IM 12D7B2-E-H
21
1. When is calibration necessary?
Calibration of conductivity instruments is not
normally required since conductivity cells are
manufactured within controlled tolerances
and do not alter in use.
If the cell has been severely fouled or sub-
ject to abrasion (possibly during cleaning) it
may be necessary to calibrate.
Alternatively calibration may be carried out
with a simulator to check the electronics
only.
2. How is calibration done?
Calibration is carried out by measuring a
solution which has a known conductivity
and adjusting the instrument to show the
correct conductivity value.
Calibration solutions can be made up in the
laboratory. A solution of salt is made with
precise concentration. Temperature is stabi-
lised to the reference temperature of the in-
strument (usually 25°C). The conductivity of
the solution is taken from tables.
Alternatively the instrument may be calibra-
ted in an unspecified solution against a
standard instrument. Here care should be
taken to make measurement at the refe-
rence temperature since differences in the
type of temperature compensation of the
instruments may cause an error.
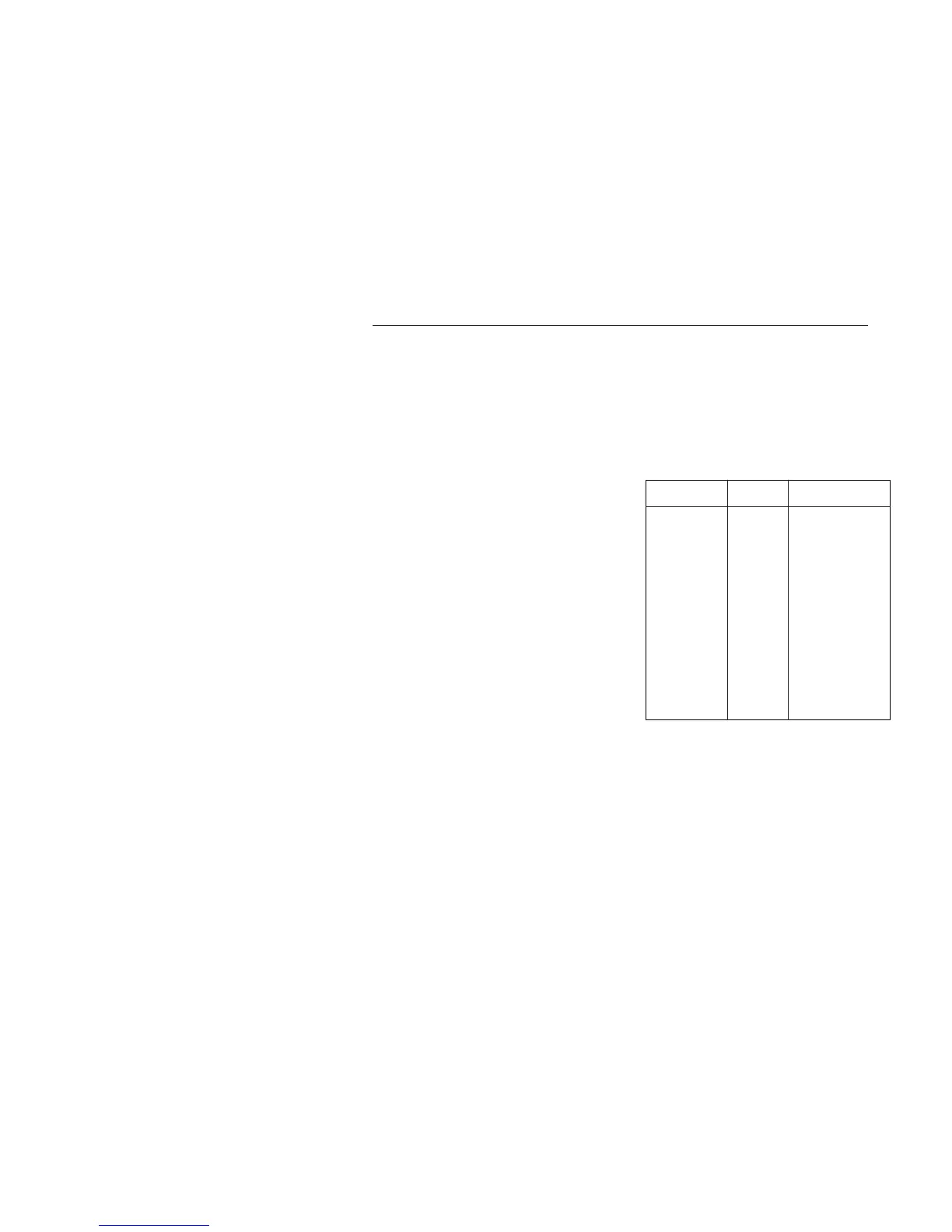
3. Typical calibration solutions
The table below shows typical conductivity
values for solutions which may be made up
in the laboratory.
Table for NaCI at 25°C
5-1. Calibration
% weight mg/kg Conductivity
00.001 10 021.40 µS/cm
00.003 30 064.00 µS/cm
00.005 50 106.00 µS/cm
00.01 100 210.00 µS/cm
00.03 300 617.00 µS/cm
00.05 500 001.03 mS/cm
00.1 1000 001.99 mS/cm
00.3 3000 005.69 mS/cm
00.5 5000 009.48 mS/cm
01 10000 017.60 mS/cm
03 30000 048.60 mS/cm
05 50000 081.00 mS/cm
10 100000 140.00 mS/cm

 Loading...
Loading...