2.
Principle
of
operation
2.1
Program
processing
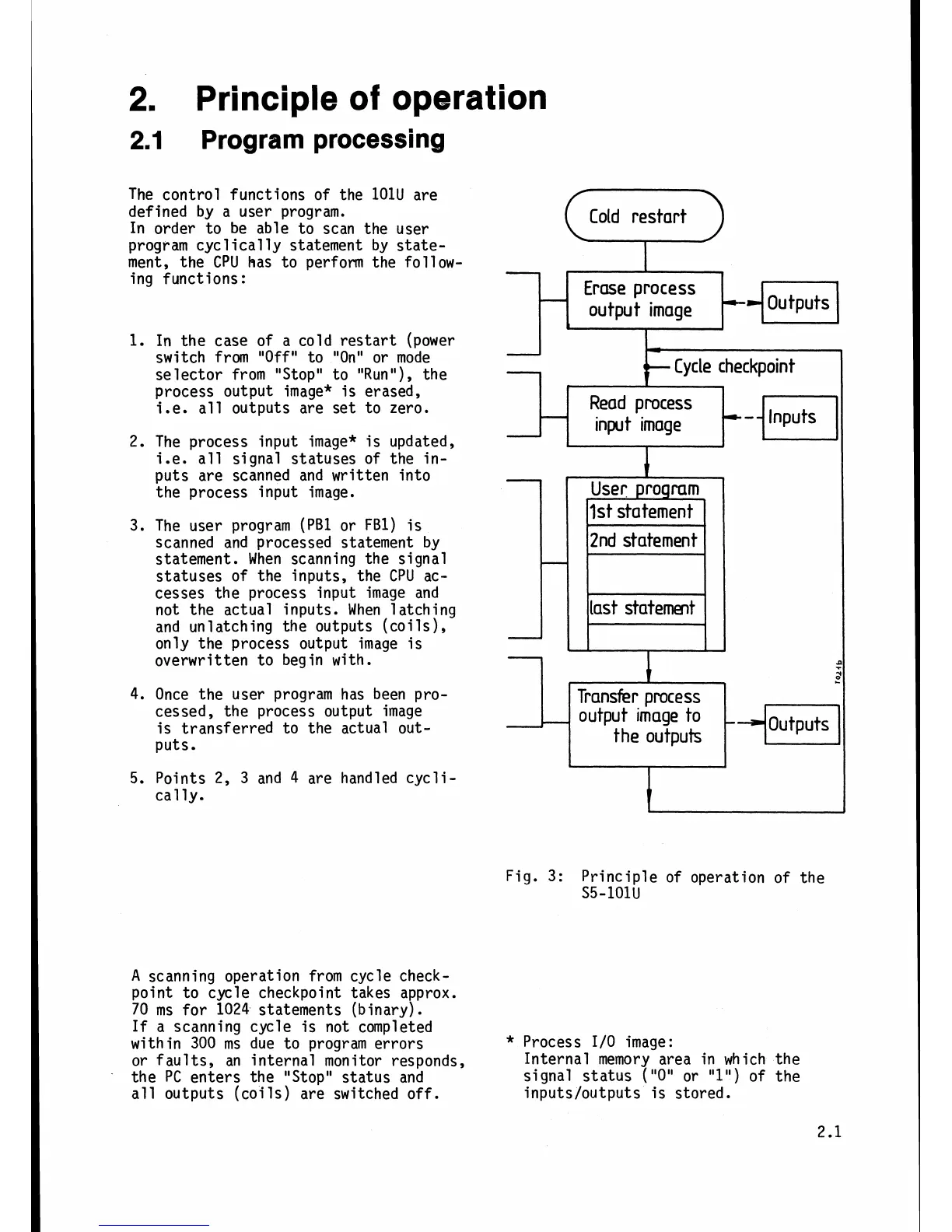
The control functions of the lOlU are
defined by a user program.
In order to be able to scan the user
program cyclically statement by state-
ment, the CPU
has to perform the follow-
ing functions:
1.
In the case of a cold restart (power
switch from
"Off"
to "On" or mode
selector from "Stop" to "Run"), the
process output image* is erased,
i.e.
all outputs are set to zero.
2.
The process input image* is updated,
i.e. all signal statuses of the in-
puts are scanned and written into
the process input image.
The user program
(PB1 or FBI) is
scanned and processed statement by
statement. When scanning the signal
statuses of the inputs, the
CPU
ac-
cesses the process input image and
not the actual inputs. When latching
and unlatching the outputs (coils),
only the process output image is
overwritten to begin with.
4. Once the user program has been pro-
cessed, the process output image
is transferred to the actual out-
puts.
5.
Points 2,
3
and
4
are handled cycli-
cal
ly.
Cold restart
Cr>
Erase process
output image
I
Cycle checkpoint
Read
process
input image
12nd statement
I
Last statement
H
Transfer process
I
output image to
the outputs
Fig.
3:
Principle of operation of the
S5-101U
A
scanning operation from cycle check-
point to cycle checkpoint takes approx.
70 ms for 1024 statements (binary).
If
a scanning cycle is not completed
within 300 ms due to program errors
*
Process 1/0 image:
or faults, an internal monitor responds,
Internal memory area in which the
the PC enters the "Stop" status and
signal
status
("0" or "1") of the
all outputs (coils) are switched off.
inputs/outputs is stored.
 Loading...
Loading...











