52 Agilent 7890 Series Troubleshooting
3 Chromatographic Symptoms
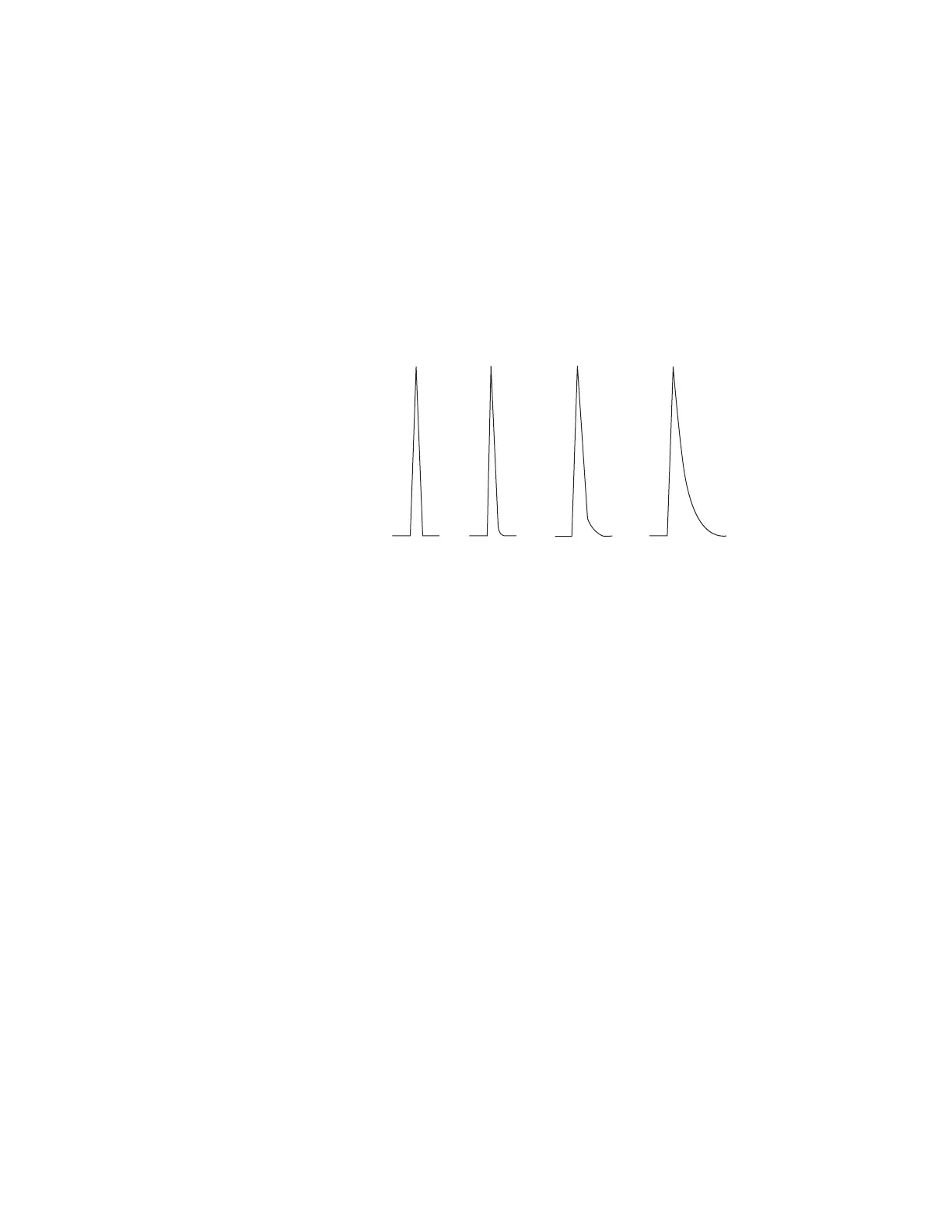
Peak Tailing
The figure below shows an example of tailing peaks. When
troubleshooting tailing peaks, consider:
• Which peaks are tailing?
• Are the tailing peaks active compounds, all compounds, or
are there trends (such as early eluters or late eluters)?
• Check the column for severe contamination.
• If using a capillary column, remove 1/ 2 to 1 meter from
the front of the column.
• For bonded and cross-linked phases, solvent rinse the
column.
• Check for inlet contamination. Tailing will sometimes
increase with compound retention. Clean the inlet and
replace contaminated inlet parts. (See the 7890 Series
Maintenance manual.)
• Consider the column stationary phase (active column). This
only affects active compounds. An active column usually
produces tailing that increases with retention time.
• Cut off 1 meter from the front of the column.
• Replace the column.
• Verify that the column was cut and installed properly.
• Re-cut and reinstall the column into the inlet and replace
the ferrules. Make a clean, square cut using a reliable tool.
• Confirm the installation is leak free. If there is a leak at
the column fitting, you will see more tailing for early
eluting peaks. (See “Checking for Leaks”.)
• Consider the type of adapter, liner, and inlet seal being used.
One or all of these may be contaminated or active.
• Use a new, deactivated liner. This only affects active
compounds.

 Loading...
Loading...











