.
66 © Weldclass 2019 | E.&O.E. | Edition 2.2
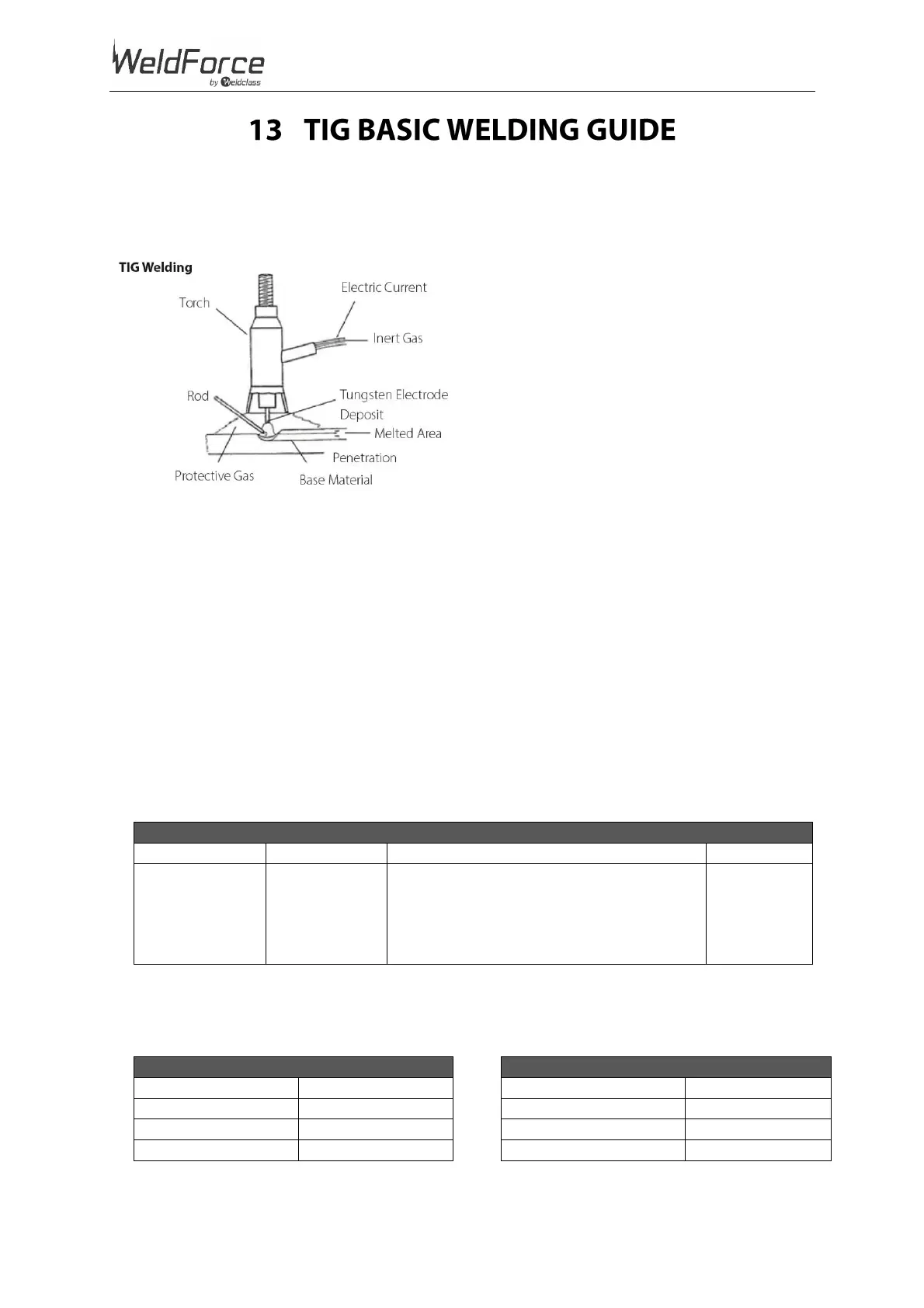
TIG Welding is a fusion procedure that uses an electric ARC created between an infusible tungsten electrode
and base material to be welded. For TIG welding an inert gas must be used (Argon) which protects the
welding bead. If filling material is used, it is made up of rods suitable to the material to be welded (steel,
stainless steel, copper etc.).
Figure 68
In TIG mode, welding is possible in all positions: flat, angle, on the edge, vertical and overhead.
Furthermore, with respect to other types of welding, the welding joint has greater mechanical resistance,
greater corrosion resistance and limited heating in the welded area which limits distortion. Welding can be
done even without weld material, guaranteeing a smooth, shiny weld with no impurities or slag.
13.1 TIG Electrode Selection and Preparation
13.1.1 Electrode Polarity
Connect the TIG torch to the negative (-) torch terminal and the work lead to the positive (+) work
terminal for direct current straight polarity. Direct current straight polarity is the most widely used
polarity for DC TIG welding. It allows limited wear of the electrode since 70% of the heat is concentrated
at the work piece.
Rare-Earth
(Weldclass RE4)
High-Performance, suitable for both DC (Steel,
Stainless steel etc) and AC (Aluminium)* TIG
welding. Maintains tip shape, reliable arc
striking, low burn off rate, long service life and
smooth/stable arc.
Table 19
* Note that the WeldForce WF-255MST machine is only capable of DC TIG welding. It cannot perform
AC TIG welding required to weld Aluminium.
Tungsten Electrode Current Ranges
Table 20
Guide For Selecting Filler Wire Diameter
Filler Electrode Diameter
Table 21

 Loading...
Loading...