1. Potentiometric measuring principles ABL800 FLEX Reference Manual
Electrolyte electrodes, Continued
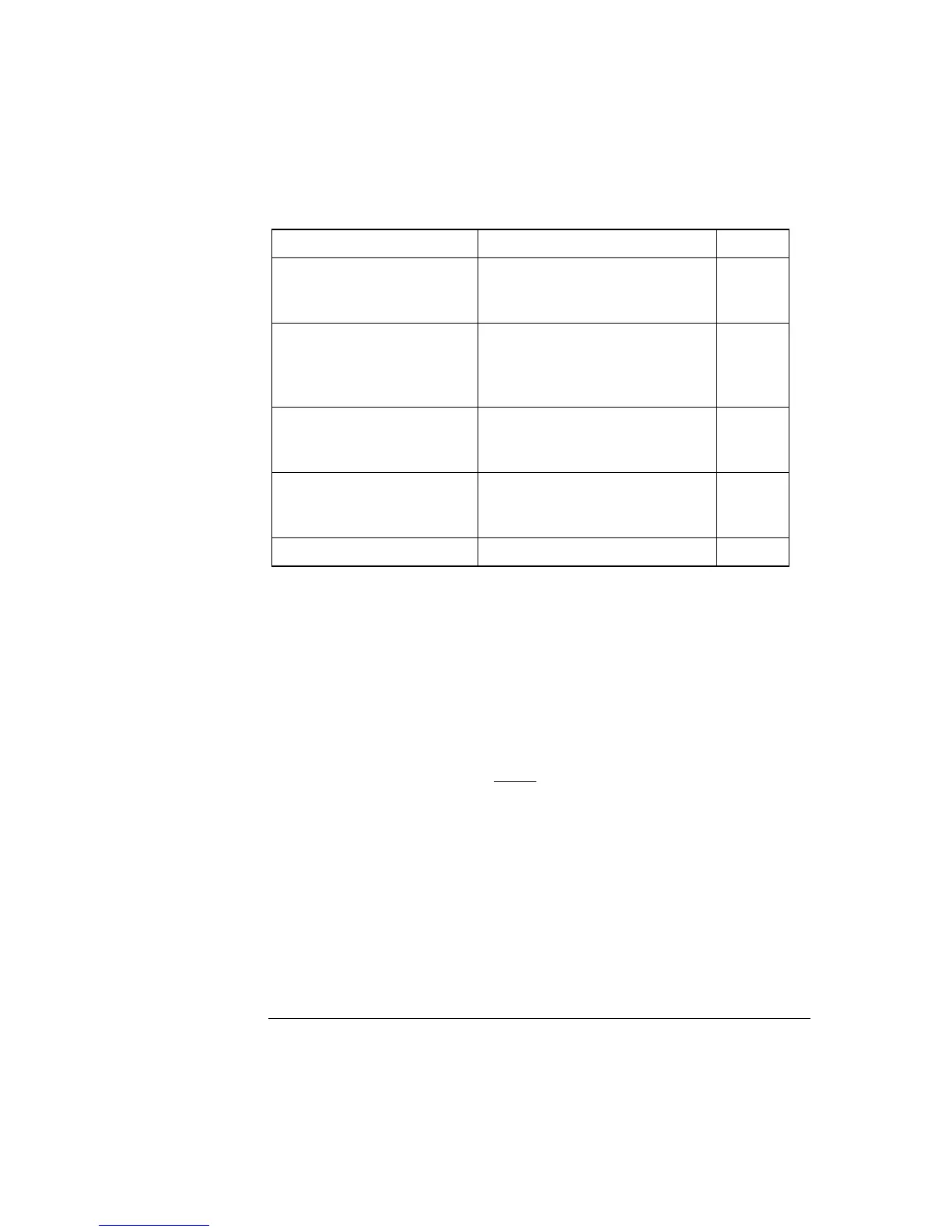
Electrode chain
potential
The total potential across the electrode chain is a sum of the potential differences at
each of the elements in the chain, all but one of which is known and constant.
Element Potential Symbol
Ag/AgCl electrode
/electrolyte solution.
(Reference electrode)
Known and constant when the
Ag/AgCl wire is immersed in the
electrolyte solution.
E
ref
Membrane junction between
the electrolyte solution in the
reference electrode and the
sample.
Known and constant, independent
of sample composition.
E
MJ
Ion-sensitive membrane (or
pin) junction separating the
sample and the electrode.
Unknown, dependent on sample
composition.
E
Sample
Ag/AgCl electrode/inner
buffer solution.
(Electrolyte electrode)
Known and constant when the
Ag/AgCl wire is immersed in the
electrolyte solution.
E
E
Total potential. Measured by the voltmeter. E
tot
The unknown potential difference across the ion-sensitive membrane or pin is then
the difference between the measured total potential and the sum of the known
potentials:
)
EEEEE
Sample tot ref MJ E
=m−++ V
Nernst equation
The potential difference at the membrane (or pin) in the electrolyte electrodes can
be expressed by the Nernst equation:
EE
T
n
a
Sample 0 ion
23R
F
log mV
=+ ×
.
where:
E
0
= standard electrode potential
R =
gas constant (8.3143 J
×K
−1
mol
−1
)
T
= absolute temperature (310.15 K at 37
o
C)
n
=
charge on the ion (n = 1 for K
+
and Na
+
, n = −1 for Cl
−
, n = 2 for Ca
2+
)
F =
Faraday constant (96487 coulomb
× mol
−1
)
a
ion
= activity of the specific ion
Continued on next page
1-24
 Loading...
Loading...