3 Product description
3.1 Structure and function
The safety laser scanner is an electro-sensitive protective device (ESPE) which scans its
sur
roundings two-dimensionally using infrared laser beams.
The safety laser scanner operates on the principle of time-of-flight measurement. It
emits light pulses in regular, very short intervals. If the light strikes an object, it is
reflected. The safety laser scanner receives the reflected light. The safety laser scanner
calculates the distance to the object based on the time interval between the moment of
transmission and moment of receipt (∆t).
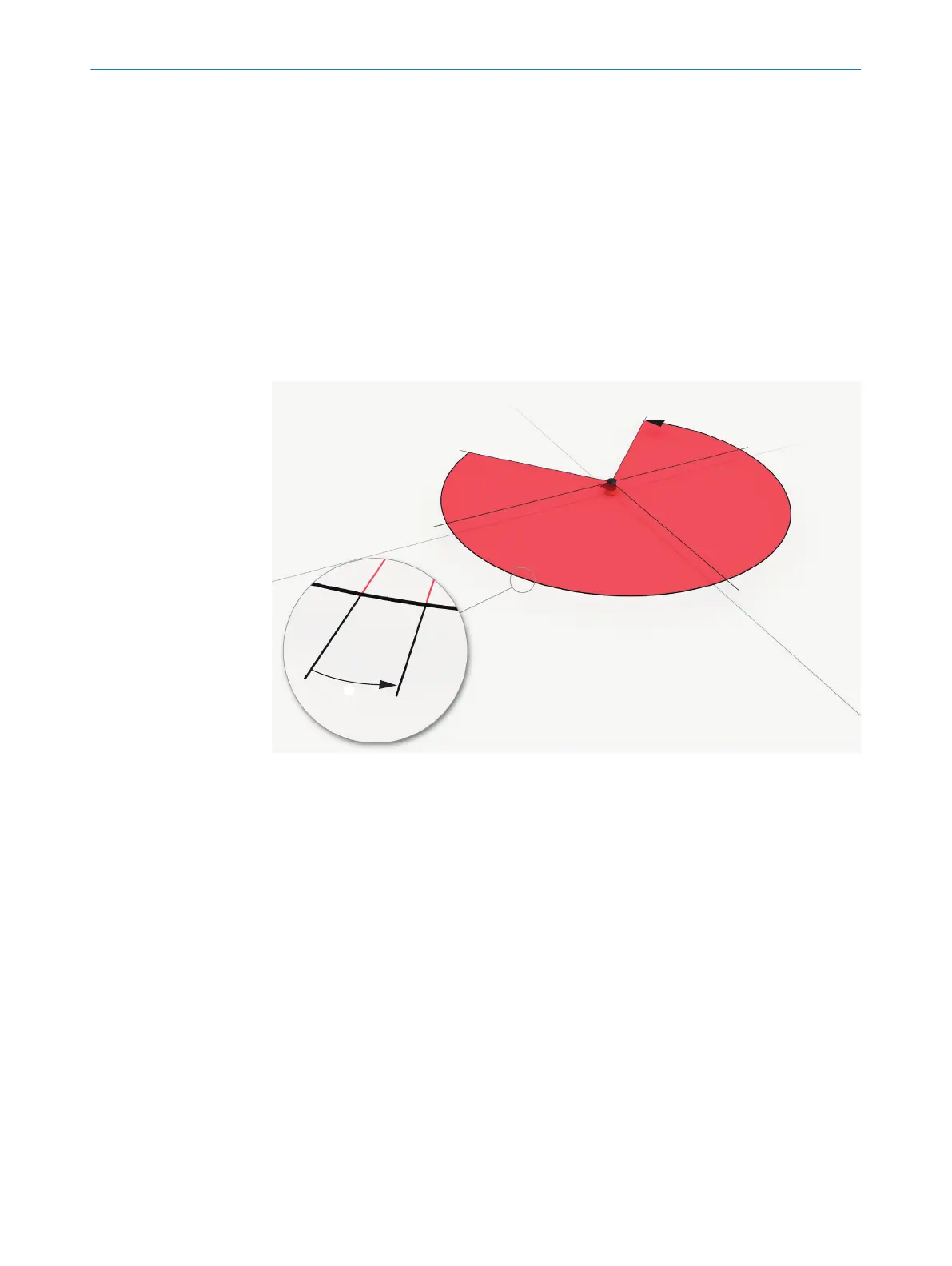
A rotating mirror is situated in the safety laser scanner. The mirror deflects the light
pulses so that they scan a fan-shaped area.
Figure 1: Light pulses scan an area
1
Angular resolution: the angular distance (in degrees) between 2 distance measurements
Geometry of the scan plane
T
he laser beams emitted cover a sector of a circle, so an object can be detected in an
area of up to 275°.
The sector of a circle covered ranges from –47.5° to 227.5°, where 90° denotes the
axis of the safety laser scanner from the back to the front. When viewing the safety
laser scanner from above, the direction of rotation of the mirror and the deflected light
pulses is counterclockwise, see figure 1, page 6.
Scan cycle time and angular resolution
T
he time that the mirror requires for one rotation is called the scan cycle time. The num‐
ber of light pulses per unit of time is constant. The scan cycle time and the number of
light pulses per unit of time determine the angular resolution.
Slightly different scan cycle times can be used to minimize mutual interference in
neighboring safety laser scanners.
3 P
RODUCT DESCRIPTION
6
T E C H N I C A L I N F O R M A T I O N | microScan3, outdoorScan3 8022708/2019-04-15 | SICK
Subject to change without notice
 Loading...
Loading...











