Instrumentation APIs
3-20
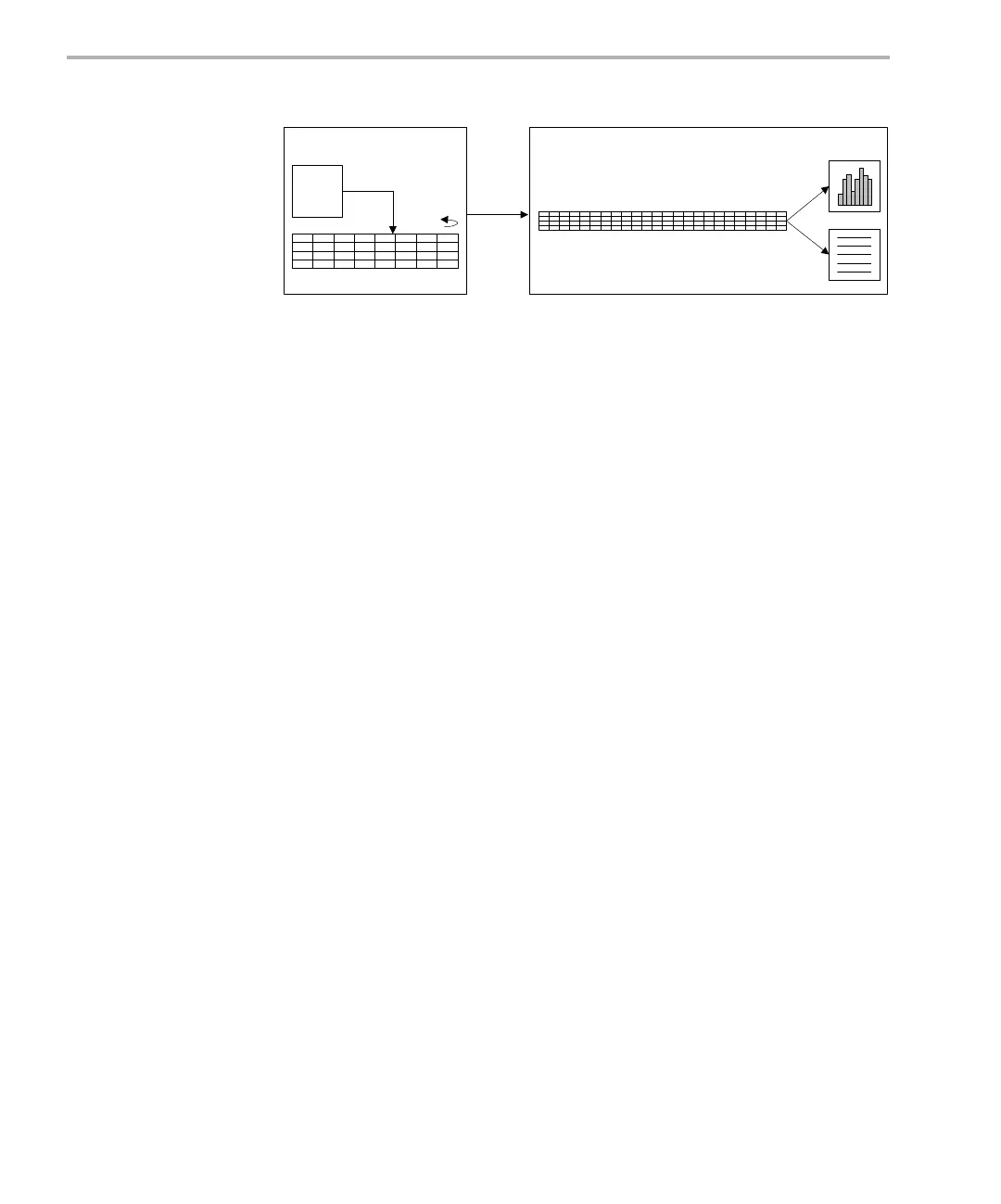
Figure 3-1. LOG Buffer Sequence
LOG_printf uses the fourth word of the message structure for the offset or
address of the format string (for example, %d, %d). The host uses this format
string and the two remaining words to format the data for display. This
minimizes both the time and code space used on the target since the actual
printf operation (and the code to perform the operation) are handled on the
host.
LOG_event and LOG_printf both operate on logs with interrupts disabled.
This allows hardware interrupts and other threads of different priorities to
write to the same log without having to worry about synchronization.
Log messages shown in a message log window are numbered to indicate the
order in which the events occurred. These numbers are an increasing
sequence starting at 0. If your log never fills up, you can use a smaller log
size. If a circular log is not long enough or you do not poll the log often
enough, you may miss some log entries that are overwritten before they are
polled. In this case, you see gaps in the log message numbers. You may want
to add an additional sequence number to the log messages to make it clear
whether log entries are being missed.
The DSP/BIOS online help describes LOG objects and their parameters. See
LOG Module in the TMS320 DSP/BIOS API Reference Guide for your
platform for information on the LOG module API calls.
HostTarget
LOG object
LOG buffer
read
&
clear
 Loading...
Loading...











