Introduction 11
Reagent handling using RFID technologyReagent handling using RFID technology
Reagent handling using RFID technologyReagent handling using RFID technology
Reagent handling using RFID technology
What’s RFID means and how does it work?What’s RFID means and how does it work?
What’s RFID means and how does it work?What’s RFID means and how does it work?
What’s RFID means and how does it work?
Radio Frequency IDentification (RFID) is a generic term that is used to
describe a system that transmits the identity (in the form of a unique serial
number) of an object or person wirelessly, using radio waves. It's grouped
under the broad category of automatic identification technologies.
It’s the combination of a “tag” and a “reader”. A typical RFID tag consists
of a microchip attached to a radio antenna mounted on a substrate. The
chip can store data. The reader is used to retrieve the data stored on an
RFID tag. A typical reader is a device that has one or more antennas that
emit radio waves and receive signals back from the tag. The reader then
passes the information in digital form to a computer system.
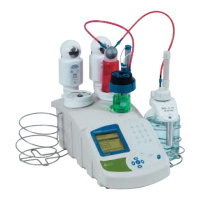
In our assembly an RFID tag is attached inside the sleeve of the burette
stand. This tag is clearly visible.
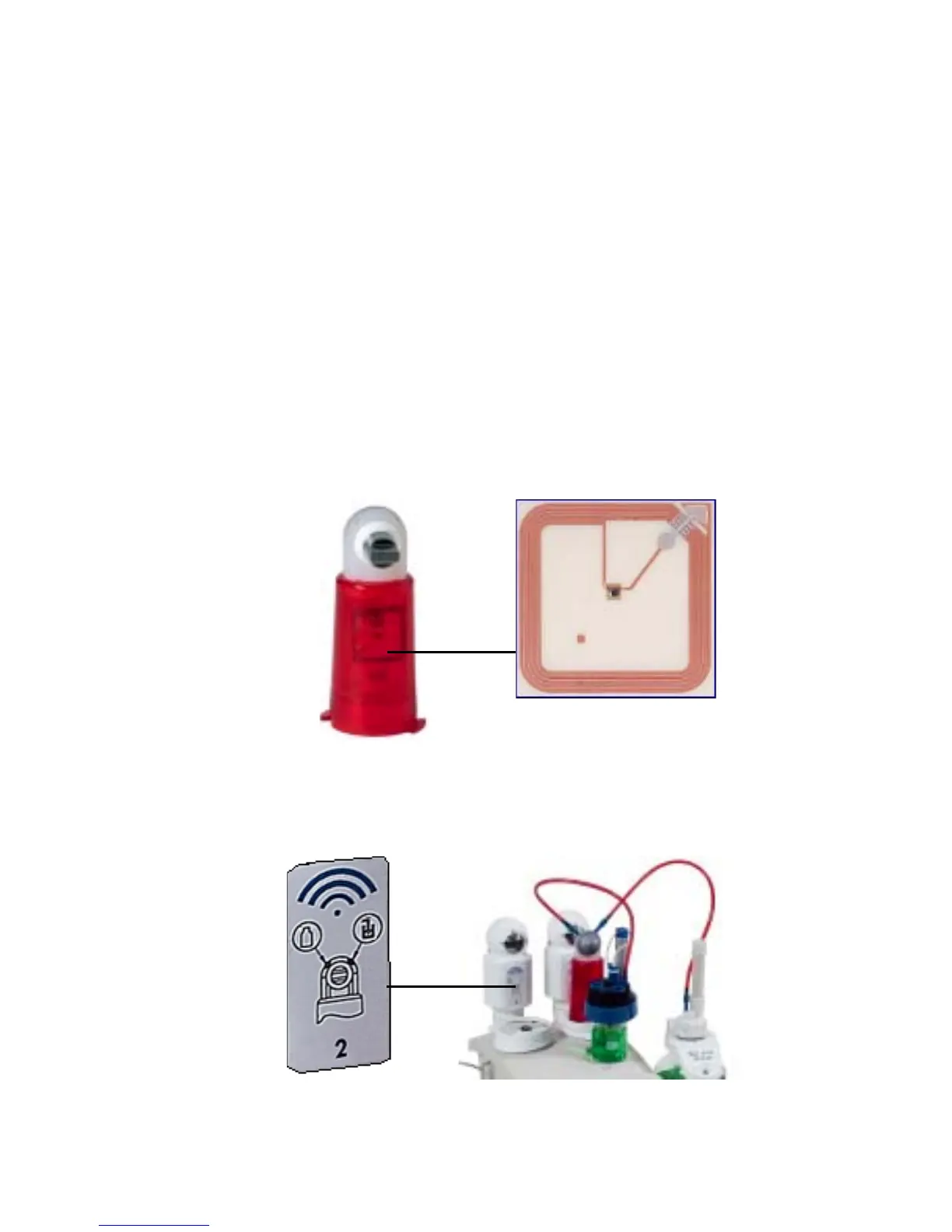
The RFID reader is mounted inside the burette tap block at the back of
the titrator and located with a small RFID graphic icon.When the burette
is installed, the tag and the reader are face to face.
RFID tag placed on the burette stand
RFID reader mounted inside the burette tap block
 Loading...
Loading...