Page 17 of 66 Pages
3.17 Water quality
3.17.1 Water for generating steam
The distilled or mineral – free water supplied to the autoclave
should have the physical characteristics and maximum
acceptable level of contaminants indicated in the table below:
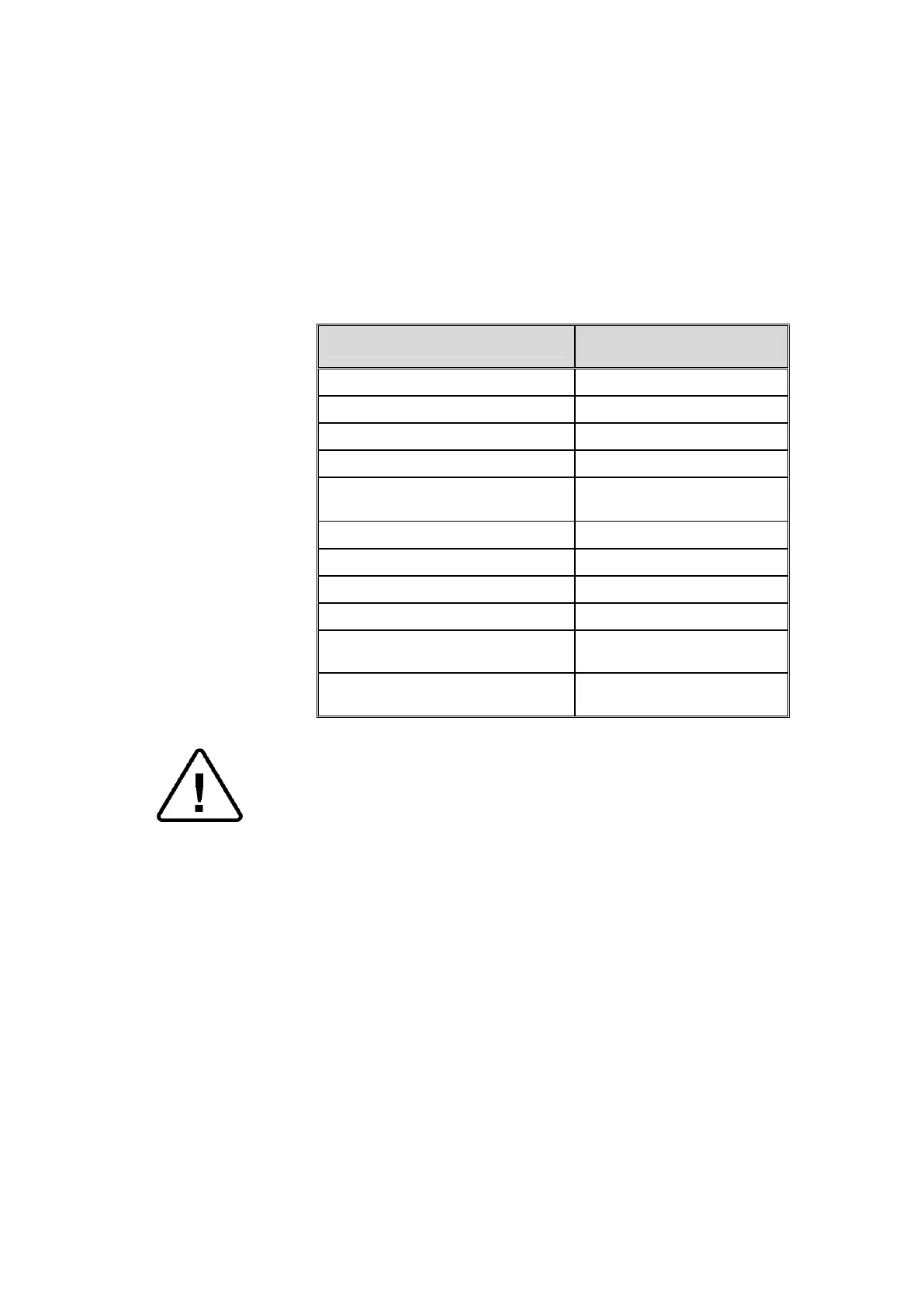
Physical Characteristics and Maximum acceptable
contaminants levels in steam for sterlizers
(According to EN 13060:2004).
Element
content
Silicium oxide. SiO
2
≤0.1 mg/kg
Iron ≤0.1 mg/kg
Cadmium ≤0.005 mg/kg
Lead ≤ 0.05 mg/kg
Rest of metals except iron,
cadmium, lead
≤0.1 mg/kg
Chloride (Cl) ≤0.1 mg/kg
Phosphate (P
2
O
5
) ≤0.1 mg/kg
Conductivity (at 20°C) ≤3 μs/cm
pH value (degree of acidity) 5 to 7
Appearance
sediment
Hardness (Σ Ions of alkaline
earth)
≤0.02 mmol/l
Compliance with the above data should be tested in accordance
with acknowledged analytical methods, by an authorized
laboratory.
Attention:
We recommend testing the water quality once a month. The use of
water for autoclaves that do not comply with the table above may
have severe impact on the working life of the sterilizer and can
invalidate the manufacturer’s guarantee.
3.17.2 Reverse Osmosis
A Reverse Osmosis (RO) system may be used to improve the
quality of the water used to generate steam in the autoclave
chamber.
In RO, the water is forced through a semi-penetrable membrane,
which filters out contaminants to a high degree of efficiency. In
deionisation (DI) ions and charged particles are removed either
by electric fields or by ion exchange in resin beds.
Although the RO cannot normally attain the degree of purity
possible with the DI methods, it is more than adequate for the
feed water intended for clean-steam generators.
Moreover the RO has several advantages:
 Loading...
Loading...