3.3.3. PHD50/PHD70 frequency input capabilities
The PHD50 and PHD70 have 2 frequency inputs. These inputs are also
configurable as digital inputs. The frequency inputs are ideal for use with hall-
effect type sensors.
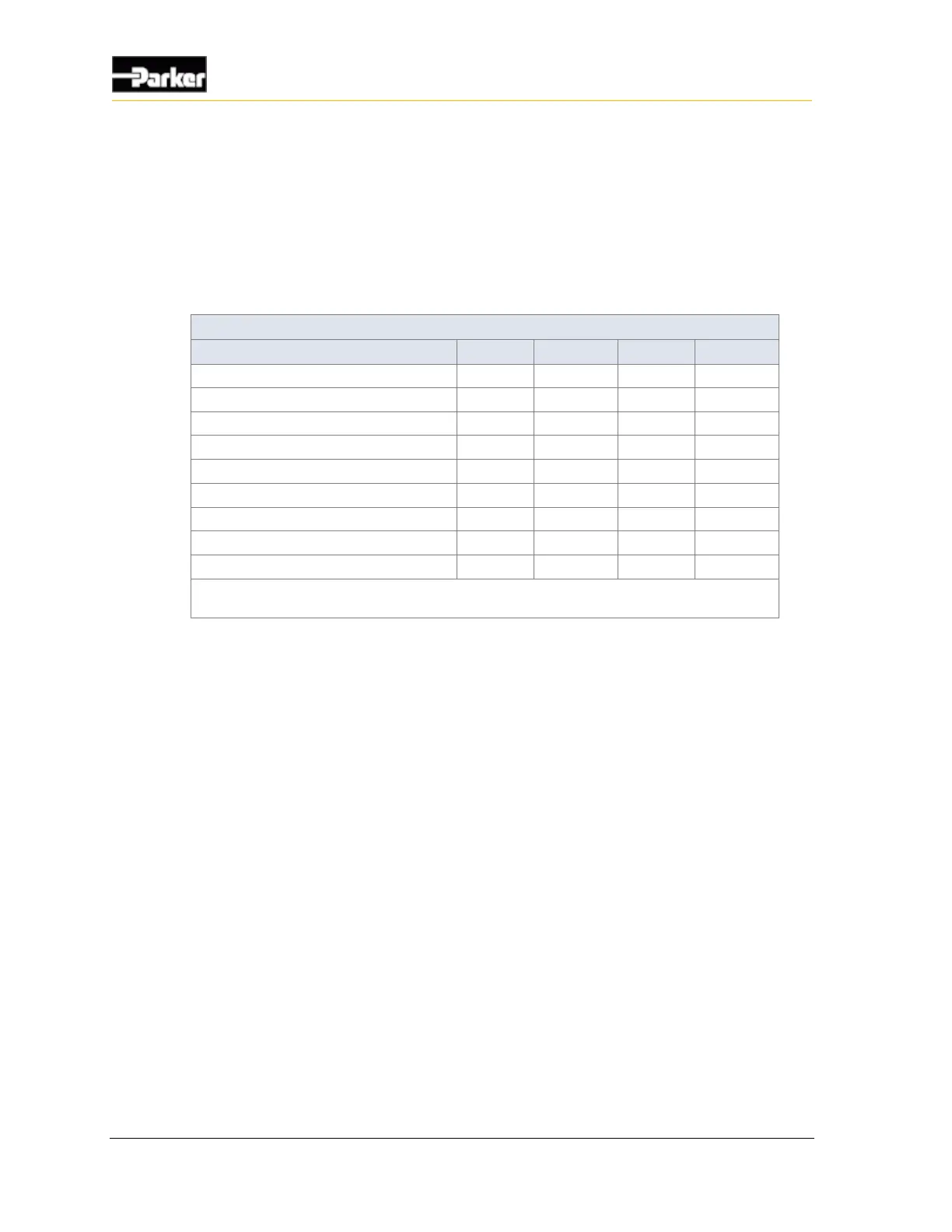
The following table provides specifications for the frequency inputs:
3.3.3.1. DC-Coupled Frequency Input Connections
When connecting DC-coupled frequency inputs, be aware of system noise and
ground level shift.
System Noise
DC-coupled frequency inputs are more susceptible to system noise than digital
inputs.
To reduce system noise:
▪ Connect DC-coupled frequency inputs to sensors that produce signals with no
DC offset.
▪ Use the shortest possible wires when connecting DC-coupled frequency inputs
to sensors to prevent noise pickup on the sensors.
Ground Level Shift
Ground level shift affects the accuracy of DC-coupled frequency inputs. Ground
level shift refers to the difference between the system ground input (GND)
voltage, and the sensor ground voltage.

 Loading...
Loading...











