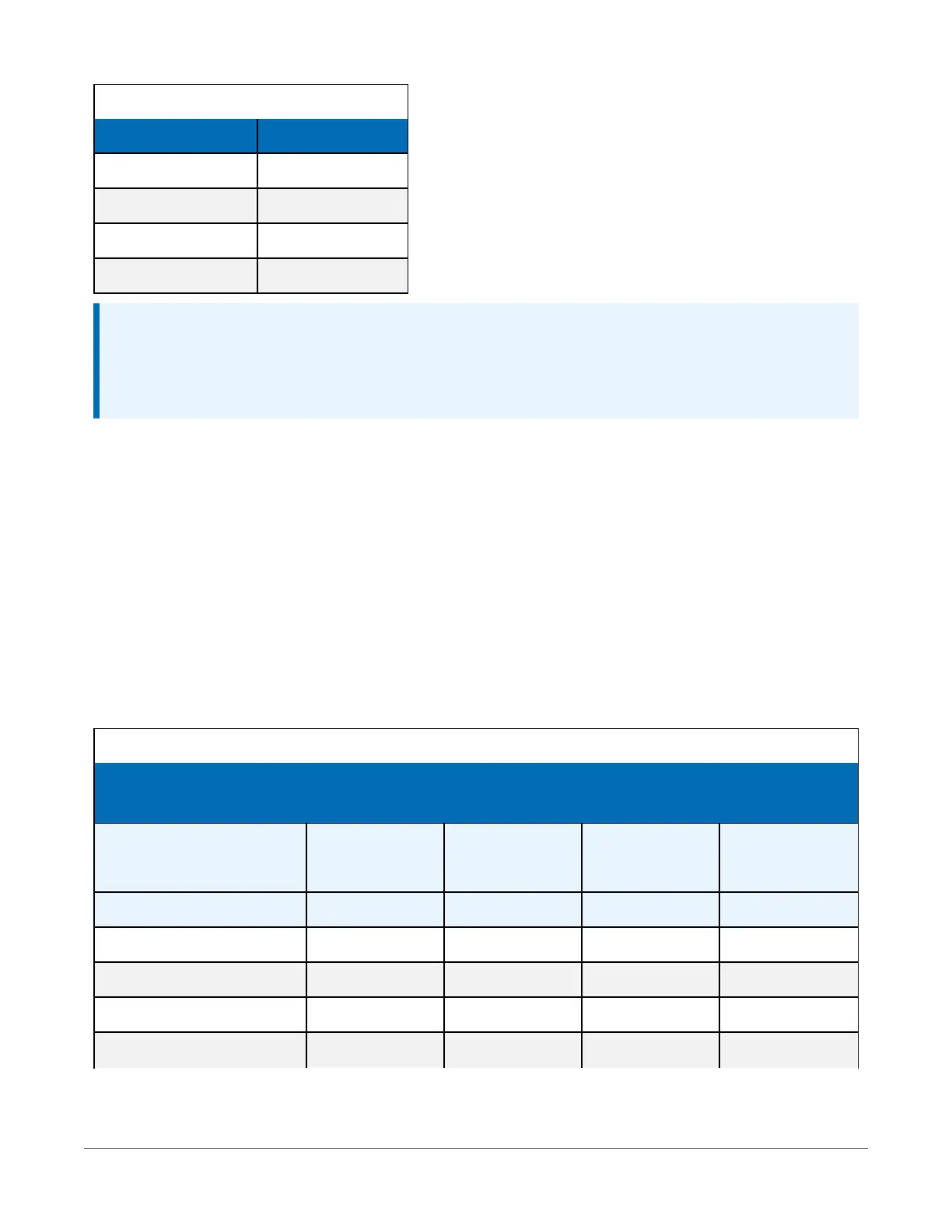
Table 4-3: FP2 decimal location
Absolute value Decimal location
0 – 7.999 X.XXX
8 – 79.99 XX.XX
80 – 799.9 XXX.X
800 – 7999. XXXX.
NOTE:
String and Boolean variables can be output with the Sample() instruction. Results of
Sampling a Booleanvariable will be either -1 or 0 in the collected Data Table. A Boolean
displays in the Numeric Monitor Public and Data Tables as true or false.
4.5 About data tables
A data table is essentially a file that resides in datalogger memory (for information on data table
storage, see Data memory (p. 38)). The file consists of five or more rows. Each row consists of
columns, or fields. The first four rows constitute the file header. Subsequent rows contain data
records. Data tables may store individual measurements, individual calculated values, or summary
data such as averages, maximums, or minimums.
Typically, files are written to based on time or event. The number of data tables is limited to 250.
You can retrieve data based on a schedule or by manually choosing to collect data using
datalogger support software (see Collecting data (p. 29)).
Table 4-4: Example data
TOA5, MyStation, CR1000X, 1142, CR1000X.Std.01, CPU:MyTemperature.CR1X, 1958,
OneMin
TIMESTAMP RECORD BattV_Avg PTemp_C_Avg Temp_C_Avg
TS RN Volts Deg C Deg C
Avg Avg Avg
2016-03-08 14:24:00 0 13.68 21.84 20.71
2016-03-08 14:25:00 1 13.65 21.84 20.63
2016-03-08 14:26:00 2 13.66 21.84 20.63
2016-03-08 14:27:00 3 13.58 21.85 20.62
4. Data 33

 Loading...
Loading...