131
7598H–AVR–07/09
ATtiny25/45/85
20.3 Performing a Page Write
To execute Page Write, set up the address in the Z-pointer, write “00000101” to SPMCSR and
execute SPM within four clock cycles after writing SPMCSR. The data in R1 and R0 is ignored.
The page address must be written to PCPAGE. Other bits in the Z-pointer must be written to
zero during this operation.
• The CPU is halted during the Page Write operation.
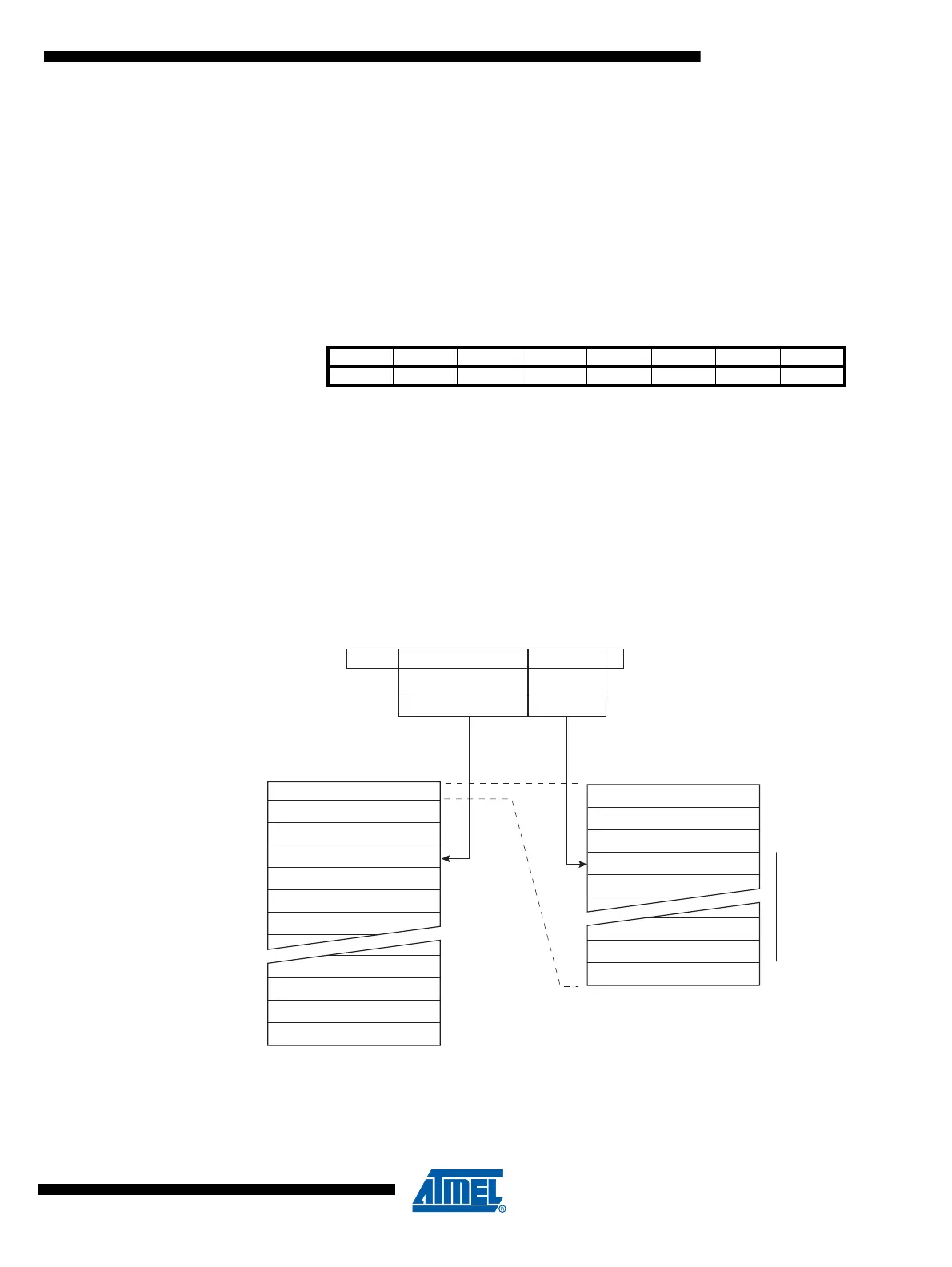
20.4 Addressing the Flash During Self-Programming
The Z-pointer is used to address the SPM commands.
Since the Flash is organized in pages (see Table 21-6 on page 137), the Program Counter can
be treated as having two different sections. One section, consisting of the least significant bits, is
addressing the words within a page, while the most significant bits are addressing the pages.
This is shown in Figure 20-1. Note that the Page Erase and Page Write operations are
addressed independently. Therefore it is of major importance that the software addresses the
same page in both the Page Erase and Page Write operation.
The LPM instruction uses the Z-pointer to store the address. Since this instruction addresses the
Flash byte-by-byte, also the LSB (bit Z0) of the Z-pointer is used.
Figure 20-1. Addressing the Flash During SPM
(1)
Note: 1. The different variables used in Figure 20-1 are listed in Table 21-6 on page 137.
Bit 151413121110 9 8
ZH (R31) Z15 Z14 Z13 Z12 Z11 Z10 Z9 Z8
ZL (R30) Z7Z6Z5Z4Z3Z2Z1Z0
76543210
PROGRAM MEMORY
0115
Z - REGISTER
BIT
0
ZPAGEMSB
WORD ADDRESS
WITHIN A PAGE
PAGE ADDRESS
WITHIN THE FLASH
ZPCMSB
INSTRUCTION WORD
PAGE
PCWORD[PAGEMSB:0]:
00
01
02
PAGEEND
PAGE
PCWORDPCPAGE
PCMSB
PAGEMSB
PROGRAM
COUNTER

 Loading...
Loading...