WF-255MST
© Weldclass 2019 | E.&O.E. | Edition 2.2 51
11.9.4 How to determine correct Wire Speed/Voltage Setting
If the Current/Amperage (Wire Speed) is too high for the welding voltage, “stubbing” will occur as the
wire dips into the molten pool and does not melt. Welding in these conditions normally produces a poor
weld due to lack of fusion.
If, however, the welding voltage is too high, large drops will form on the end of the wire, causing spatter.
The correct setting of voltage and Current (Wire Speed) can be seen in the shape of the weld deposit
and heard by a smooth regular arc sound.
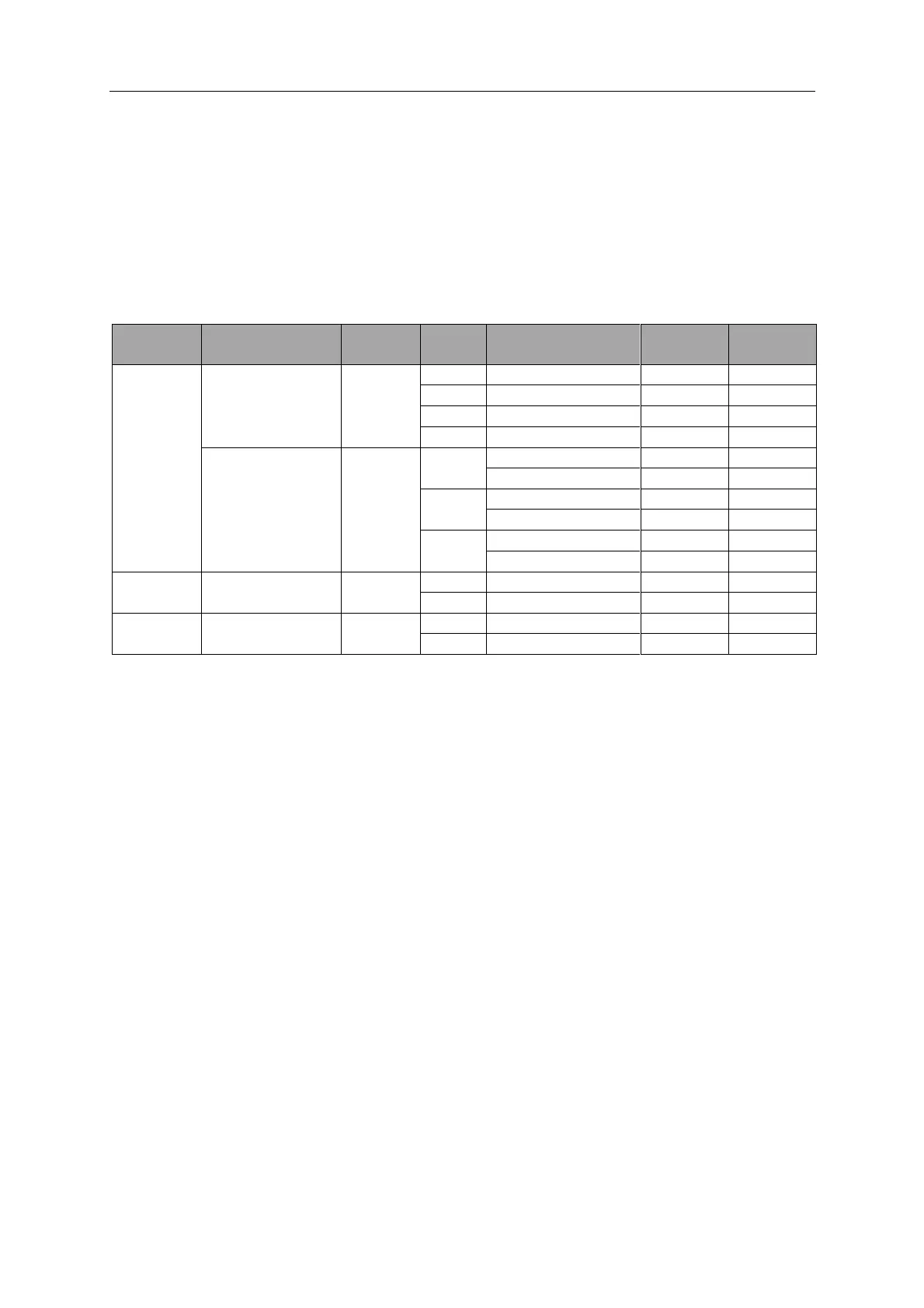
11.10 Suggested Settings for Typical MIG Applications
Solid Mild Steel
Weldclass XT6
(E70S-6)
Gasless Flux-cored
Mild Steel
Weldclass GL-11
(E71T-11)
Table 12
These settings are a guide only. Actual settings required will depend on plate thickness, operator technique,
environment, etc.
11.11 Welding wire Size Selection
The choice of Welding wire size and shielding gas used depends on the following:
1. Thickness of the metal to be welded
2. Type of joint
3. Capacity of the wire feed unit and power source
4. The amount of penetration required
5. The deposition rate required
6. The bead profile desired
7. The position of welding
8. Cost of the wire
9. Environment (can shielding gas be used or not?)

 Loading...
Loading...