10 - 60 10 - 60
MELSEC-Q
10 DEVICES
10.11.5 Macro instruction argument device (VD)
(1) Definition
Macro instruction argument devices are used with ladders registered as macros.
When a VD
setting is designated for a ladder registered as a macro,
conversion to the designated device is performed when the macro instruction is
executed.
(2) Designating macro instruction argument devices
Specify the devices transferred from sequence programs to macro registration
ladders as macro instruction argument devices among the devices used in the
ladders registered as macro with GX Developer.
1
Designate devices that correspond to the macro argument devices used in the
macro registration ladders in ascending order, when using macro instructions in a
sequence program.
Transfer to VD2
VD0MOV VD2VD0>VD1D0M.MAX D1 R0
Transfer to VD1
Transfer to VD0
VD1MOV VD2VD0<= VD1
Name of ladder registered as a macro
Actual sequence program executed at CPU
Sequence program Ladder registered as a macro (registration name: MAX
D0MOV R0D0
>D1
D1MOV R0D0<= D1
REMARK
1) 1 : With the macro instruction argument device, VD0 to VD9 can be used in one
ladder registered as a macro instruction.
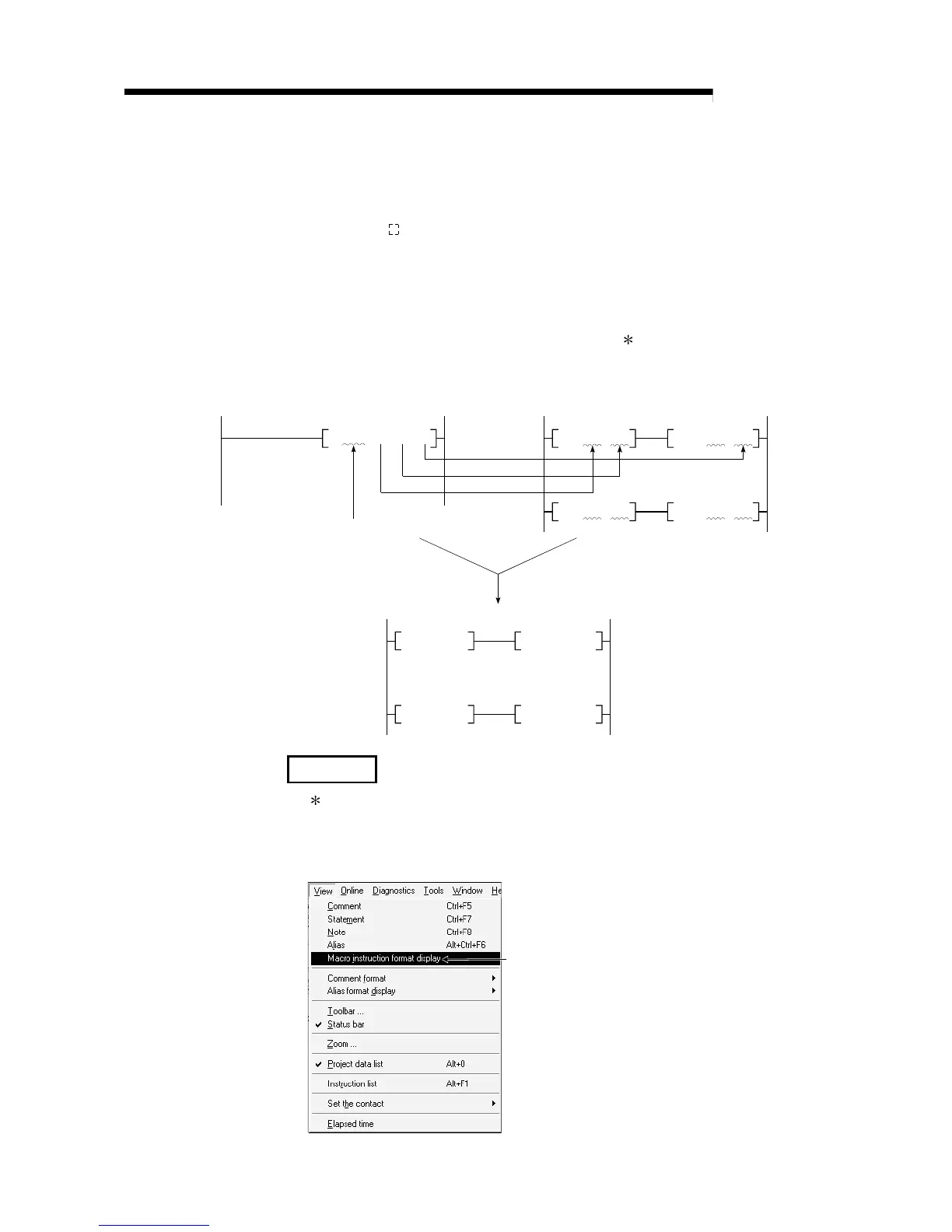
2) The GX Developer read mode provides an option to view a program in macro
instruction format.(Choose "View" - "Macro Instruction format display" to view
macro instructions.)
Change of macro instruction display

 Loading...
Loading...











