AN4989 Rev 3 71/118
AN4989 Printf debugging
117
HAL_UART_Transmit(&UartHandle, (uint8_t *)&ch, 1, 0xFFFF);
return ch;
}
Without syscall.c integrated, a customized _write function has to be defined:
int _write(int file, char *ptr, int len)
{
int DataIdx;
for (DataIdx = 0; DataIdx < len; DataIdx++){ __io_putchar( *ptr++ );}
return len;
}
Refer to STM32Cube provided example UART_Printf() available for almost all STM32
Series. An example is available in STM32Cube_FW_F3_V1.7.0\Projects\
STM32F303ZE-Nucleo\Examples\UART\UART_Printf.
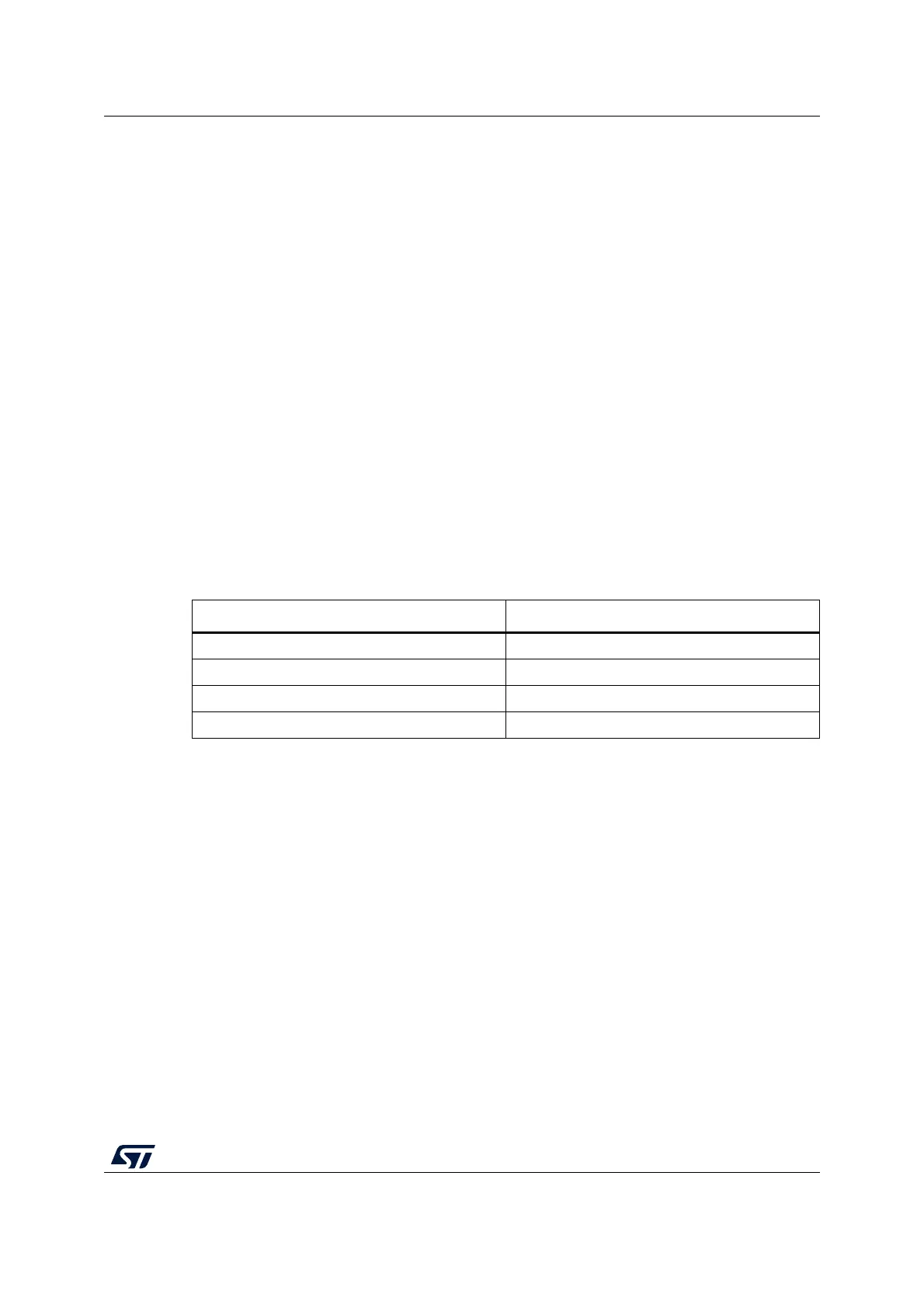
Caution: USART word length includes parity which is not the case for most of UART terminal. Word
length 8 with parity require 7 bits + parity on terminal side to match.
VCP does not support Word length of 7 bits and below (whatever the parity). Table 5 gives
examples of compatible configurations:
7.3 Printf via SWO/SWV
Serial Wire Output (SWO) is single pin, asynchronous serial communication channel
available on Cortex-M3/M4/M7 and supported by the main debugger probes.
It is using the ITM (instrumentation trace macrocell) module of the Cortex Core-Sight.
The asynchronous mode (SWO) requires 1 extra pin and is available on all packages for
STM32 based on Cortex-M3, -M4, and -M7.
It is only available if a Serial Wire mode is used. It is not available in JTAG mode.
By default, this pin is NOT assigned. It can be assigned by setting the TRACE_IOEN and
TRACE_MODE bits in the Debug MCU configuration register (DBGMCU_CR). This
configuration has to be done by the debugger host.
Refer to the related chapter of STMicroelectronics reference manual.
In debug context it can be a good alternative to UART in system where pinout constraints
are strong (alternate function preempting UART GPIOs).
Table 5. STM32 USART vs. PC terminal WordLength example
STM32 UART PC Terminal
Word Length: 8, Parity: Odd Data: 7, Parity: Odd
Word Length: 8, Parity: None Data: 8, Parity: None
Word Length: 9, Parity: Odd Data 8, Parity: Odd
Word Length: 7, Parity: Odd/None Not Working with VCP
 Loading...
Loading...