1. Potentiometric measuring principles ABL800 FLEX Reference Manual
General information
Potentiometric
method
The potential of an electrode chain is recorded using a voltmeter, and related to the
concentration of the sample (the Nernst equation).
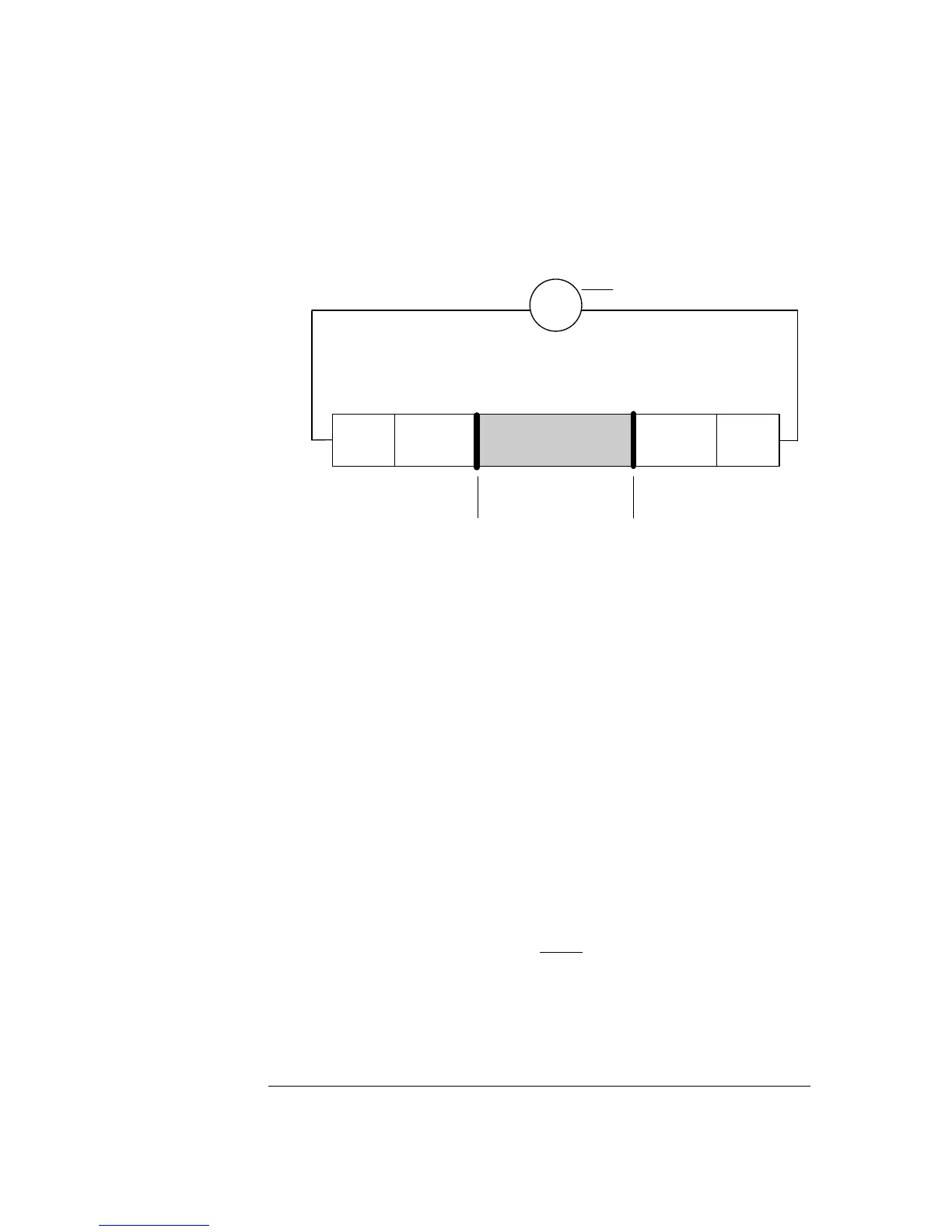
An electrode chain describes an electrical circuit consisting of a sample, electrode,
reference electrode, voltmeter, membranes, and electrolyte solutions.
Sample
Electrolyte
solution
Electrolyte
solution
Reference
electrode
Electrode
V
Membrane
Membrane
Voltmeter
Every element in the electrode chain contributes a voltage to the total potential
drop through the chain. Thus:
• When immersed in the appropriate electrolyte solution, both electrodes have
separate potentials.
• The membrane junctions between the sample and electrolyte solutions also have
separate potentials.
The potentiometric measuring principle is applied to pH,
pCO
2
, and electrolyte
electrodes.
Nernst equation
The complete electrode chain potential therefore, is the sum of these separate
potentials and is the quantity measured by the voltmeter.
E = E + E
total 0 sample
where the final unknown potential (E
sample
) can be calculated knowing the total
electrode chain potential (E
total
) and the standard potential (E
0
).
Having measured the unknown potential (E
sample
), the Nernst equation is then
applied to determine the activity (a
x
) of the species under study:
EE
T
n
a
sample
=+
0
23R
F
log
.
x
where:
E
0
= standard electrode potential
R =
gas constant (8.3143 Joule
× K
−1
× mol
−1
)
T
= absolute temperature (310 K (37
o
C ))
Continued on next page
1-2
 Loading...
Loading...