Message Queues
Input/Output Methods 6-15
6.5 Message Queues
The MSGQ module supports the structured sending and receiving of variable
length messages. This module can be used for homogeneous or
heterogeneous multi-processor messaging. A substantially similar MSGQ
API is implemented in DSP/BIOS Link for certain TI general-purpose
processors (GPPs), particularly those used in OMAP devices.
MSGQ provides more sophisticated messaging than other modules. It is
typically used for complex situations such as multi-processor messaging. The
following are key features of the MSGQ module:
❏ Writers and readers can be relocated to another processor with no
runtime code changes.
❏ Timeouts are allowed when receiving messages.
❏ Readers can determine the writer and reply back.
❏ Receiving a message is deterministic when the timeout is zero.
❏ Sending a message is deterministic (the call, but not the delivery).
❏ Messages can reside on any message queue.
❏ Supports zero-copy transfers.
❏ Can send and receive from HWIs, SWIs and TSKs.
❏ Notification mechanism is specified by application.
❏ Allows QoS (quality of service) on message buffer pools. For example,
using specific buffer pools for specific message queues.
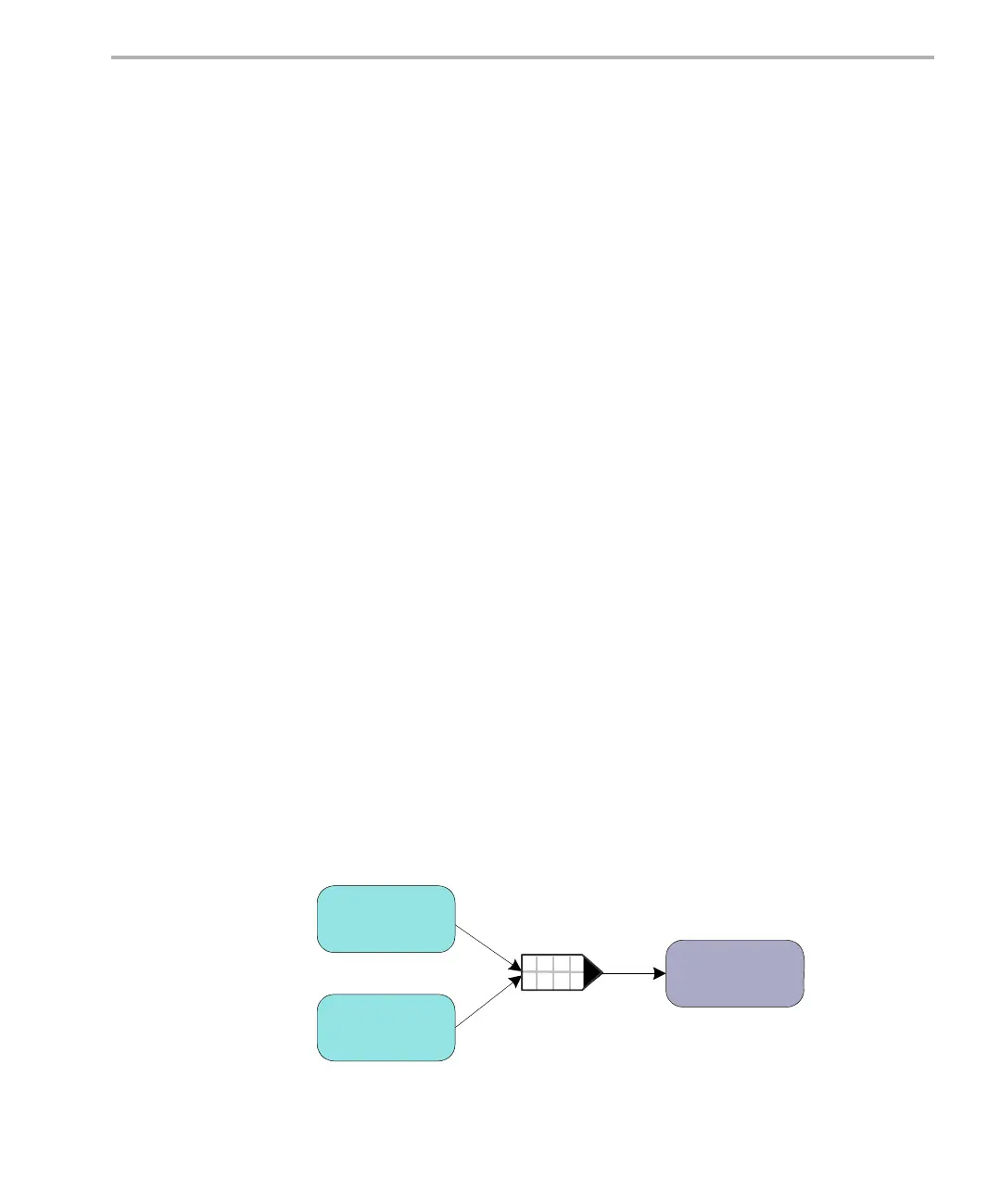
Messages are sent and received via a message queue. A reader is a thread
that gets (reads) messages from a message queue. A writer is a thread that
puts (writes) a message to a message queue. Each message queue has one
reader and can have many writers. A thread may read from or write to multiple
message queues.
Figure 6-3. Writers and Reader of a Message Queue
MSGQ
object
Writer 1
Reader
Writer 2
 Loading...
Loading...











