1-11
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch and Cisco 7600 Series Router Firewall Services Module Configuration Guide
OL-6392-01
Chapter 1 Introduction to the Firewall Services Module
How the Firewall Services Module Works
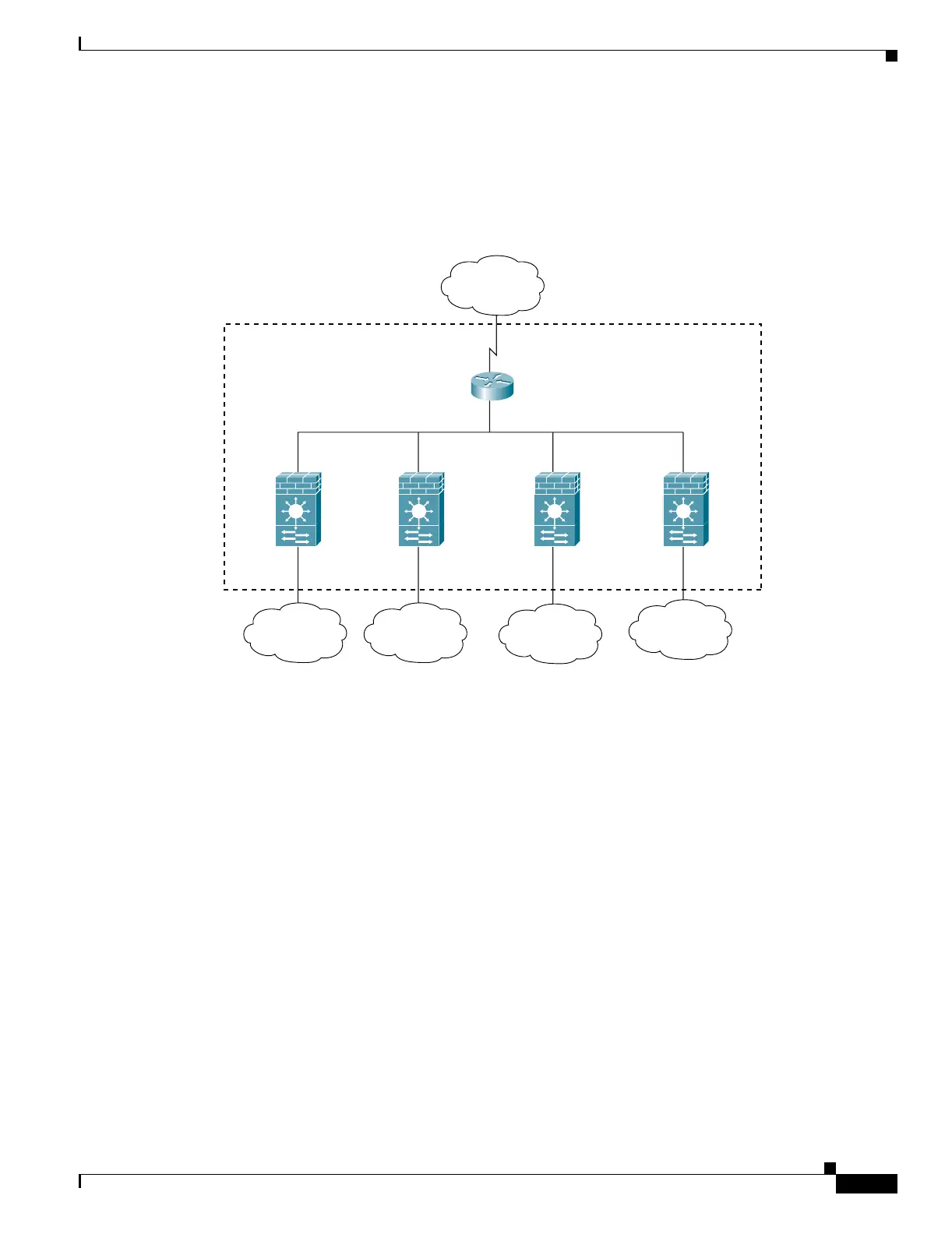
For multiple context mode, if you place the MSFC behind the FWSM, you should only connect it to a
single context. If you connect the MSFC to multiple contexts, the MSFC will route between the contexts,
which might not be your intention. The typical scenario for multiple contexts is to use the MSFC in front
of all the contexts to route between the Internet and the switched networks (see Figure 1-3).
Figure 1-3 MSFC Placement with Multiple Contexts
Routed Firewall and Transparent Firewall Modes
The FWSM can run in two firewall modes:
• Routed
• Transparent
In routed mode, the FWSM is considered to be a router hop in the network. It performs NAT between
connected networks, and can use OSPF or passive RIP (in single context mode). Routed mode supports
up to 256 interfaces per context or in single mode, with a maximum of 1000 interfaces divided between
all contexts.
In transparent mode, the FWSM acts like a “bump in the wire,” or a “stealth firewall,” and is not a router
hop. The FWSM connects the same network on its inside and outside interfaces, but each interface must
be on a different VLAN. No dynamic routing protocols or NAT are required. However, like routed mode,
transparent mode also requires ACLs to allow traffic through. Transparent mode can also optionally use
EtherType ACLs to allow non-IP traffic. Transparent mode only supports two interfaces, an inside
interface and an outside interface.
Inside
Customer A
Inside
Customer B
Inside
Customer C
Context A Context B Context C
VLAN 204VLAN 203VLAN 202
VLAN 100
Switch
Internet
Admin
Network
Admin
Context
VLAN 201
VLAN 200
MSFC
104659

 Loading...
Loading...

















