(1*,1((5,1*,1)250$7,21 ,QWHUQDWLRQDO(QJOLVK
MICROMASTER 420 Reference Manual
8 Issue A1
2.1
Current Limit and Overload Operation
The inverter will always protect itself, the motor and the system from possible
damage. Where a short circuit exists on the output of the inverter, the unit will trip
almost instantaneously to protect itself. In the event of short and/or long term
overload conditions, current limit facilities now operate very rapidly to reduce the
current and prevent a trip occurring. Table 2-1 describes the facilities available.
Table 2-1 Current Limit and Overload
(OHFWURQLF7ULS
This is a very fast current limit, which operates if
there is a short circuit (line to line or line to earth) on
the output. It is a fixed level trip and operates within
a few microseconds.
2YHUORDG/LPLW
This is a very fast limit, which operates within a few
microseconds and removes some of the output
pulses to limit the current and protect the inverter. If
this pulse dropping occurs during overload, the
operating condition will usually recover and the
motor will continue to run without tripping.
/RQJ7HUP2YHUORDG/LPLW
This is a slower limit which allows an overload of at
least 60 seconds where the current lies above the
motor limit but below the Electronic Trip and
Overload Limit.
&RQWLQXRXV/LPLW
This is the level set as the maximum continuous
motor current. The inverter will control the current to
this level after other overloads have timed out.
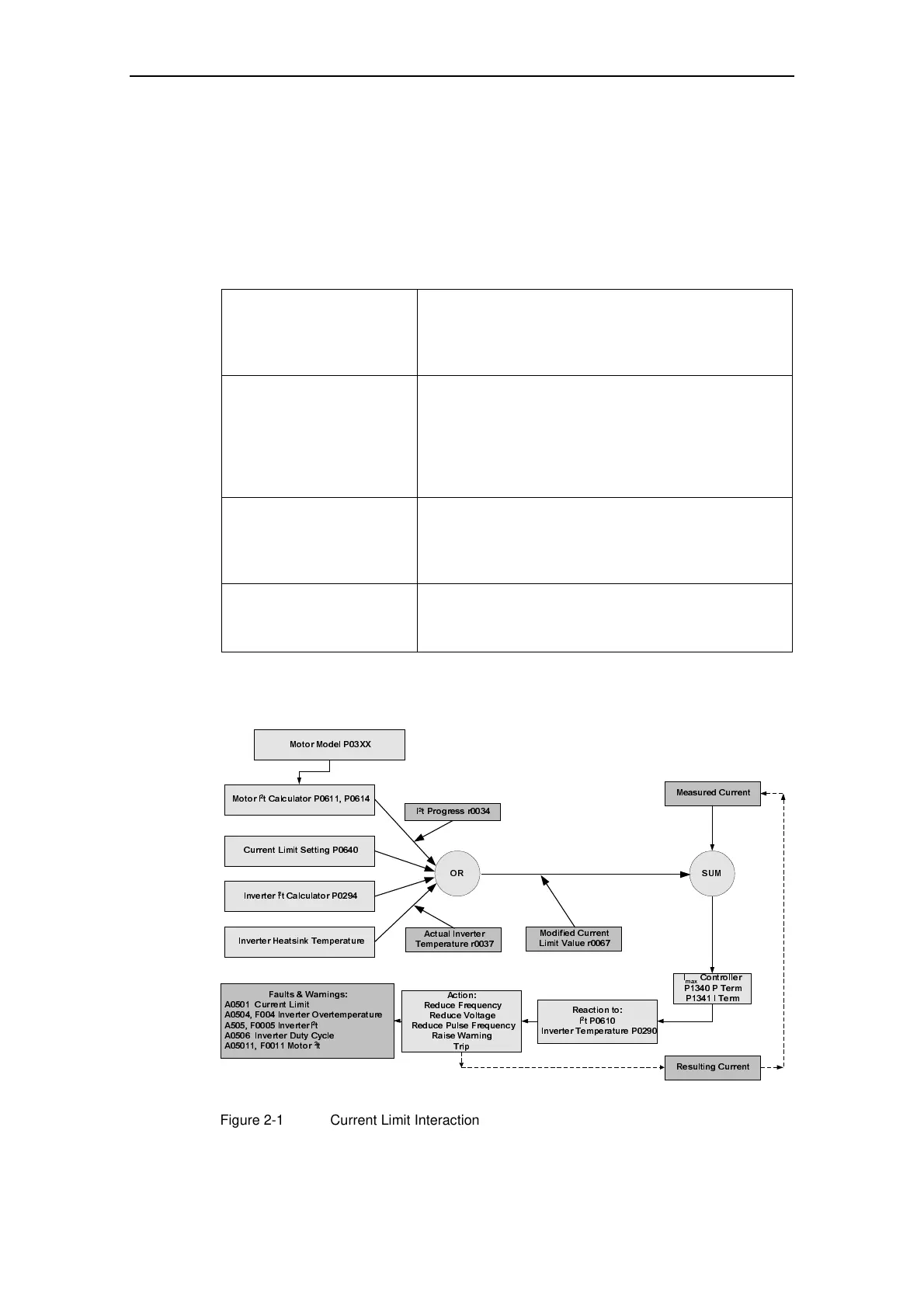
Figure 2-1 illustrates the interaction of the parameters associated with current limit.
The Read Only parameters r0027, r0034, r0037 and r0067 will help with fault
diagnosis.
25 680
0RWRU,
W&DOFXODWRU33
&XUUHQW/LPLW6HWWLQJ3
,QYHUWHU,
W&DOFXODWRU3
,QYHUWHU+HDWVLQN7HPSHUDWXUH
0RWRU0RGHO3;;
,
W3URJUHVVU
$FWXDO,QYHUWHU
7HPSHUDWXUHU
0RGLILHG&XUUHQW
/LPLW9DOXHU
0HDVXUHG&XUUHQW
5HVXOWLQJ&XUUHQW
,
PD[
&RQWUROOHU
337HUP
3,7HUP
5HDFWLRQWR
,
W3
,QYHUWHU7HPSHUDWXUH3
$FWLRQ
5HGXFH)UHTXHQF\
5HGXFH9ROWDJH
5HGXFH3XOVH)UHTXHQF\
5DLVH:DUQLQJ
7ULS
)DXOWV:DUQLQJV
$&XUUHQW/LPLW
$),QYHUWHU2YHUWHPSHUDWXUH
$),QYHUWHU,
W
$,QYHUWHU'XW\&\FOH
$)0RWRU,
W
Figure 2-1 Current Limit Interaction

 Loading...
Loading...















