5.2.5
Condition codes
Generating condition codes in connection
with digital logic.
The processor of the
SIMATIC S5-101U
programable controller has three con-
di tion codes:
Digital logic operations result in the
setting of condition codes CC
0 and
CC
1.
The overflow bit is not affected.
Setting of the condition codes depends
on the contents of the accumulator after
the operation has been executed.
o
CC
1
Value positive
o CC
0 Value negative
o OVF
&erflow
The condition codes are affected- by
comparison operations, arithmetic oper-
ations, shift operations and a number
of conversion operations.
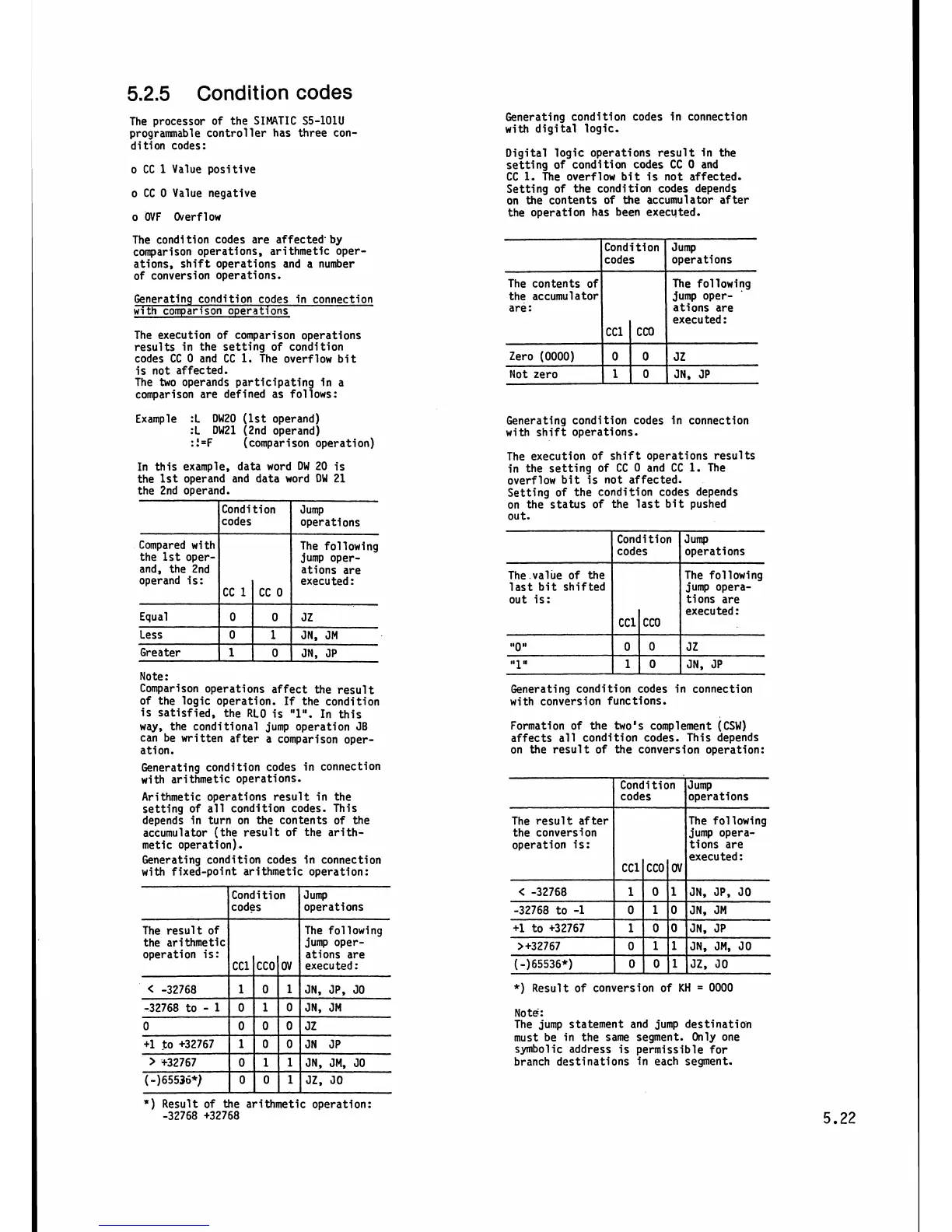
The contents of
the accumulator
are:
Condition
codes
The following
jump oper-
ations are
executed
:
Jump
operations
Generating condition codes in connection
with comparison operations
CC1
Cc0
Zero (0000)
Not zero
The execution of comparison operations
results in the setting of condition
codes CC
0 and CC
l.
The overflow bit
is not affected.
The two operands participating in a
comparison are defined as follows:
JN, JP
Example :L
DW20 (1st operand)
:L
DW21 (2nd operand)
:!=F
(comparison operation)
Generating condition codes in connection
with shift operations.
The execution of shift operations results
in the setting of CC
0 and CC
1.
The
overflow bit is not affected.
Setting of the condition codes depends
on the status of the last bit pushed
out.
In this example, data word DW 20 is
the 1st operand and data word
DW
21
the 2nd operand.
Condition
codes
the 1st oper-
and, the 2nd
operand is:
CC
l
I
CC
0
Jump
operations
The following
jump oper-
ations are
executed
:
codes
The.value of the
last bit shifted
out is:
Jump
operations
The following
jump opera-
tions are
--
Equal
10
I
0
IJZ
Less
Greater
Note:
Comparison operations affect the result
of the logic operation.
If
the condition
is satisfied, the RLO is
"l".
In this
way, the conditional jump operation
JB
can be written after a comparison oper-
ation.
now
Generating condition codes in connection
with conversion functions.
0
1
Formation of the two's complement (CSW)
affects all condition codes. This depends
on the result of the conversion operation:
~101
I
l
l
0
I
JN, JP
0
Generating condition codes in connection
with arithmetic operations.
1
0
I
Condition 1Jumti
JN, JM
JN, JP
0
Arithmetic operations result in the
setting of all condition codes. This
depends in turn on the contents of the
accumulator (the result of the arith-
metic operation).
JZ
I
codes lop&ations
The result after
the conversion
operation is:
The following
jump opera-
tions are
executed
:
Generating condition codes in connection
with
f
ixed-point arithmetic operation:
JN, JP,
JO
Condition
I
Jump
Icodes operations
JN. JM
JN, JP
JN. JM,
JO
The result of
the arithmetic
operation is:
The following
jump oper-
ations are
executed
:
*)
Result of conversion of
KH
=
0000
<
-32768
-32768 to
-
l
I
O
(
1
I
O
1
JN. JM
Notei:
The jump statement and jump destination
must be in the same segment. Only one
symbolic address is permissible for
branch destinations in each segment.
1
I
0
*)
Result of the arithmetic operation:
-32768
+32768
1
JN, JP, JO
 Loading...
Loading...











