9-20
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch and Cisco 7600 Series Router Firewall Services Module Configuration Guide
OL-6392-01
Chapter 9 Configuring Network Address Translation
Using Dynamic NAT and PAT
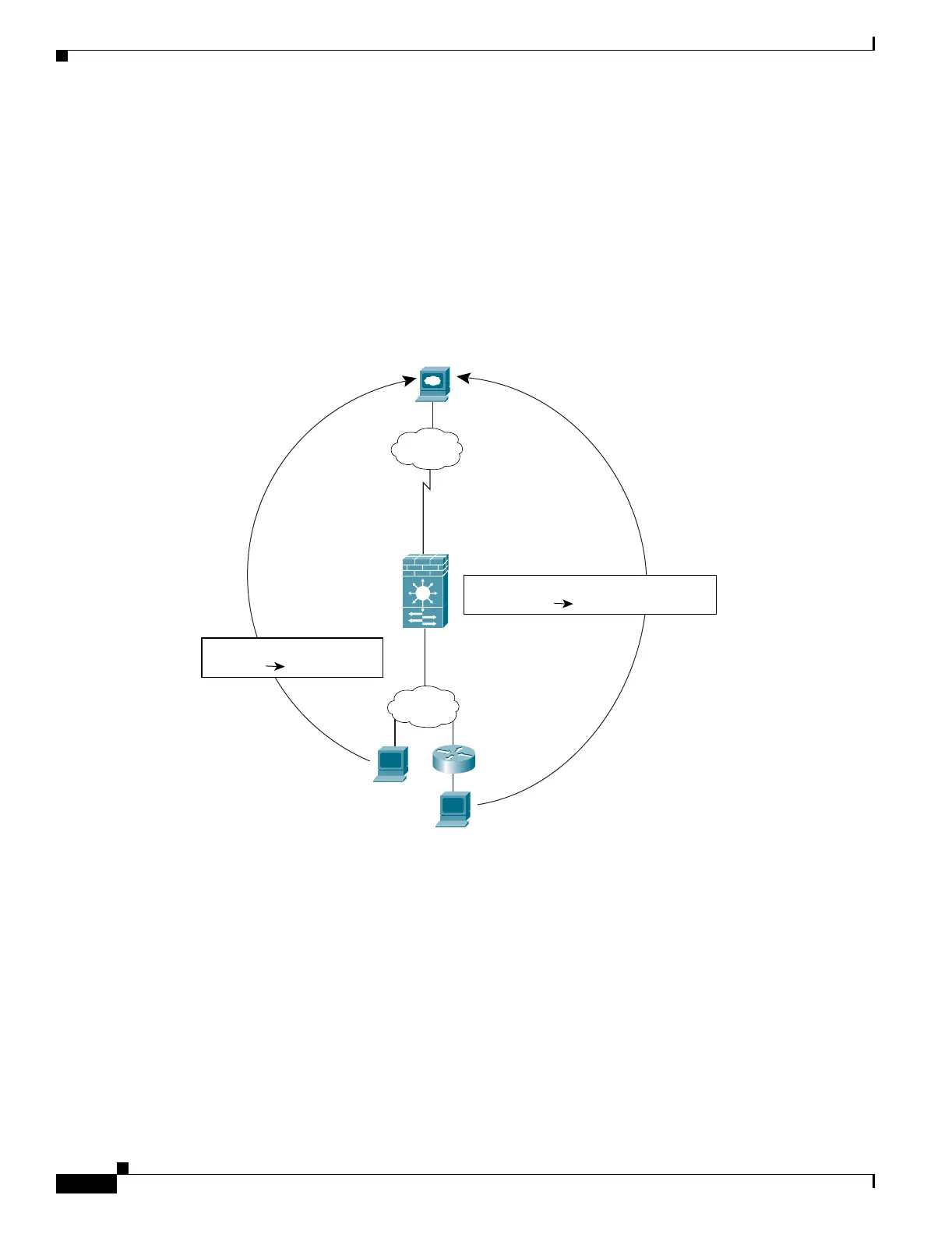
If you use different NAT IDs, you can identify different sets of host addresses to have different global
addresses. For example, on the Inside interface, you can have two NAT statements on two different
NAT IDs. On the Outside interface, you configure two global statements for these two IDs. Then, when
traffic from Inside network A exits the Outside interface, the IP addresses are translated to pool A
addresses; while traffic from Inside network B are translated to pool B addresses (see Figure 9-11). If
you use policy NAT, you can specify the same local addresses for multiple NAT statements, as long as
the source address/port and destination address/port is unique for each statement. For regular NAT, you
must identify different local addresses for each statement.
Figure 9-11 Different NAT IDs
See the following commands for this example:
FWSM/contexta(config)# nat (inside) 1 10.1.2.0 255.255.255.0
FWSM/contexta(config)# nat (inside) 2 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
FWSM/contexta(config)# global (outside) 1 209.165.201.3-209.165.201.10
FWSM/contexta(config)# global (outside) 2 209.165.201.11
Web Server:
www.cisco.com
Outside
Inside
Global 1: 209.165.201.3-
209.165.201.10
Global 2: 209.165.201.11
NAT 1: 10.1.2.0/24
NAT 2: 192.168.1.0/24
10.1.2.27
192.168.1.14
Source Addr Translation
209.165.201.310.1.2.27
Source Addr Translation
209.165.201.11:4567192.168.1.14
104671

 Loading...
Loading...

















