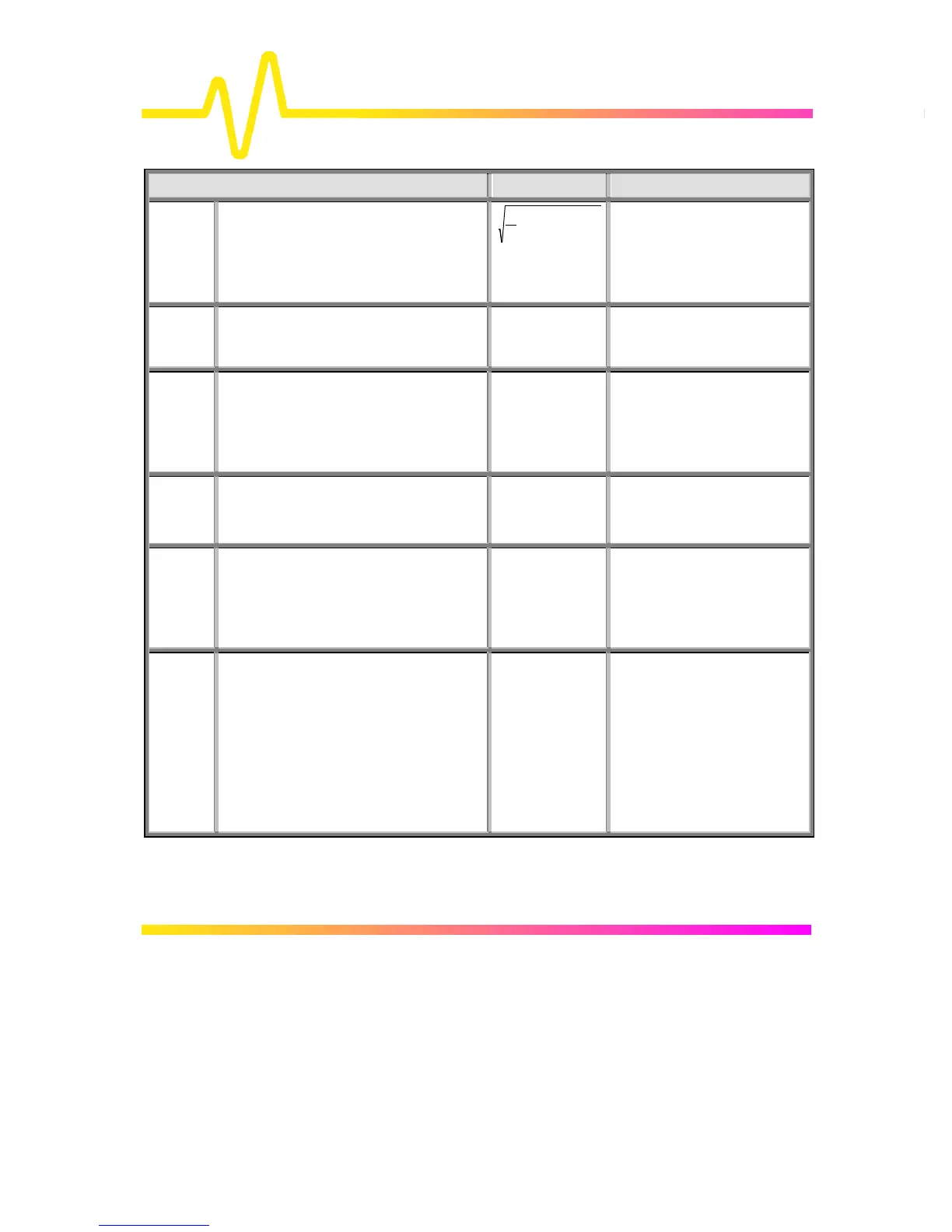
∑
=
−
N
i
i
)meanv(
N
1
2
1
Where:
v
i
denotes measured
sample values, and N = number
of data points within the periods
found up to maximum of 100
periods.
data
Returns average of all data points. All data values in
analyzed region
(See Fig. D–2)
Multi-value parameter especially
valuable for histograms and
trends.
delay
Time from trigger to transition: Measures
time between trigger and first 50 %
crossing after left cursor. Can measure
propagation delay between two signals
by triggering on one and determining
delay of other.
Time between
trigger and first
50 % crossing
after left cursor
(See Fig. D–2)
∆dly ∆delay: Computes time between 50 %
level of two sources.
Time between
midpoint
transition of two
sources
∆t@lv ∆t at level: Computes transition between
selected levels or sources.
Time between
transition levels
of two sources,
or from trigger to
transition level of
a single source
Reference levels and edge-
transition polarity can be
selected. Hysteresis argument
used to discriminate levels
from noise in data.
∆c2d± ∆clock to data ±: Computes difference in
time from clock threshold crossing to either
the next (∆c2d+) or previous (∆c2d−) data
threshold crossing.
Time from clock
threshold
crossing to next
or previous edge
(See Fig. D–3)
Threshold levels of clock and
data signals, and edge-transition
polarity can be selected.
Hysteresis argument used to
differentiate peaks from noise in
data, with good hysteresis value
between half expected peak–
to–peak value of signal and
twice expected peak–to–peak
value of noise.

 Loading...
Loading...





