Controller Board Audio and Signaling Circuits Section 3: 1-13
Section : 6881091C63-F
2.2.3 TX Secure Audio (Optional)
The audio follows the normal transmit audio processing until it emerges from the ASFIC CMP TX
SND pin (U0221-44), which is fed to the Secure board residing at option connector J0551-33. The
Secure board contains circuitry to amplify, encrypt, and filter the audio. The encrypted signal is then
fed back from J0551-32 to the ASFIC CMP TX RTN input (U0221-36). The signal level at this pin
should be about 65mVrms. The signal is then routed through the TX path in the ASFIC CMP and
emerges at MOD IN pin 40.
2.2.4 Option Board Transmit Audio
The audio follows the normal transmit audio processing until it emerges from the ASFIC CMP TX
SND pin (U0221-44), which is fed to the option board residing at option connector J0551-33. The
option board contains circuitry to process the audio. The processed signal is then fed back from
J0551-32 to the ASFIC CMP TX RTN input (U0221-36). The signal level at this pin should be about
65 mVrms. The signal is then routed through the TX path in the ASFIC CMP and emerges at MOD
IN pin 40.
2.3 Transmit Signaling Circuits
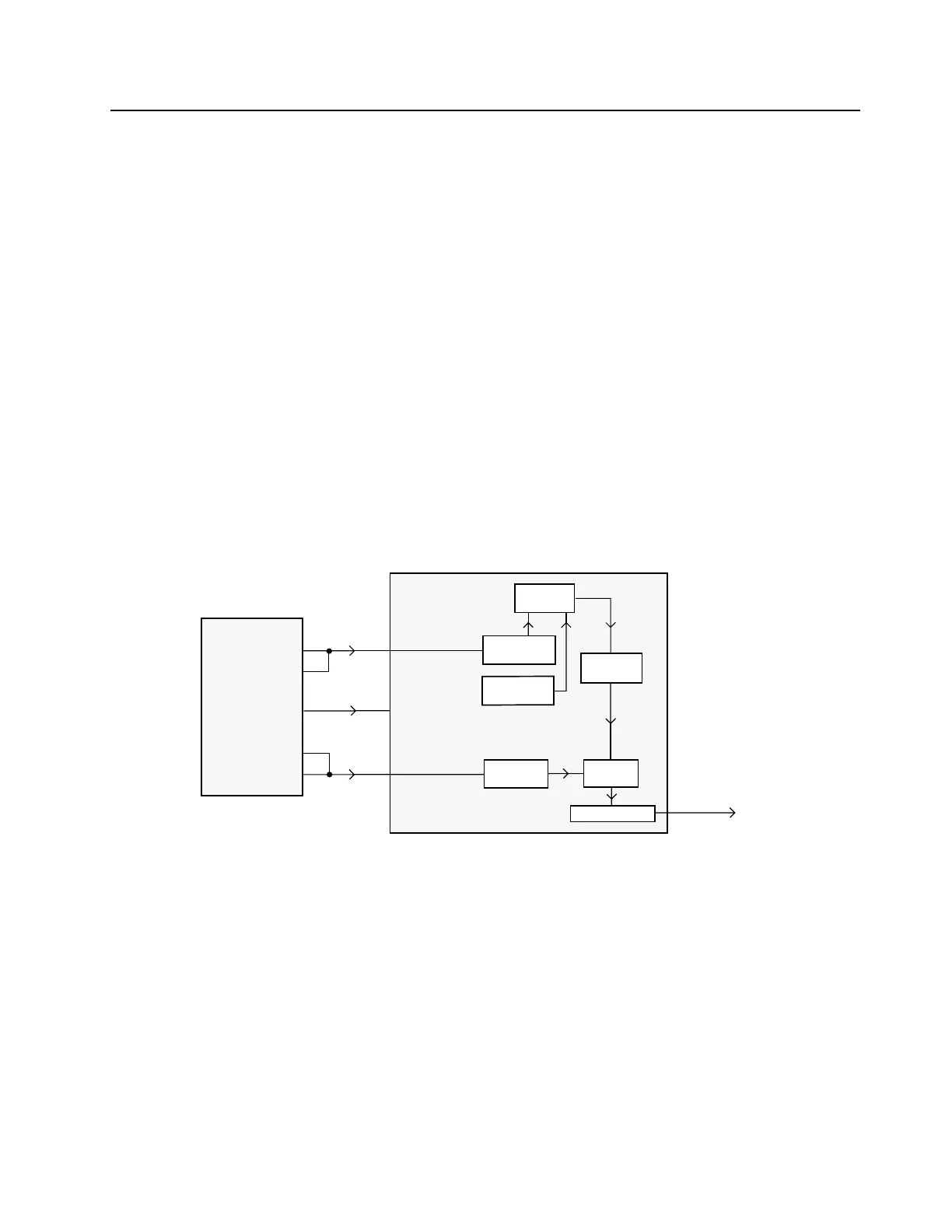
Refer to Figure 3-4 for reference for the following sections.
Figure 3-4 Transmit Signaling Paths
From a hardware point of view, there are 3 types of signaling:
• Sub-audible data (PL / DPL / Connect Tone) that gets summed with transmit voice or
signaling,
• DTMF data for telephone communication in trunked and conventional systems, and
• Audible signaling including MDC and high-speed trunking.
NOTE
All three types are supported by the hardware while the radio software determines which
signaling type is available.
19
18
40
MOD IN
TO RF
SECTION
(SYNTHESIZER
80
44
HIGH SPEED
CLOCK IN
(HSIO)
LOW SPEED
CLOCK IN
(LSIO)
ASFIC_CMP U0221
MICRO
CONTROLLER
U0101
HS
SUMMER
5-3-2 STATE
ENCODER
DTMF
ENCODER
SPLATTER
FILTER
PL
ENCODER
LS
SUMMER
ATTENUATOR
85
82
SPI
BUS

 Loading...
Loading...











