107
7598H–AVR–07/09
ATtiny25/45/85
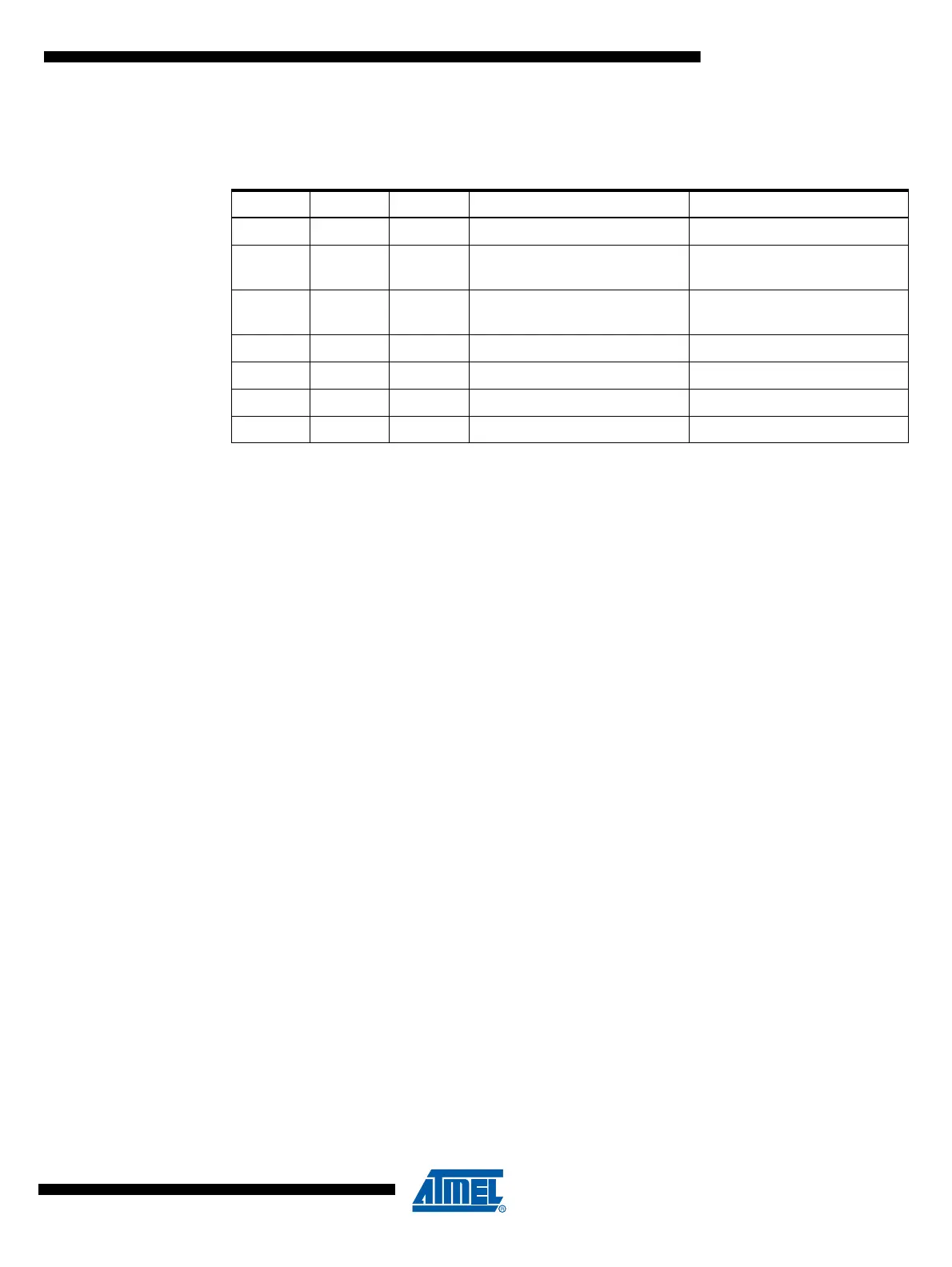
Table 16-2 shows the relationship between the USICS1..0 and USICLK setting and clock source
used for the Shift Register and the 4-bit counter.
• Bit 1 – USICLK: Clock Strobe
Writing a one to this bit location strobes the Shift Register to shift one step and the counter to
increment by one, provided that the USICS1..0 bits are set to zero and by doing so the software
clock strobe option is selected. The output will change immediately when the clock strobe is exe-
cuted, i.e., in the same instruction cycle. The value shifted into the Shift Register is sampled the
previous instruction cycle. The bit will be read as zero.
When an external clock source is selected (USICS1 = 1), the USICLK function is changed from
a clock strobe to a Clock Select Register. Setting the USICLK bit in this case will select the
USITC strobe bit as clock source for the 4-bit counter (see Table 16-2).
• Bit 0 – USITC: Toggle Clock Port Pin
Writing a one to this bit location toggles the USCK/SCL value either from 0 to 1, or from 1 to 0.
The toggling is independent of the setting in the Data Direction Register, but if the PORT value is
to be shown on the pin the DDRE4 must be set as output (to one). This feature allows easy clock
generation when implementing master devices. The bit will be read as zero.
When an external clock source is selected (USICS1 = 1) and the USICLK bit is set to one, writ-
ing to the USITC strobe bit will directly clock the 4-bit counter. This allows an early detection of
when the transfer is done when operating as a master device.
Table 16-2. Relations between the USICS1..0 and USICLK Setting
USICS1 USICS0 USICLK Shift Register Clock Source 4-bit Counter Clock Source
0 0 0 No Clock No Clock
001
Software clock strobe
(USICLK)
Software clock strobe
(USICLK)
01X
Timer/Counter0 Compare
Match
Timer/Counter0 Compare
Match
1 0 0 External, positive edge External, both edges
1 1 0 External, negative edge External, both edges
1 0 1 External, positive edge Software clock strobe (USITC)
1 1 1 External, negative edge Software clock strobe (USITC)

 Loading...
Loading...