PID CONTROL
Proportional Band
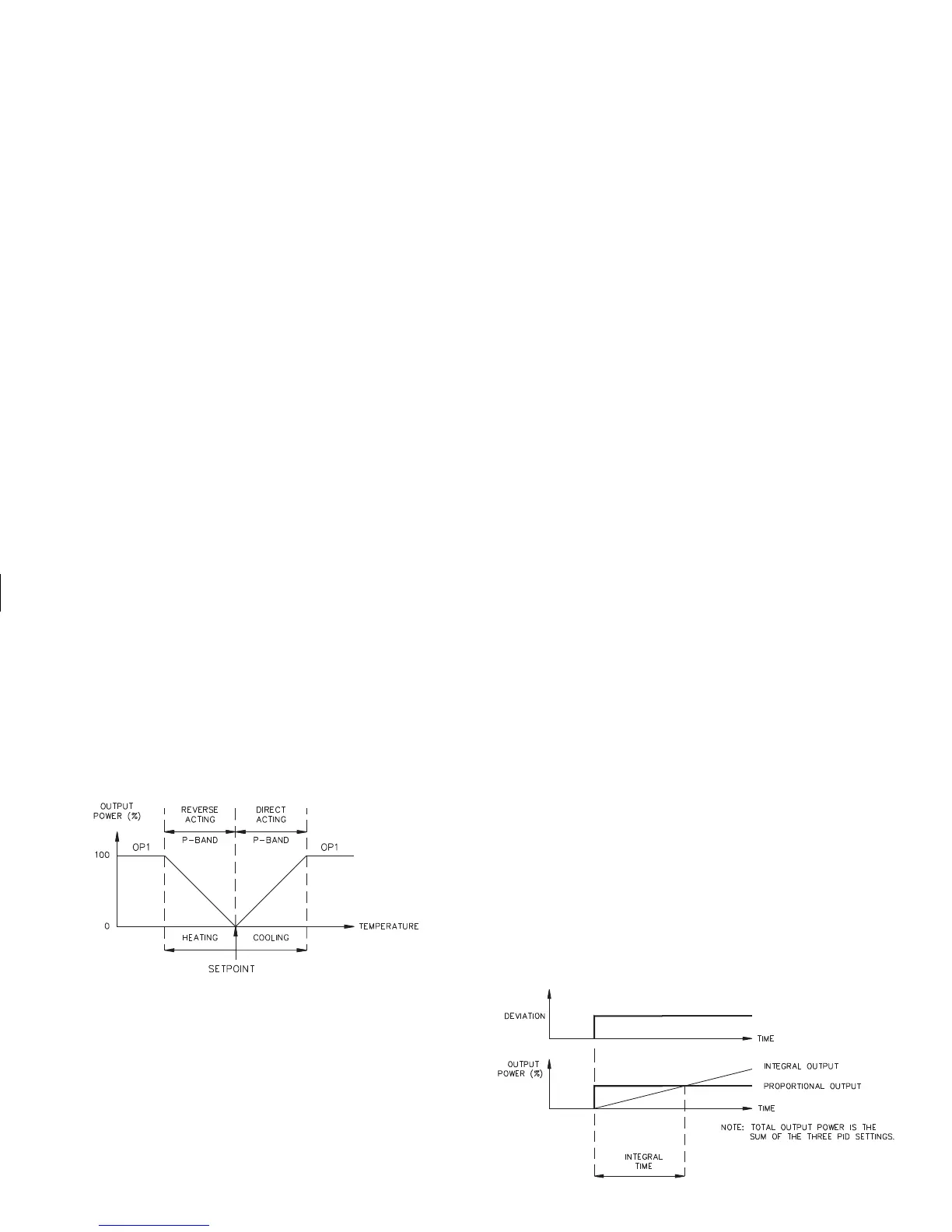
Proportional band is defined as the “band” of temperature the process
changes to cause the percent output power to change from 0% to 100%. The
band mayo r maynot be centeredabout thesetpoint valued epending uponthe
steady staterequirementsof the process.The band isshifted by manual offset
or integral action (automatic reset) to maintain zero error. Proportional band
is expressed as percent of input sensor range.
Example: Thermocouple type T with a temperature range of 600°C is used
and is indicated in degrees Celsius with a p roportional band of 5%. This
yields a band of 600°C X 5% = 30°C.
The proportional band should be set to obtain the best response to a
disturbance while minimizing overshoot. Low proportional band settings
(high gain) result in quick controller response at expense of stability and
increased overshoot. Settings that are excessively low produce continuous
oscillations at setpoint.High proportional band settings (low gain)result in a
sluggish responsewith long periods of process“ droop”. A proportional band
of 0.0% forces the controller into ON/OFF control mode with its
characteristic cycling at setpoint (See ON/OFF Control, page 66, for more
information).
Integral Time
Integral time is defined as the time, in seconds, in which the output due to
integral action alone equals the output due to proportional action with a
constant process error. As long as a constant error exists, integral action
repeats the proportional action every integral time. Integral action shifts the
center point position of the proportional band to eliminate error in the steady
state. The units of integral time are seconds per repeat.
Integral action (also known as “automatic reset”) changes the output
power to bring the process to setpoint. Integral times that are too fast (small
times) do not allow the process to respond to the new output value. This
causes over compensation and leads to an unstable process with excessive
overshoot.Integraltimesthat aretooslow (largetimes)causea slowresponse
to steady state errors. Integral action may be disabled by setting the time to
zero. If time is set to zero, the previous integral output power value is
maintained.
If integral action is disabled, manual reset is available by modifying the
output power offset (“OPOF” initially set to zero) to eliminate s teady state
errors. This parameter appears in unprotected parameter mode when integral
time is set to zero. The controller has the feature to prevent integral action
when operating outside the proportional band. This prevents “reset
wind-up”.
Figure 31, Proportional Band
Figure 32, Integral Time
Note: The Proportional band shift due to integral action
may itself be “reset” by temporarily setting the controller
into the ON/OFF control mode (proportional band =0).

 Loading...
Loading...