Shure Incorporated
22/87
• Like all microphones, tonality changes as the distance from the source increases.
• The intelligibility scale helps to predict how the microphone will sound at a given height.
• The coverage area of the lobes increases at farther distances.
[1] Room conditions: RT60 (reverb time) = 500 ms @ 1kHz, A weighted room noise = 40dBSPL(A)
[2] IEC-602682-16 standard
Intelligibility Scale
The intelligibility scale objectively compares the acoustic performance of the array microphone with a cardioid
gooseneck microphone at various distances. This information is useful for predicting how the array microphone will
perform at a given distance and to determine an ideal mounting height. The data in the intelligibility scale table is
derived from measuring the microphones to meet an equivalent value from the Speech Transmission Index
IEC-602682-16 standard.
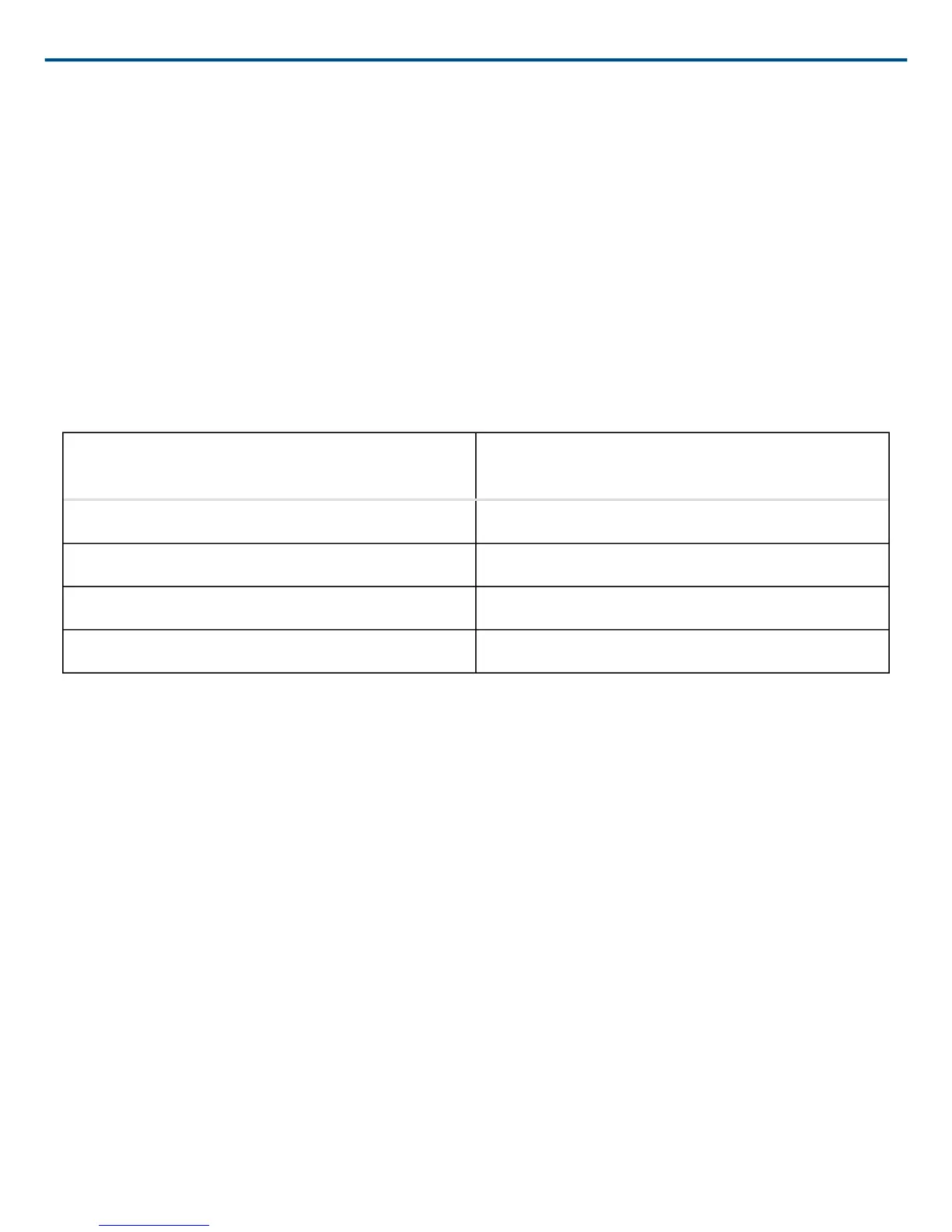
Distances With Equivalent Speech Transmission Index Values
Ceiling Array Microphone (Distance to Talker)
Cardioid Gooseneck Microphone (Distance to
Talker)
6 ft (1.83 m) 3.75 feet (1.14 m)
8 ft (2.44 m) 5 feet (1.52 m)
10 ft (3.05 m) 6.25 feet (1.91 m)
12 ft (3.66 m) 7.5 feet (2.29 m)
Data was collected in a typical huddle room with the following measurements:
• Reverberation decay time: 500 ms @ 1kHz
• Noise floor: 40 dB SPL (A-weighted)
Note: These values are specific to the described room. In a well-controlled acoustic environment, the array micro
phone may perform with equivalent Speech Transmission Index values at even greater distances. In highly rever
berant rooms, the performance is less predictable.
A = Distance between array microphone and talker
B = Distance between cardioid microphone and talker
 Loading...
Loading...