4-5
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch and Cisco 7600 Series Router Firewall Services Module Configuration Guide
OL-6392-01
Chapter 4 Configuring the Firewall Mode
Firewall Mode Overview
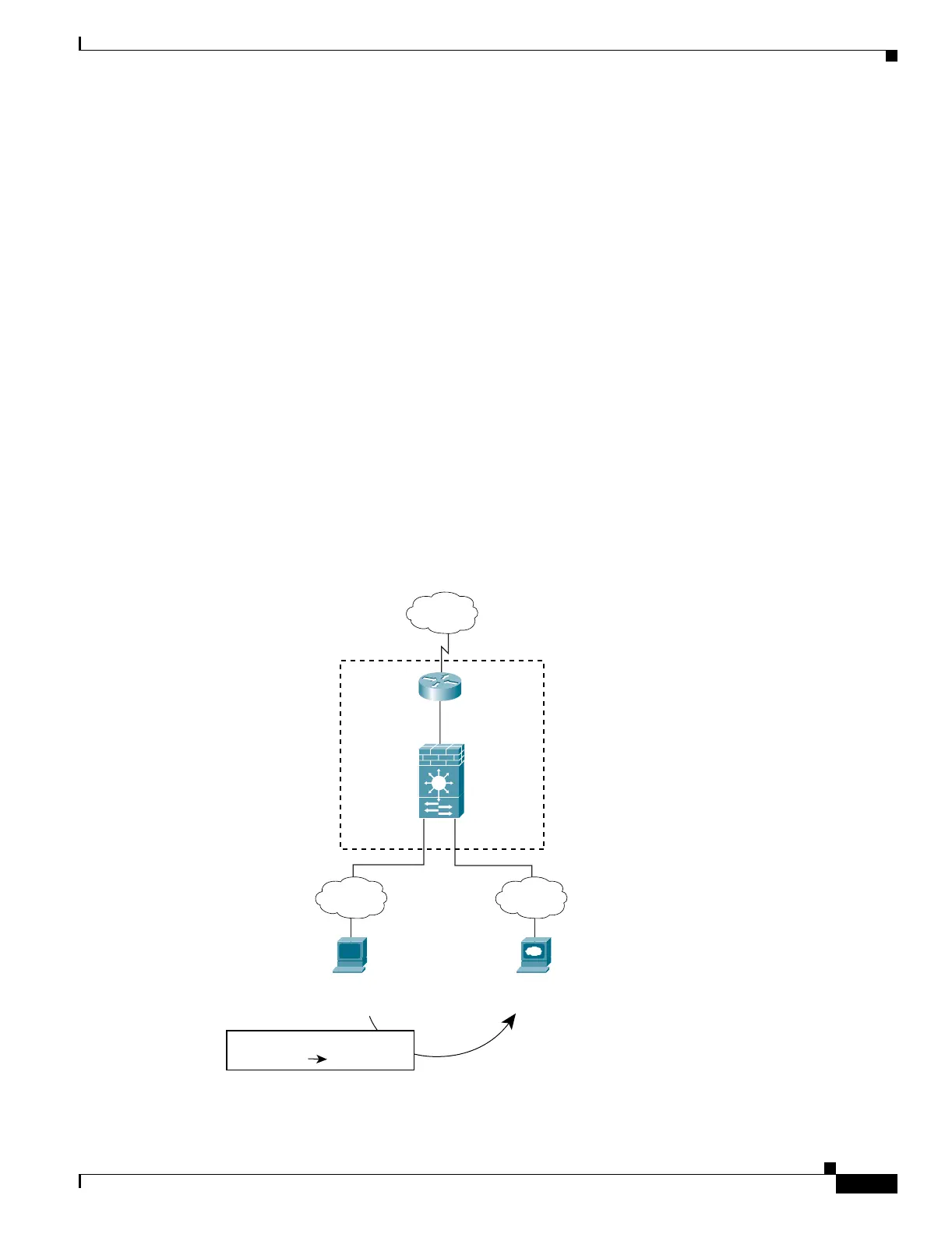
The steps below describe how data moves through the FWSM (see Figure 4-3):
1. A user on the outside network requests a web page from the DMZ website using the global
destination address of 209.165.201.3, which is on the outside interface subnet.
2. The FWSM receives the packet, and because it is a new session, the FWSM verifies that the packet
is allowed according to the terms of the security policy (ACLs, filters, AAA).
For multiple context mode, the FWSM first classifies the packet according to either a unique VLAN
or a unique destination address. In this case, even if the VLAN is not unique, the classifier “knows”
that the DMZ web server address belongs to a certain context because of the NAT configuration.
3. The FWSM translates the destination address to the local address 10.1.1.3.
4. The FWSM then adds a session entry to the fast path and forwards the packet from the DMZ
interface.
5. When the DMZ website responds to the request, the packet goes through the FWSM and because
the session is already established, the packet bypasses the many lookups associated with a new
connection. The fast path performs NAT by translating the local source address to 209.165.201.3.
6. The FWSM forwards the packet to the outside user.
An Inside User Visits a Website on the DMZ
Figure 4-4 shows an inside user accessing the DMZ website.
Figure 4-4 Inside to DMZ
Web Server
10.1.1.3
User
10.1.2.27
FWSM
Outside
Inside DMZ
Switch
209.165.201.2
10.1.1.110.1.2.1
Source Addr Translation
10.1.1.1510.1.2.27
104655
 Loading...
Loading...

















