SINAMICS Safety Integrated (Booksize)
Commissioning the “SH” and “SBC” functions
5-168
E Siemens AG, 2004. All rights reserved
SINAMICS S120 Installation and Start-Up Manual, 12/04 Edition
5.4.3 Safety faults
Stop reaction
When Safety Integrated faults occur, the following stop reactions can be triggered:
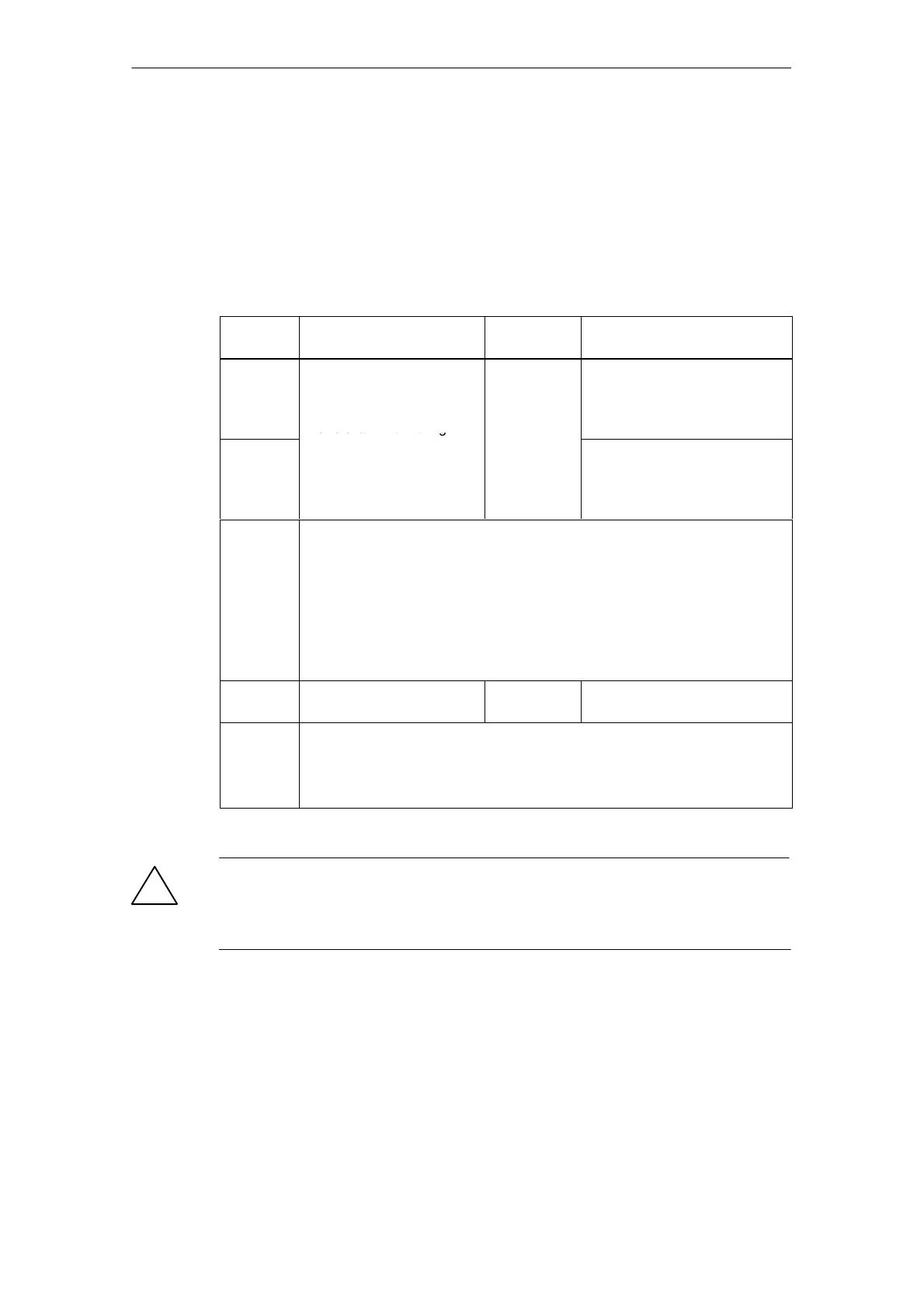
Table 5-2 Safety Integrated stop reactions
Stop
reaction
Action Effect Triggered when...
STOP A
Cannot be
acknowled
ged
Trigger safe pulse disable
via the shutdown path for
the relevant monitoring
The motor
coasts to a
standstill or
For all non-acknowledgeable
Safety faults with pulse disable.
STOP A
channel.
During operation with SBC:
apply motor holding brake.
is braked by
the holding
brake.
For all acknowledgeable Safety
faults with pulse disable.
As a follow-up reaction of
STOP F.
STOP A is identical to stop category 0 to EN 60204-1.
With STOP A, the motor is switched directly to zero torque via the “Safe
standstill (SH)” function.
A motor at standstill cannot be started again accidentally.
A moving motor coasts to standstill. This can be prevented by using external
braking mechanisms (e.g. armature short-circuiting, holding or operational
brake).
When STOP A is present, “Safe standstill (SH)” is effective.
STOP F Transition to STOP A None
If an error occurs in the
crosswise data comparison.
STOP F is permanently assigned to the crosswise data comparison (CDC). In
this way, errors are detected in the monitoring channels.
After STOP F, STOP A is triggered.
When STOP A is present, “Safe standstill (SH)” is effective.
!
Warning
With a vertical axis or pulling load, there is a risk of uncontrolled axis movements
when STOP A/F is triggered. This can be prevented by using ”Safe brake control
(SBC)” and a holding brake with sufficient retention force (non-safe).

 Loading...
Loading...























