FUNCTIONAL OPERATION ROI-S04488
2-18
2.2.2 Scrambling
To smooth the RF spectrum and to restore the clock at the receiving end,
the multiplexed data streams are scrambled with the 12th (for 4 x 2 MB) or
14th (for 2 x 2 MB, 8 x 2 MB and 16 x 2 MB,) pseudo random pattern
generated by the timing generator (TIM GEN) so that the transmission
mark ratio is 1/2. Then the scrambled data stream is sent to the differential
encoder (DIFF ENCOD).
2.2.3 Parity Check
For detecting the bit error at the receiving end, the parity check bits are
calculated and multiplexed into the radio frame signal streams.
2.3 Modulation
This section describes the differential encoding, 4-phase shift keying
modulation and orderwire signal modulation.
2.3.1 Differential Encoding
In the 4-phase shift keying modulation system, the demodulator phase may
not coincide with the modulation signal of the opposite transmitting end
which give raise to phase ambiguity. To avoid this, an absolute reference
phase is needed between the transmitting and receiving ends.
As shown in Table 2-1, the two independent data streams fed from the
SCRB circuit are represented as an arrangement of Gray-coded binary
digits. The two-bit Gray-coded data streams are then converted into pulse
streams in natural binary code for facilitating differential encoding.
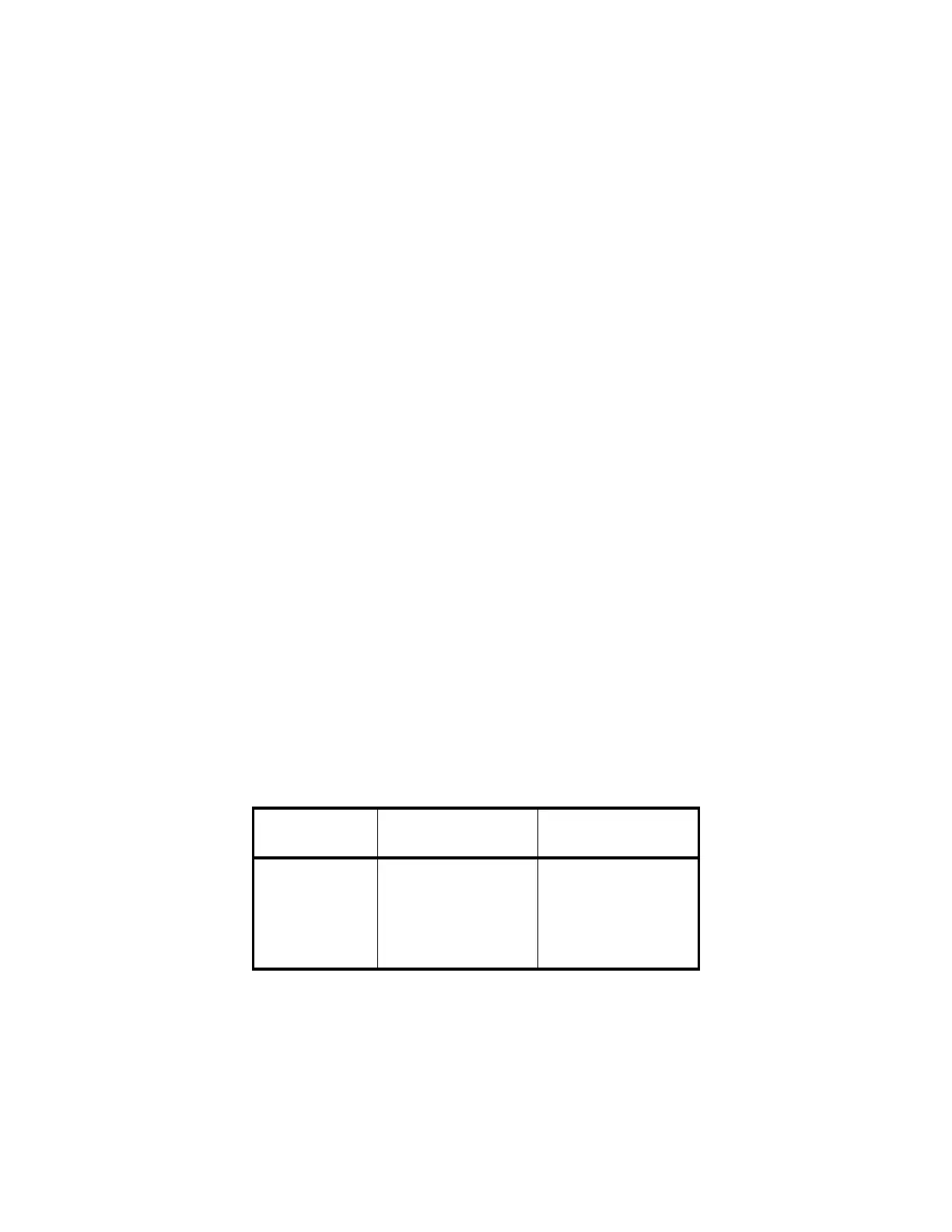
Table 2-1 Binary Combinations
DECIMAL GRAY CODE
NATURAL
BINARY CODE
0 0 0 0 0
1 0 1 0 1
2 1 1 1 0
3 1 0 1 1
 Loading...
Loading...