Cooling Mode - Direct Expansion Cooling (DX)
Single EC Inverter Driven Compressor
Comprising of an EC inverter driven scroll compressor which provides variable control of the system performance, by
adjusting its speed. This output allows external load demands to be met with greater precision, eliminating unnecessary
temperature and humidity variations. Consequently, system efciency and reliability are much improved by extending
major component working hours.
Tandem EC Inverter and Fixed Speed Compressors
Combining a xed speed compressor and EC inverter driven scroll compressor provides a more exible variable control
of the system performance, by adjusting one compressors speed.
This output allows greater external load demands to be met than with the single inverter option with greater precision,
eliminating unnecessary temperature and humidity variations.
Consequently, system efciency and reliability are much improved by extending major component working hours.
Electronic Expansion Valves (EEV)
Electronic expansion valves differ to the traditional thermostatic expansion valves in their ability to maintain control of the
suction superheat at reduced head pressures. This can lead to signicant energy savings particularly at reduced loading
and low ambient temperatures.
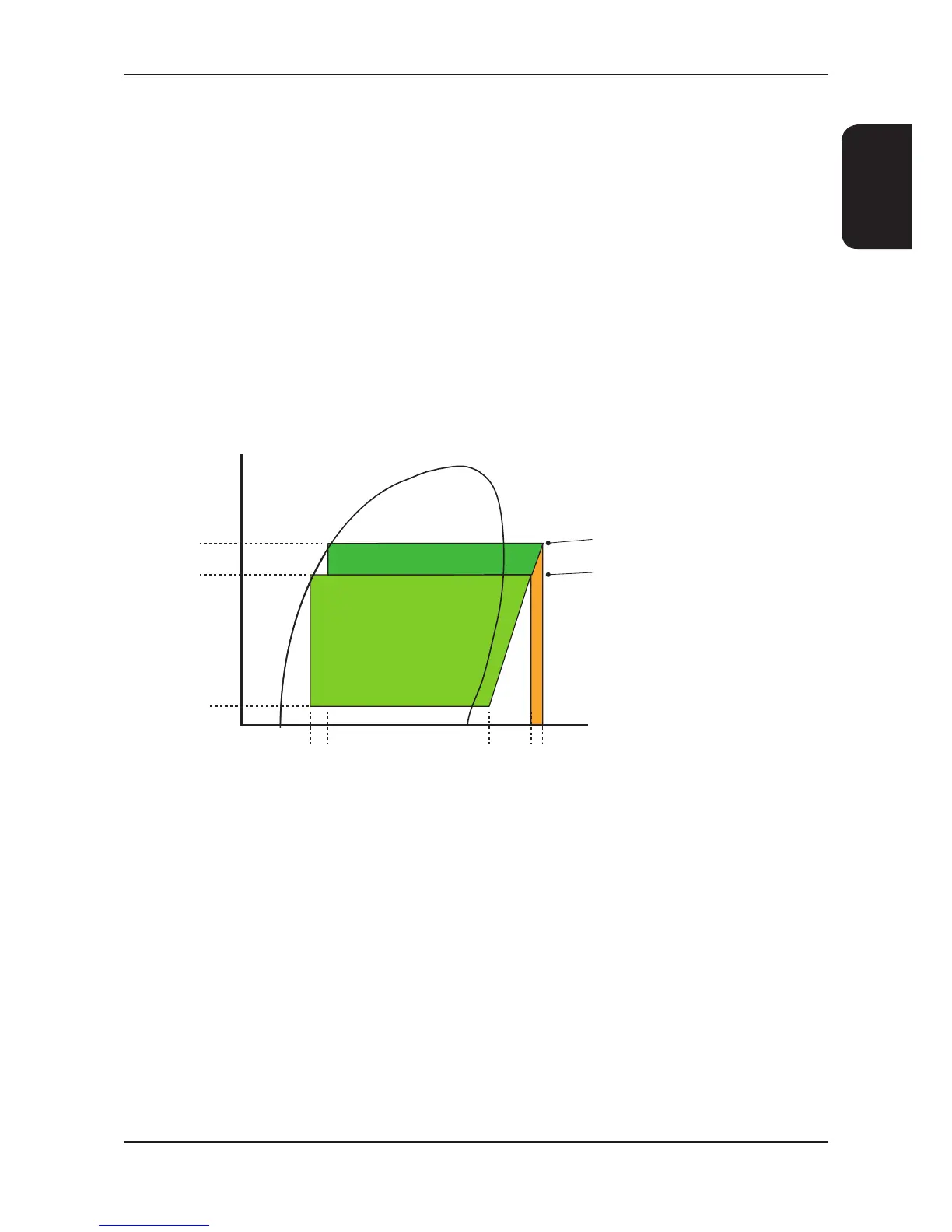
Heat of Rejection
Reduction in
Compressor Input
Power
Enthalpy kJ/kgIncrease in
Cooling Duty
Evaporating
Pressure
Reduced
Condensing
Pressure
Presssure
Bara
Thermostatic Expansion Valve (1)
Electronic Expansion Valve (2)
1
2
3
4
(1) Cooling Cycle @ 22°C ambient with a conventional TEV tted.
(2) Cooling cycle @ 22°C ambient, demonstrating a typical EEV condensing temperature taking full advantage of lower
ambient air temperatures (below 35°C).
1 Compression
2 Condensation
3 Expansion
4 Evaporation

 Loading...
Loading...



