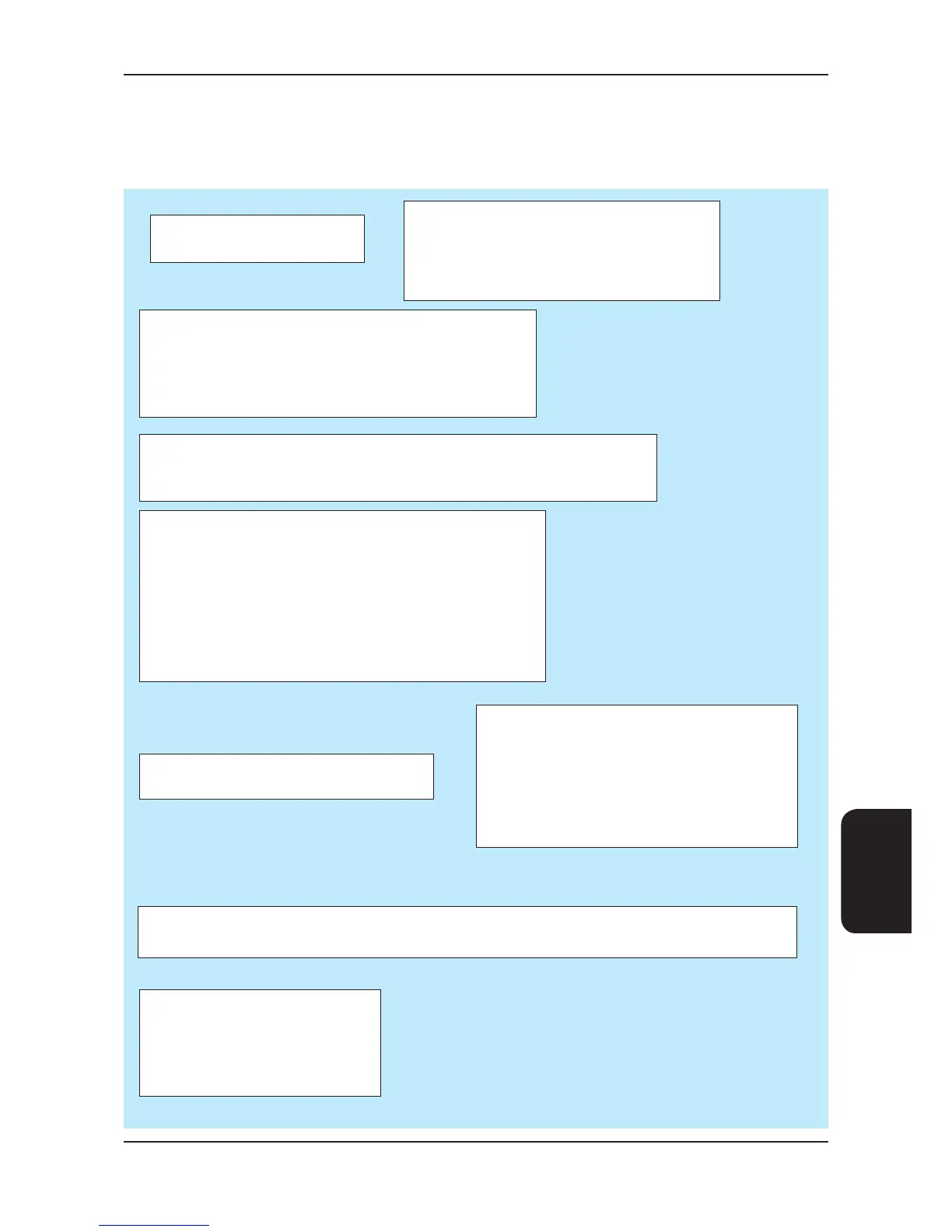
Oil Charging Guide
In order to determine if a system requires additional oil to accommodate for long interconnecting pipe lines and oil traps,
a simple calculation can be used to approximate the volume of oil required as follows:
OT = (RC / 200) - (OC x 0.09)
Where
OT = Additional Oil Charge / Circuit (kg)
RC = Total Refrigerant Charge / Circuit (kg)
OC = Total Compressor Oil Charge / Circuit (l)
This calculation is based on the following assumptions:
1) 10% of the total compressor oil charge enters the system
2) A specic gravity of 0.09 between oil and water
3) Oil is added at a rate of 5 grams per kilogram of refrigerant
Example
What is the additional oil charge required per circuit for an LIR6042U-X250-0 matched
with a CR80 and a 5/8” 10m interconnecting liquid line?
Refrigerant charge of an LIR6042U-X250-0= 4.2 kg
Refrigerant charge of a CR80 = 8.4 kg
Interconnecting pipe line = 10 x 0.15 = 1.5kg
Total system refrigerant charge = 4.2 + 8.4 + 1.5 = 14.1 kg
Compressor oil charge(s) = 4.4 litre
So,
OT = (RC / 200) - (OC x 0.09)
OT = (14.1 / 200) - (4.4 x 0.09)
OT = -0.326 litre
A negative value (as above) suggests that there is already sufcient oil in the system. You can calculate the
maximum refrigerant charge for this system when additional oil charge is required as follows:
OT = (RC / 200) - (OC x 0.09)
RC = OT + (OC x 0.09 x 200)
RC = 0 + (4.4x 0.09 x 200)
RC = 79.2 kg
 Loading...
Loading...



