- 10 -
Consequences of an electrical shock
The risk level from an electrical current is dependant, amongst other factors,
on the voltage (U), resistance (R), current (I), duration of the current effect,
type of current (direct or alternating current), the route of the current through the
body and the frequency of the current. As an example, the following table
details the consequences of an electric shock with alternating current.
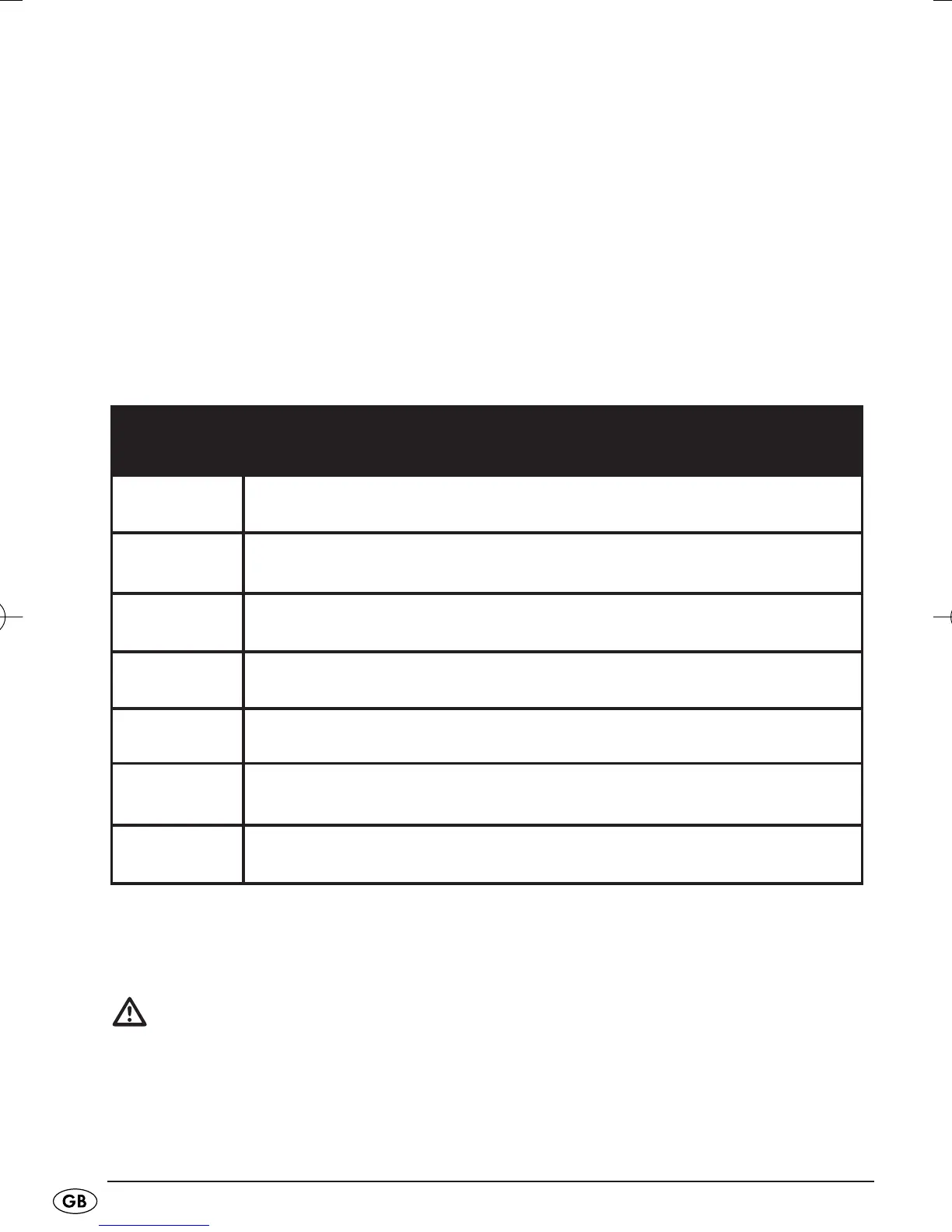
Consequences of an electric shock by an alternating current:
Interaction with batteries
Risk of explosion!
Do not throw batteries into a fire. Do not recharge the batteries.
Current
strength
Physiological Effects
< 0,5 mA Electrification not perceptible; perceivable with the tongue from approx. 45 µA
> 0,5 - 15 Tingling perceptible; From approx. 10–15 mA the release limit is reached
(adherence, clinging)
> 15 - 25 Paroxysmal contractions of the hand and arm musculature, breathing difficul-
ties, rise in blood pressure
25 – 30 Critical, due to the impact variations - body resistance (esp. skin resistance)
decreases, amperage increases
>25 - 50 Muscle contractions, severe increase in blood pressure and interference with
the heart
> 50 to several
hundred mA
decisive is the duration of the influence, the risk of ventricular fibrillation and
cardiac standstill
Ampère range Damage through large local temperature increases, destruction and pulping
of tissue, bursting of red blood corpuscles

 Loading...
Loading...