PAL-AT Installation Manual
10
2 PAL-AT Alarm/Locator Panel
2.1 Alarm/Locator Panel Installation
The PAL-AT panel is designed to be permanently mounted indoors in a dry area. The enclosure is rated
Type 12 [IP52]. It must not be located in direct sunlight to prevent excessive heat buildup. In all
installations, the ambient temperature surrounding the PAL-AT panel must be within the limits
below. The equipment is designed to be safe in the following range of environmental conditions:
a) Indoor use;
b) Altitude up to 6,560 ft [2000 m];
c) Temperature -4°F [-20°C] to 122°F [50°C];
d) Maximum relative humidity 95%;
e) Pollution degree 2.
Warning: Do not mount the PAL-AT panel in a hazardous location. The panel must be in an
ordinary location even though sensor cables may be located in hazardous locations. Refer to the
Zener Barrier Panel section of this manual.
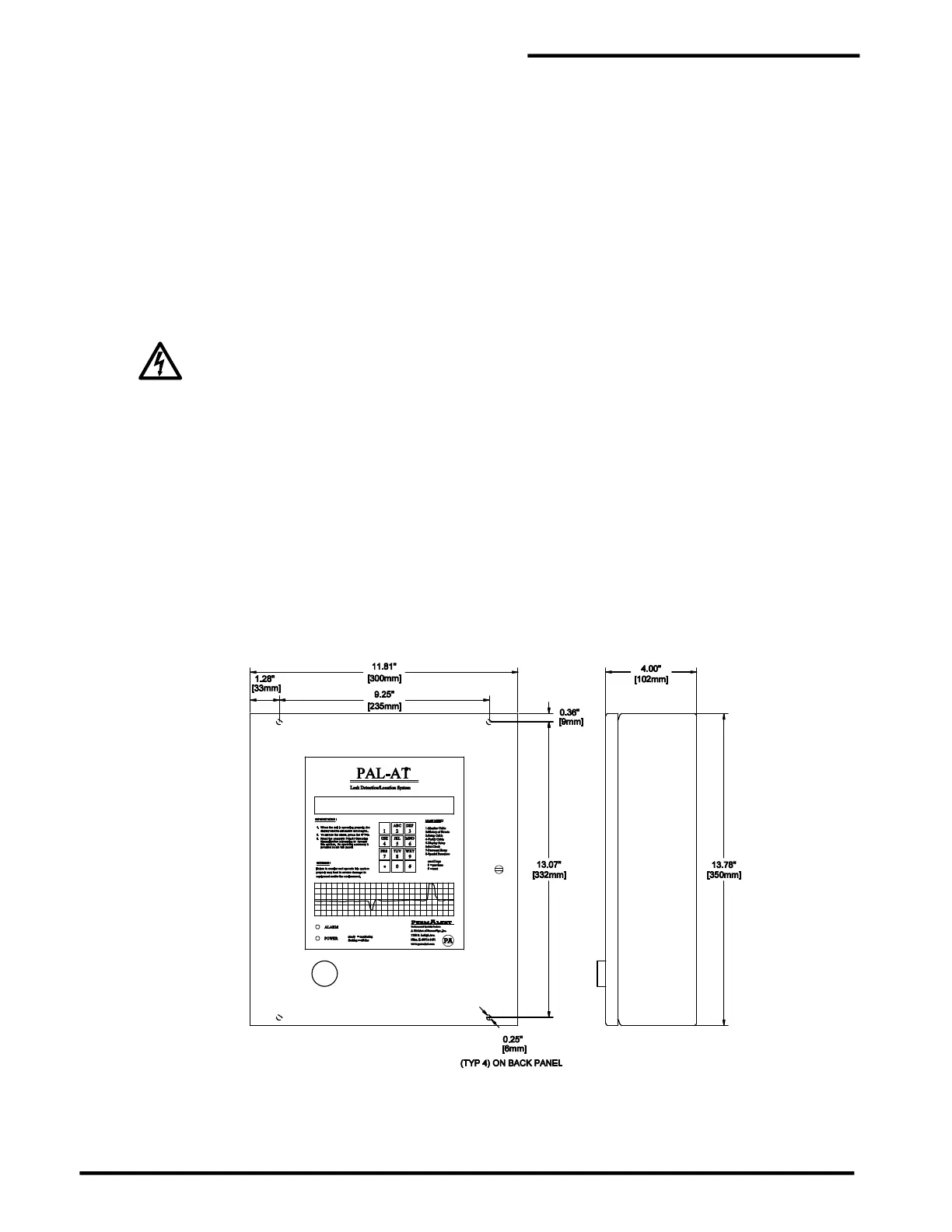
Mount the PAL-AT panel securely to a wall, using ¼” [M6] hardware in the 4 holes on the back of the panel
(see figure 2-1). If it is mounted to a typical ½” plasterboard wall, use ¼” x 1 ½” [M6 x 40mm] lag screws
to secure it to the studs (nominal 2” x 4” [50mm x 100mm]). The panel can also be mounted to steel
mounting channel struts using ¼” [M6] machine screws.
The PAL-AT panel is connected to the sensor cable using jumper cable (Type JMP-U, JMP-UD or JPP).
An exception to this requirement is ATP cable that uses 50’ [15 m] of ATP for jumper (see section 9). At
least 50' [15 m] of jumper cable (65' [20 m] if JPP) must be connected between the panel and the
connection to the sensor cable.
The jumper cable must be run in a separate conduit from the power supply cable. All conduit fittings must
be appropriately rated and installed properly to maintain the rating of the enclosure. All electrical
connections must comply with local codes. Remove the system board from the white back panel (six
#6-32 screws) before drilling holes in the enclosure for conduit openings to prevent damage and
contamination from metal shavings.
Models AT30C, AT75C and AT30K
Mounting Dimensions
Figure 2-1

 Loading...
Loading...