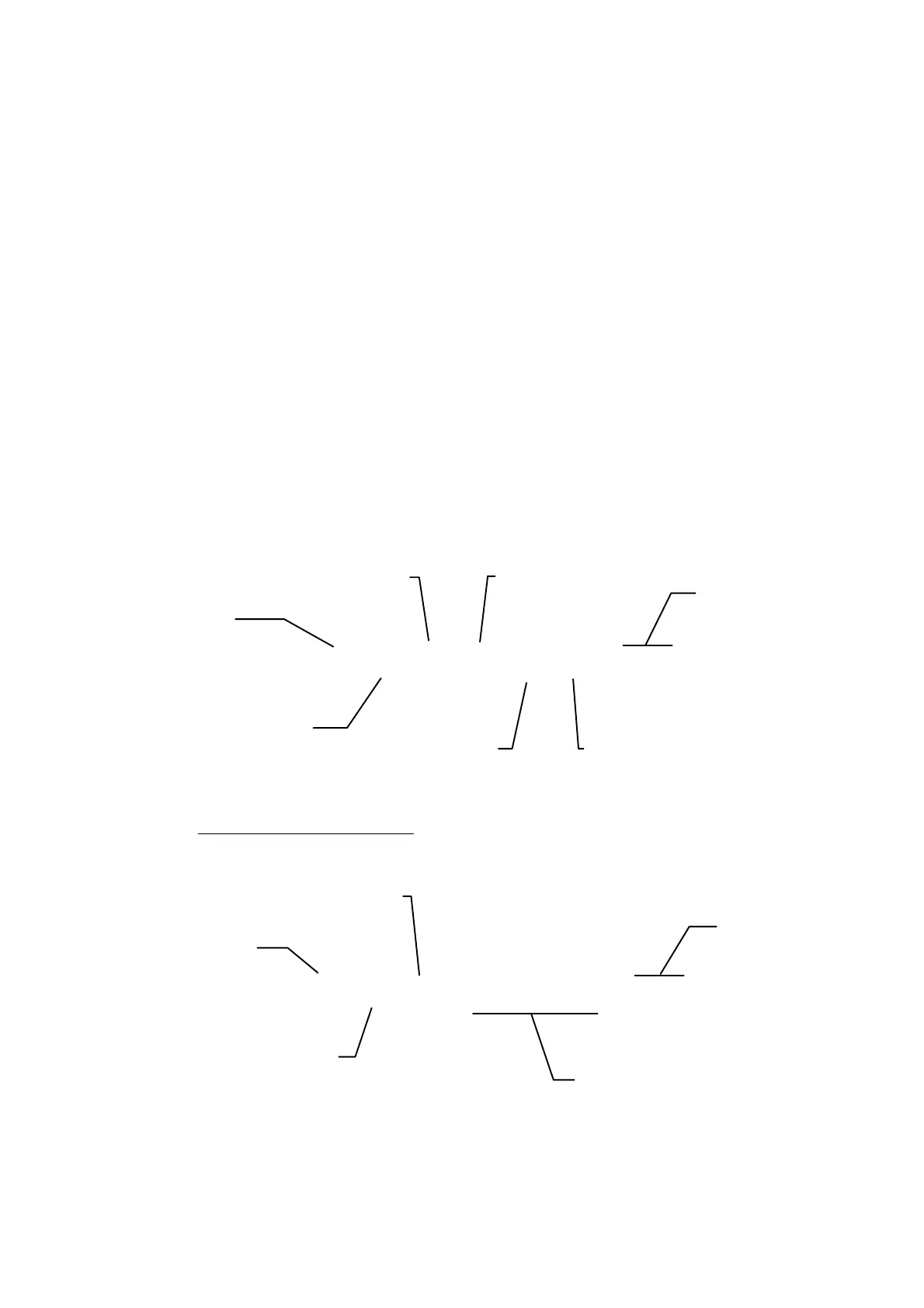7828 Density Transmitter Technical Manual Modbus Communications
78285000_AA D-15
D.7 EXAMPLE OF DIRECT MODBUS ACCESS
In many applications, direct access to Modbus will be unnecessary; ADView provides a
way of configuring the 7828, and for accessing individual registers. This example
describes how to access the 7828 directly, without the help of ADView.
However, before you start, you should configure the transmitter using ADView (described
in Section 4), and also set the Modbus Byte Order and Register Size (see section D.3.1).
Note: You can use ADView’s Direct Communications tool to test out the following
sequences, or any others you want to try. This has the added advantage that
ADView calculates and inserts the checksum value for you.
D.7.1 EXAMPLE 1: READING LINE DENSITY (16-BIT REGISTER SIZE)
The 7828 is assumed to have been configured with Register Size = 16-bit (Register 48 =
0), and has slave address = 1
The following string will read the line density, which is held in Register 257 (0101
16
)
01 03 01 01 00 02 94 37
The reply from the 7828 will be:
01 03 04 xx xx xx xx cs cs
Slave address
(hex)
Slave address
(hex)
Command number: 3
(Read Register)
Command number: 3
(Read Register)
Register address
Hi byte
Reply byte count
Register address
Lo byte
Number of
registers to read
Hi byte)
Line density value
as a 32-bit floating
point number
Number of
registers to read
Lo byte
Checksum
(Automatically inserted
if you are using
DView.
Checksum
 Loading...
Loading...