What to do if Miller Welding System shuts down due to overload?
- ZzfosterJul 29, 2025
If the Miller Welding System shuts down due to overload, it may be because CB1 opens. In this case, reset the supplementary protector.
What to do if Miller Welding System shuts down due to overload?
If the Miller Welding System shuts down due to overload, it may be because CB1 opens. In this case, reset the supplementary protector.
Explains the meaning of warning symbols used throughout the manual.
Details hazards like electric shock, moving parts, and hot parts during arc welding.
Warns about fire, explosion, and overheating risks during installation and operation.
Details risks from falling equipment, sparks, moving parts, wire, and batteries.
Warns about electrostatic discharge damaging electronic components.
Emphasizes reading all labels and the owner's manual before operation.
Advises medical implant wearers to consult doctors before operating near welding equipment.
Explains additional safety symbols and their meanings.
Provides definitions for various symbols related to welding parameters and functions.
Covers serial number location and software licensing agreement.
Notes on default parameters and specifications for MIG, TIG, and Stick welding.
Details the Ingress Protection (IP) rating and suitability for indoor use.
Outlines operating and storage temperature ranges for the equipment.
Provides guidelines for selecting a suitable and safe location for the unit.
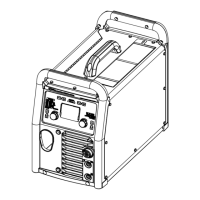
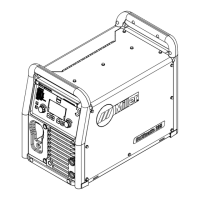
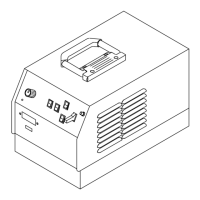
Identifies and explains the function of the main controls on the unit.
Outlines routine maintenance tasks and their recommended frequency.
Explains the overload protection mechanism and how to reset it.
Identifies welding processes that utilize high frequency.
Illustrates potential sources of high-frequency interference in the installation.
Guides on selecting the correct tungsten electrode based on diameter and composition.
Details different tungsten electrode compositions and their application notes.
Provides guidance on proper torch positioning for TIG welding.
Shows typical connection diagrams for the MIG welding process.
Provides typical control settings for MIG welding, including wire size and voltage.
Details the procedure for performing stick welding.
Provides a chart for selecting electrodes and appropriate amperage.
Lists recommended spare parts for MIG welding consumables.
Lists recommended spare parts for TIG welding accessories.
| Input Voltage | 120/240 V |
|---|---|
| Weight | 56 lb (25.4 kg) |
| Input Phase | 1-Phase |
| Input Hz | 50/60 Hz |
| TIG Lift Arc | Yes |
| TIG HF Start | Yes |
| Wire Size Range | 0.024 - 0.035 in (0.6 - 0.9 mm) |
| Processes | MIG, Stick, TIG |
| Output Voltage Range | 10 - 24.5 V |