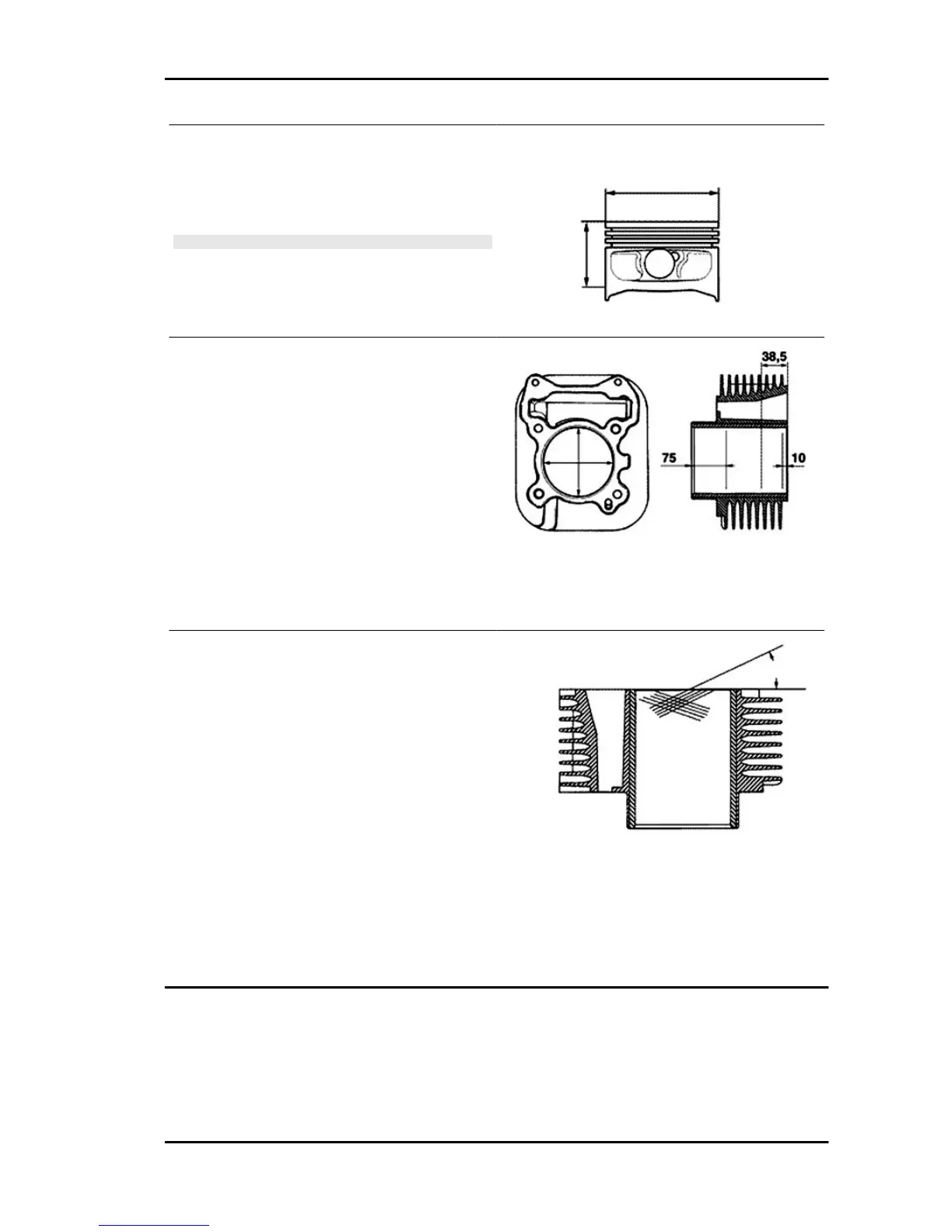
- Measure the outside diameter of the piston, per-
pendicular to the gudgeon pin axis.
- Measure 36.5 mm from the piston crown's shown
in the figure.
N.B.
THE PIN HOUSINGS HAVE 2 LUBRICATION CHANNELS.
FOR THIS REASON MEASUREMENT OF THE DIAMETER
MUST BE CARRIED OUT ACCORDING TO THE AXIS OF
THE PISTON.
- Using a bore meter, measure the inner cylinder
diameter at three different points according to the
directions shown in the figure.
- Check that the coupling surface with the head is
not worn or misshapen.
- Pistons and cylinders are classified into catego-
ries based on their diameter. The coupling is car-
ried out in pairs (A-A, B-B, C-C, D-D).
Characteristic
Maximum allowable run-out:
0.05 mm
- The cylinder rectifying operation should be car-
ried out with a surfacing that respects the original
angle.
- The cylinder surface roughness should be 0.9
micron.
- This is indispensable for a good seating of the
sealing rings, which in turn minimises oil consump-
tion and guarantees optimum performance.
- The pistons are oversized due to cylinder rectifi-
cation and are subdivided into three categories
1st, 2nd, 3rd with 0.2-0.4-0.6 mm oversize. They
are also classified into 4 categories A-A, B-B, C-
C, D-D.
Inspecting the piston
- Carefully clean the sealing ring housings.
- Measure the coupling clearance between the sealing rings and the piston grooves using suitable
sensors, as shown in the diagram.
- If the clearance is greater than that indicated in the table, replace the piston.
Vespa LX 125 - 150 i.e. Engine
ENG - 117
 Loading...
Loading...











