29
SC-1
3.5 THEORY
The SC-1 Leaf Porometer measures stomatal conductance of leaves. Stomata are small
pores on the top and bottom of a leaf that are responsible for taking in and expelling CO
2
and
moisture. Stomatal conductance is the rate of passage of CO
2
or water vapor through the
stomata and is a function of the density, size, and degree of opening of stomata.
The SC-1 measures this rate by putting a leaf in series with two known conductance
elements and comparing the RH measurements between them. The RH difference across the
known conductance elements gives the water vapor flux. The conductance of the leaf can be
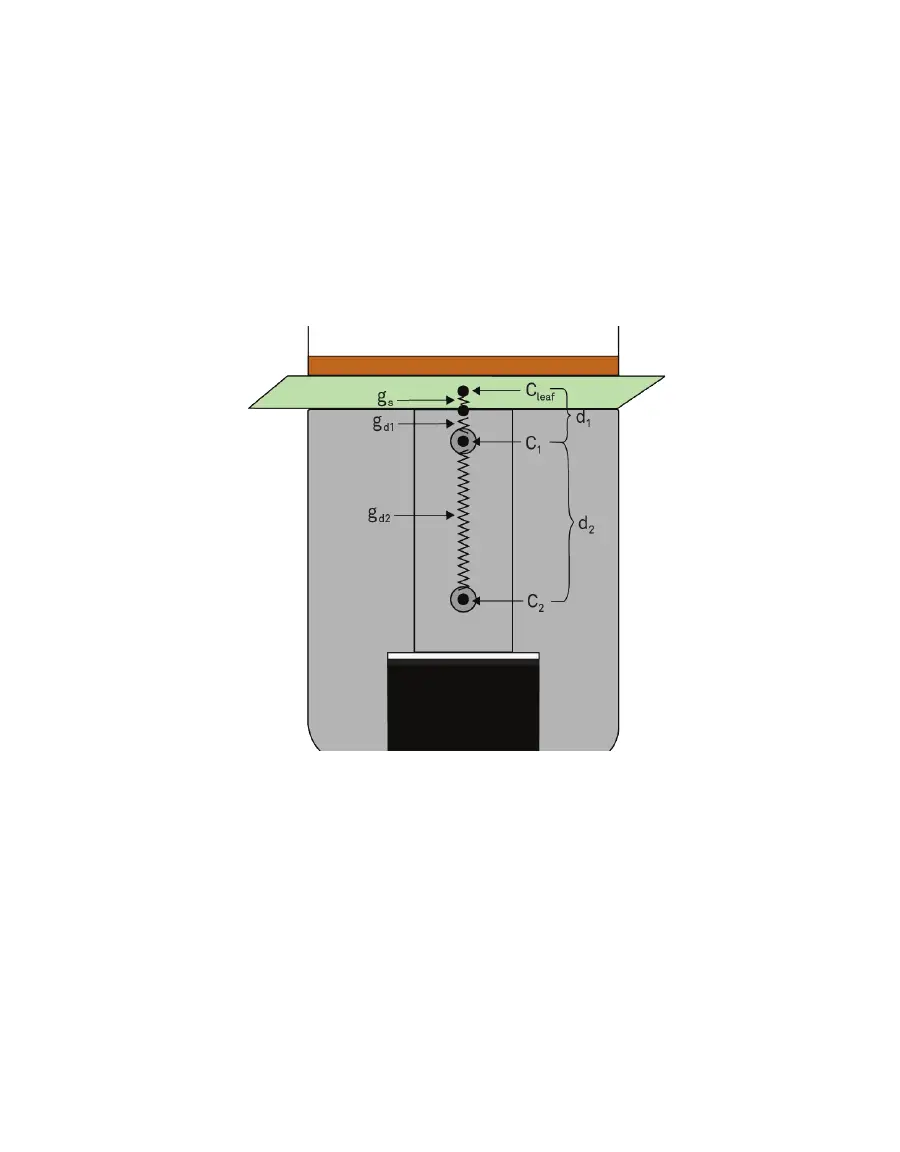
calculated from the known conductances and the RH gradient. The SC-1 diagram represents
these measurement processes (Figure42).
Figure42 Diagram of SC-1 measurements
The parameters listed in Figure42 represent the following:
C
leaf
= mole fraction of vapor inside the leaf
C
1
= mole fraction of vapor at node 1
C
2
= mole fraction of vapor at node 2
g
s
= stomatal conductance of the leaf surface
g
d1
= vapor conductance of the diffusion path between leaf surface and node 1
g
d2
= vapor conductance of the diffusion path between node 1 and node 2
d
1
= distance between the leaf surface and the first RH sensor
d
2
= distance between the two RH sensors
 Loading...
Loading...