Programming via CANopen
network (Routing)
03/05 AWB2724-1453G
56
Alternatively, you can use the BlockSizeEditor application to
change the block size.
The download block size is defined in the following Registry key:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\3S-Smart Software Solutions
GmbH\Gateway Server\Drivers\Standard\Settings\Tcp/Ip (Level 2
Route)]
"Blocksize"=dword:00020000
The default block size is 20000
hex
(=128 Kbyte), the block size for
routing is 1000
hex
(= 4 Kbyte).
Notes
• If large files are written to the target PLC or read from the PLC,
it is possible that the online connection will be interrupted after
the transfer process has been completed. Renewed connection
is possible.
• If a program with a modified routing node ID is loaded into the
target PLC, the target PLC accepts the modified routing node ID;
however, the communication connection will be interrupted.
Reconnection with a corrected routing node ID is possible.
• If a PLC receives a program without valid routing parameters
(baud rate/node ID), this PLC cannot be connected via a routing
connection.
• The routing is independent of the configuration (master/slave):
a target PLC that has not been configured as a master or as a
slave can be accessed. It must only receive the basic parameters
such as node ID and baud rate, as well as a simple program.
Addressing
PLCs on the CANopen bus can be configured as a master or as a
device. The PLCs are assigned with a Node ID/node number
(address) in order to uniquely identify them. If you wish to use the
routing function to access a (target) PLC, you must assign the
target PLC with a further (Routing) Node ID.
Procedure
X Connect the PC to a PLC.
X Select the target PLC with which you want to communicate for
the project.
X Determine the communication settings for the PC and the PLC
connected to the PC.
X Enter the target ID (target ID = Node ID!) of the target PLC as
in the example and log on.
You can run the following functions:
• Program download
• Online modification
• Program test (Debugging)
• Create bootable project
• Filing source code.
Note for project creation:
The node ID/node number and the baud rate of the target PLC to
the routing function can be defined in the Additional parame-
ters tab in the PLC Configuration window:
Enter the baud rate on the CANopen bus and the Node-ID/node
number in the “RS232 l CAN routing settings” field.
This field appears with the XC200, after you have confirmed it in
the Activate field. This activation is necessary to ensure that the
PLC can communicate via the CANopen bus.
Node ID and baud rate are transferred with the project download.
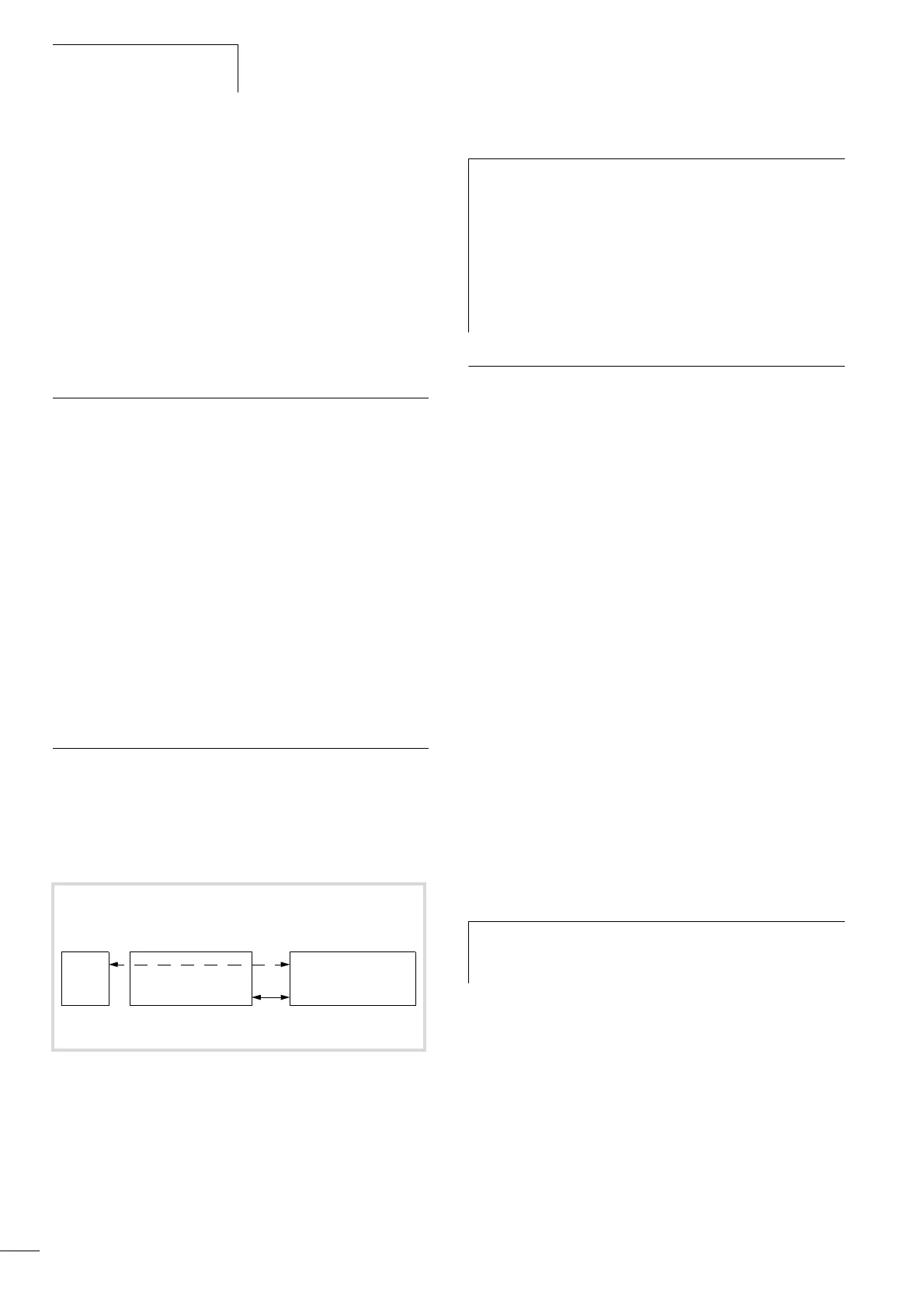
Figure 76: XC100/200, XN-PLC on the CANopen bus, routing principle
PC
Routing PLC XC100/
200/XN-PLC
(master/device)
Node ID 1
Target PLC
XC100/200/XN-PLC
(device)
(Routing) Node ID n
1)
Node ID n
1)
CANopen
h
The following applies for the Node ID of the device func-
tion and the Node ID of the routing function:
XC100 with operating system < V2.0 or XC200:
The routing node ID must be not equal to the device
node ID.
XC100 with operating system f V2.0 or XN-PLC:
The (routing) Node ID must be equal to the Node ID
(device)!
h
In order to guarantee a speedy transfer of data, the
routing with the CANopen should only be performed with
a baud rate of at least 125 Kbit/s.

 Loading...
Loading...