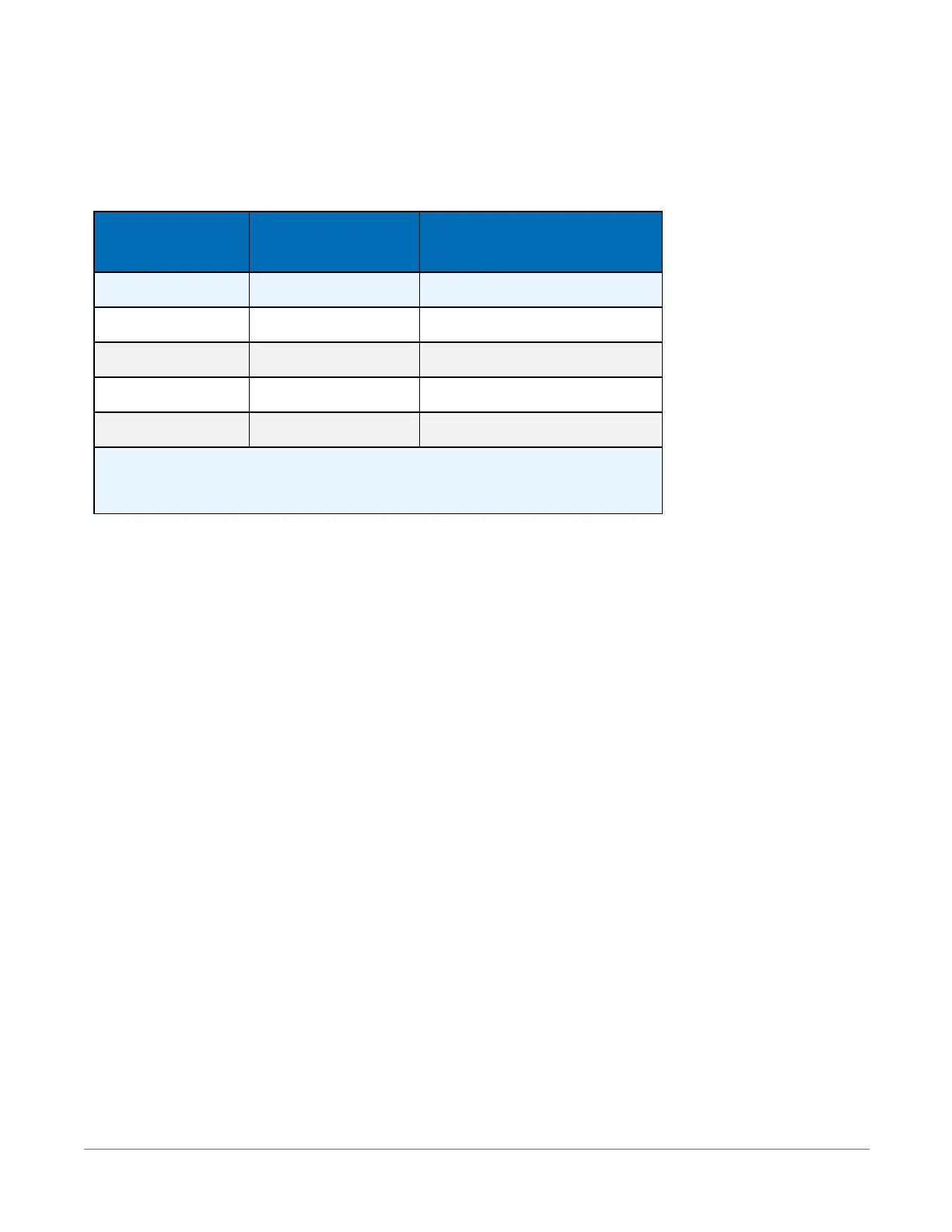
Multiplexed Measurement Time:
These are not maximum speeds. Multiplexed denotes circuitry inside the datalogger that switches
signals into the ADC.
Measurement time = INT(multiplexed measurement time • (reps+1) + 2ms
Differential
with Input Reversal
Single-Ended or Differential
without Input Reversal
Example fN1
1
(Hz) Time
2
(ms) Time
2
(ms)
15000 2.04 1.02
60 35.24 17.62
50 41.9 20.95
5 401.9 200.95
1
Notch frequency (1/integration time).
2
Default settling time of 500 µs used.
See also Voltage measurements (p. 46).
10.5.2 Resistance measurements specifications
The datalogger makes ratiometric-resistance measurements for four- and six-wire full-bridge
circuits and two-, three-, and four-wire half-bridge circuits using voltage excitation. Excitation
polarity reversal is available to minimize dc error. Typically, at least one terminal is configured for
excitation output. Multiple sensors may be able to use a common excitation terminal.
Accuracy: Assumes input reversal for differential measurements RevDiff and excitation reversal
RevEx for excitation voltage <1000 mV. Does not include bridge resistor errors or sensor and
measurement noise.
Ratiometric accuracy, rather than absolute accuracy, determines overall measurement accuracy.
Offset is the same as specified for analogue voltage measurements.
l 0 to 40 °C: ±(0.01% of voltage measurement + offset)
l –40 to 70 °C: ±(0.015% of voltage measurement + offset)
l –55 to 85 °C (XT): ±(0.02% of voltage measurement + offset)
10.5.3 Period-averaging measurement specifications
Use PeriodAvg() to measure the period (in microseconds) or the frequency (in Hz) of a signal
on a single-ended channel.
10. Specifications 168

 Loading...
Loading...