Overview of Thread Scheduling
Thread Scheduling 4-7
4.1.4 Thread Priorities
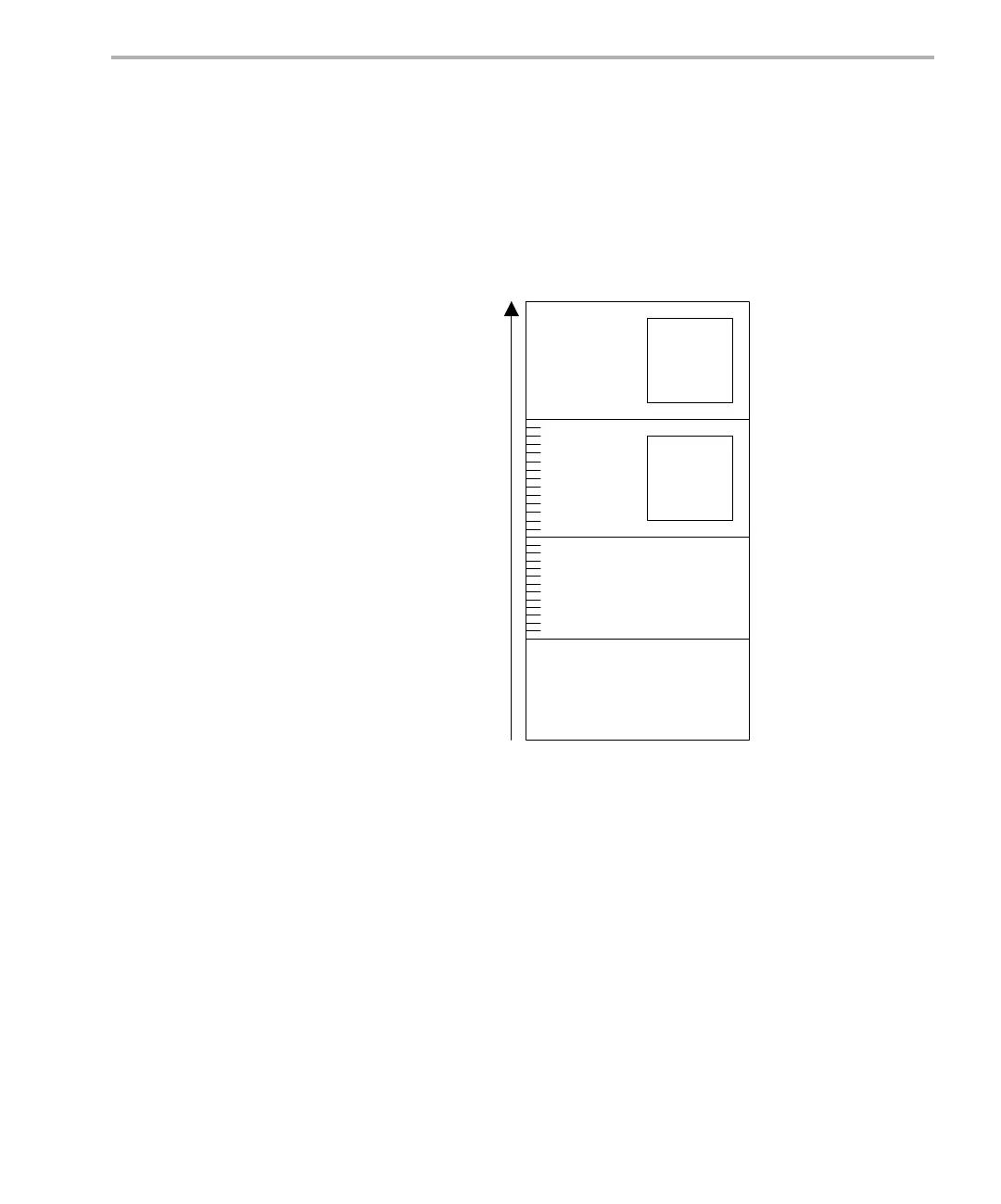
Within DSP/BIOS, hardware interrupts have the highest priority. The priorities
among the set of HWI objects are not maintained implicitly by DSP/BIOS. The
HWI priority only applies to the order in which multiple interrupts that are
ready on a given CPU cycle are serviced by the CPU. Hardware interrupts are
preempted by another interrupt unless that interrupt is disabled by resetting
the GIE bit in the CSR, or by setting the corresponding bit in the IER.
Figure 4-1. Thread Priorities
Software interrupts have lower priority than hardware interrupts. There are 14
priority levels available for software interrupts. Software interrupts can be
preempted by a higher-priority software interrupt or any hardware interrupt.
Software interrupts cannot block.
Tasks have lower priority than software interrupts. There are 15 task priority
levels. Tasks can be preempted by any higher-priority thread. Tasks can block
while waiting for resource availability and lower-priority threads.
The background idle loop is the thread with the lowest priority of all. It runs in
a loop when the CPU is not busy running another thread.
Clock
Functions
(CLK)
Hardware
Interrupts
(HWI)
Periodic
Functions
(PRD)
Software
Signals
(SWI)
14 levels
Tasks
(TSK)
15 levels
Priority
Background
Thread
(IDL)
 Loading...
Loading...











