82 3064298_201507
33. Conguringthedualmodepoint
Congurationexample
Central heating demand (building heat load) to DIN 4701 or EN 12831 of 7.7 kW. A DHW demand for 4 people (0.25 kW/person)
and a standard outside temperature of -16 °C are assumed.
Thepowersupplyutilityspeciesablockingtimeof2x2hours.TheblockingtimefactorZis1.1.
Usingthesegures,therequiredheatpumpoutputiscalculatedasfollows:
Q
HP
= (Q
B
+ Q
DHW
) x Z = (7.7 kW + 1.0 kW) x 1.1 = 9.6 kW
Q
E-rod
= Q
HP
- Q
HP,Tn
= 9.6 kW - 5.6 kW = 4.0 kW
. .
.
.
.
.
Q
HP
: Required peak output of the heat pump system
Q
B
: Building heat load (building heat demand, central heating demand)
Q
DHW
: Output demand for DHW heating
Q
E-rod
: Heater rod output
Q
HP,Tn
: Heating output of heat pump for standard design point
Z : Blocking time factor
.
.
.
.
.
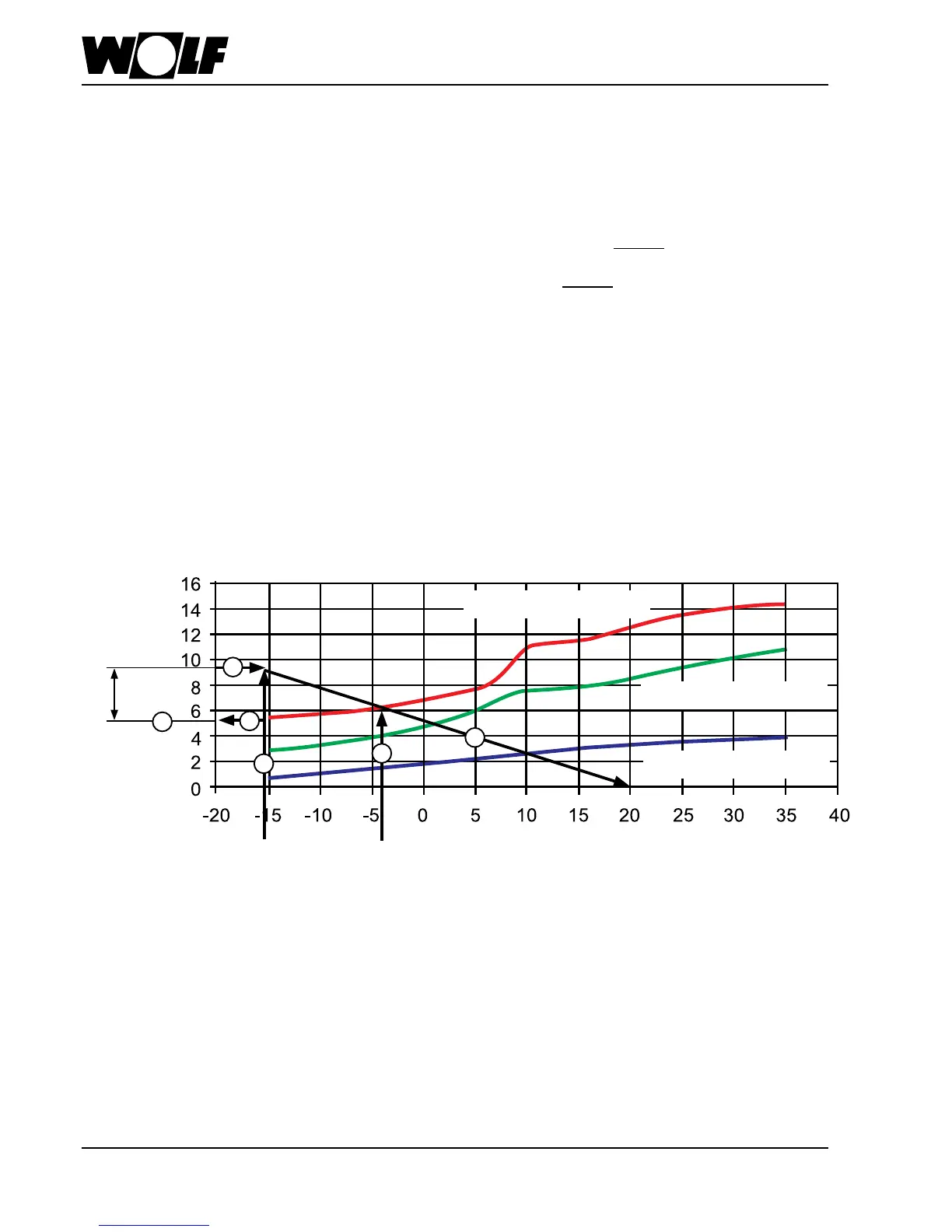
Diagram for calculating the dual
mode point and the output of the
electric heating rod
As can be seen from the diagram, the theoretical heating output for the standard design point is approx. 5.6 kW. Since a 4 kW
heater rod is also installed, the maximum available heating output is 9.6 kW at an outside temperature of -16 °C.
This results in a dual mode point of approx. -4 °C.
The closer the dual mode point gets to the standard outside temperature, the lower the proportion of booster heating.
As a rule, the booster heater is responsible for approx. 30 - 60 % of the required heating output. Though the proportion of output
attributable to the booster heater is relatively large, the proportion of work is only approx. 2 - 5 % of the annual heating load.
In the example shown, a DHW cylinder with a water capacity of 300 litres can meet the daily requirements of a 4-person
household (detached house, high demand of 4 x 70 litres/day = 400 l DHW cylinder).
No changes would be made to the selected heat pump type in this example.
Air inlet temperature [°C]
Standard outside temperature
Heating output [kW]
-16
Dual mode point
-4
1
2
3
4
5
Max. compressor speed
Nominal compressor speed
Min. compressor speed
4.0 kW
Q
HP
.
Q
E-rod
.
Q
HP,Tn
.
5.6
9.6
6
Heating limit temperature
 Loading...
Loading...