70
Developing Methods
This chapter discusses various parameters that can affect the sensitivity,
precision, and accuracy of an analysis.
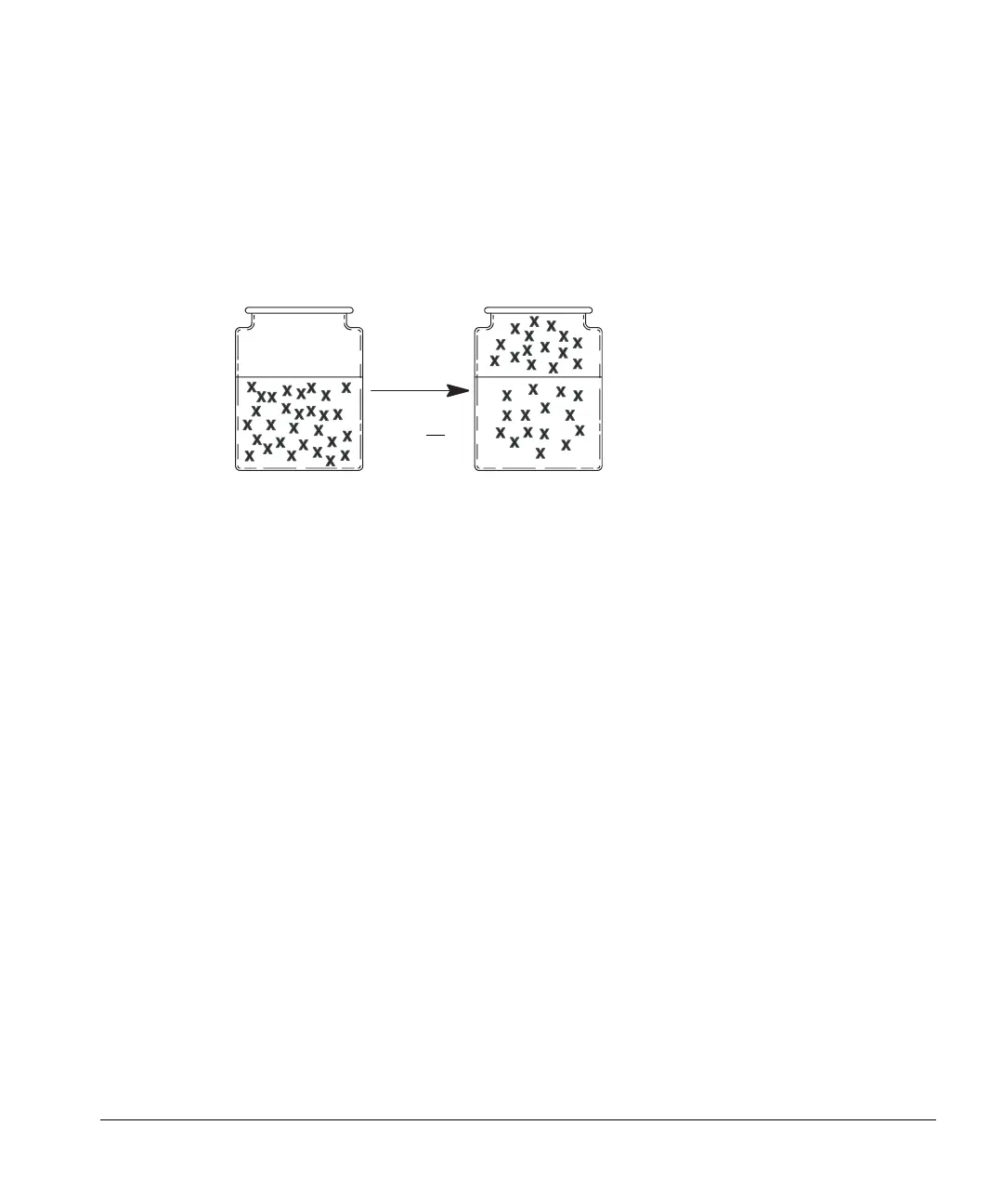
Figure 11. Illustration of partition coefficient
The tendency of a material to go into the gaseous phase is the partition
coefficient, K, where C
c
is the concentration of the analyte in the condensed
phase (the sample matrix) and C
g
is the concentration of the analyte in the
gaseous phase (the headspace). The partition coefficient, K is related to the
degree of solubility that the analyte has in the matrix. For example, benzene is
not very soluble in water, and has a K of approximately seven. Ethanol, which
is very soluble in water, has a K of 7000. A high value of K implies it is difficult
for the analyte to leave the matrix and go into the headspace.
K is also very dependent on temperature, as demonstrated by the following
equation:
Processes that reduce the value of K will increase the sensitivity of the
headspace analysis. The following operations can be used to decrease K:
1. Add mineral salts to the matrix (aqueous samples)
2. Add another liquid to the matrix
3. Increase the temperature
Equilibration
K =
C
c
C
g
dK
dT
---------
1
T
2
-------=

 Loading...
Loading...











